Abstract
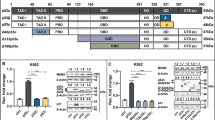
p51A, or TAp63γ, a translation product of gene p51, or p63, was identified as a homolog of p53 in its primary structure and transactivating function. p53 plays a decision-making role in inducing either cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in response to DNA damage, and thereby preserves genome integrity of living cells. To compare the biological activities between p51A and p53, cell lines with low-level, constitutive expression of each protein were obtained by cDNA transfection of mouse erythroleukemic cells. Production of p51A with an apparent molecular mass of 57-kilodalton (kD) accompanied induction of p21waf1 and appearance of hemoglobin-producing cells. After DNA-damaging treatment either with ultraviolet light (UV) irradiation or with actinomycin D, the p51A protein accumulated in time courses corresponding to those of wild-type p53, and caused an increase in the hemoglobin-positive cell count. In contrast, p53-accumulated cells underwent apoptosis without exhibiting the feature of erythroid differentiation. The mode of p21waf1 and Bax-α upregulations varied between p51A- and p53-expressing cells and between the types of DNA damage. These results suggest the possibility that p51A induces differentiation under genotoxic circumstances. There may be cellular factors that control p51A protein stability and transactivating ability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agami R, Blandino G, Oren M and Shaul Y. . 1999 Nature 399: 809–813.
Aizawa S, Suda Y, Furuta Y, Yagi T, Takeda N, Watanabe N, Nagayoshi M and Ikawa Y. . 1990 EMBO J. 9: 2107–2116.
Banin S, Moyal L, Shieh S-Y, Taya Y, Anderson CW, Chessa L, Smorodinsky NI, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y and Ziv Y. . 1998 Science 281: 1674–1677.
Canman CE, Lim D-S, Cimprich KA, Taya Y, Tamai K, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Kastan MB and Siliciano JD. . 1998 Science 281: 1677–1679.
Celli J, Duijf P, Hamel BCJ, Bamshad M, Kramer B, Smits APT, Newbury-Ecob R, Hennekam RCM, Buggenhout GV, Haeringen AV, Woods CG, Essen AJV, Waal RD, Vriend G, Haver DA, Yang A, McKeon F, Brunner HG and Bokhoven HV. . 1999 Cell 99: 143–153.
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B. . 1993 Cell 75: 817–825.
Gong JG, Costanzo C, Yang H-Q, Melino G, Kaelin Jr WG, Levrero M and Wang JY. . 1999 Nature 399: 806–809.
Gu Y, Turk CW and Morgan DO. . 1993 Nature 366: 707–710.
Haapajärvi T, Pitkänen K, Tsubari M and Laiho M. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 3074–3080.
Hagiwara K, McMenamin MG, Miura K and Harris CC. . 1999 Cancer Res. 59: 4165–4169.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M. . 1997 Nature 387: 296–299.
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan JC, Valent A, Minty A, Chalon P, Ferrara P, McKeon F and Caput D. . 1997 Cell 90: 809–819.
Kato MV, Sato H, Nagayoshi M and Ikawa Y. . 1997 Blood 90: 1373–1378.
Ko LJ and Prives C. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 1054–1072.
Kubbutat MHG, Jones SN and Vousden KH. . 1997 Nature 387: 299–308.
Levine AJ. . 1997 Cell 88: 323–331.
Lu X and Lane DP. . 1993 Cell 75: 765–778.
Lu X, Burbidge SA, Griffin S and Smith HM. . 1996 Oncogene 13: 413–418.
Martinez J, Georgoff I, Martinez J and Levine AJ. . 1991 Genes Dev. 5: 151–159.
Michalovitz D, Halevy O and Oren M. . 1990 Cell 62: 671–680.
Mills AA, Zheng B, Wang X-J, Voge H, Roop DR and Bradley A. . 1999 Nature 398: 708–713.
Miyashita T and Reed JC. . 1995 Cell 80: 293–299.
Nelson WG and Kastan MB. . 1994 Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 1815–1823.
Oltvai ZN, Milliman C and Korsmeyer SJ. . 1993 Cell 74: 609–619.
Osada M, Ohba M, Kawahara C, Ishioka C, Kanamaru R, Katoh I, Ikawa Y, Nimura Y, Nakagawara A, Obinata M and Ikawa S. . 1998 Nature Med. 4: 839–843.
Shieh S-Y, Ikeda M, Taya T and Prives C. . 1997 Cell 91: 325–334.
Shimada A, Kato S, Enjo K, Osada M, Ikawa Y, Obinata M, Ikawa S and Ishioka C. . 1999 Cancer Res. 59: 2781–2786.
Sunahara M, Shishikura T, Takahashi M, Todo S, Yamamoto N, Kimura H, Kato S, Ishioka C, Ikawa S, Ikawa Y and Nakagawara A. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 3761–3765.
White E and Prives C. . 1999 Nature 399: 734–737.
Woo RA, McLure KG, Lees-Miller SP, Rancourt DE and Lee PWK. . 1998 Nature 394: 700–704.
Xu X, Yamamura Y, Tsukada T, Yoshida MA, Senda H, Nagayoshi M, Ikeuchi T and Ikawa Y. . 1995 Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 86: 284–291.
Yang A, Kaghad M, Wang Y, Gillet E, Flemming MD, Dötsch V, Andrews NC, Caput D and McKeon F. . 1998 Mol. Cell. 2: 305–316.
Yang A, Schweizer R, Sun D, Kaghad M, Walker N, Bronson RT, Tabin C, Sharpe A, Caput D, Crum C and McKeon F. . 1999 Nature 398: 714–719.
Yuan Z-M, Shioya H, Ishiko T, Sun X, Gu J, Huang YY, Lu H, Kharbanda S, Weichselbaum R and Kufe D. . 1999 Nature 399: 814–817.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katoh, I., Aisaki, Ki., Kurata, Si. et al. p51A (TAp63γ), a p53 homolog, accumulates in response to DNA damage for cell regulation. Oncogene 19, 3126–3130 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203644
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203644
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lovastatin causes FaDu hypopharyngeal carcinoma cell death via AMPK-p63-survivin signaling cascade
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Improvement of gemcitabine sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer MiaPaCa-2 cells by RUNX2 depletion-mediated augmentation of TAp73-dependent cell death
Oncogenesis (2016)
-
Common genetic variants on 3q28 contribute to non-small cell lung cancer susceptibility: evidence from 10 case-control studies
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2015)
-
Rare variants of large effect in BRCA2 and CHEK2 affect risk of lung cancer
Nature Genetics (2014)
-
Role of p63 in Development, Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression
Cancer Microenvironment (2012)