Abstract
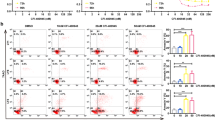
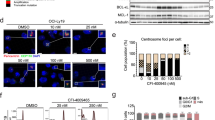
The tumor suppressor gene product p53 can bind to and inhibit the helicase activity of the multisubunit transcription-repair factor TFIIH. We previously reported that p53-mediated apoptosis is attenuated in primary human fibroblasts from individuals with Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP) that harbor mutations in the TFIIH DNA helicases XPD or XPB. In this study we show that apoptosis is reduced and delayed in three XPD lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs), but not in an XPD heterozygote LCL, after exposure to doxorubicin, a DNA-damaging agent and topoisomerase II inhibitor frequently used in cancer therapy. Apoptosis was assessed by quantitation of Annexin V binding to exposed phosphatidylserine residues and by caspase-mediated cleavage of Poly(ADP)Ribose Polymerase (PARP). Apoptosis induced by doxorubicin was suppressed in LCLs retrovirally transduced with the Human Papillomavirus 16 E6 oncoprotein, consistent with the hypothesis that this is a p53-dependent process. PARP cleavage was not delayed in XPD LCLs in response to anti-Fas (CD95) antibody-mediated apoptosis, thus, the defect in the apoptotic pathway in these cells lies upstream of caspase activation. Similar changes in the expression of apoptosis-effector genes, p53, and p53-responsive genes p21Cip1/WAF-1/Sid1 (p21), gadd45, bcl-2 and bax were observed in normal and XPD LCLs after treatment with doxorubicin, indicating that delayed apoptosis was not a consequence of defective transcription of these genes. Thus, our studies provide further support to the hypothesis that XPD and p53 can functionally interact in a p53-mediated apoptotic pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banin S, Moyal L, Shieh S, Taya Y, Anderson CW, Chessa L, Smorodinsky NI, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y and Ziv Y. . 1998 Science 281: 1674–1677.
Blaydes JP and Hupp TR. . 1998 Oncogene 17: 1045–1052.
Buckbinder L, Talbott R, Valesco-Miguel S, Takenaka I, Faha B, Seizinger BR and Kley N. . 1995 Nature 377: 646–649.
Canman CE, Lim DS, Cimprich KA, Taya Y, Tamai K, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Kastan MB and Siliciano JD. . 1998 Science 281: 1677–1679.
de Boer J, Donker I, de Wit J, Hoeijmakers JH and Weeda G. . 1998a Cancer Res. 58: 89–94.
de Boer J, de Wit J, van Steeg H, Berg RJW, Morreau H, Visser P, Lehmann AR, Duran M, Hoeijmakers JHJ and Weeda G. . 1998b Mol. Cell 1: 981–990.
el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B. . 1993 Cell 75: 817–825.
Ford JM and Hanawalt PC. . 1995 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 8876–8880.
Ford JM and Hanawalt PC. . 1997 J. Biol. Chem. 272: 28073–28080.
Friesen C, Herr I, Krammer PH and Debatin K-M. . 1996 Nature Med. 2: 574–577.
Gottlieb E, Lindner S and Oren M. . 1996 Cell Growth Differ. 7: 301–310.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K and Elledge SJ. . 1993 Cell 75: 805–816.
Haupt Y, Rowan S, Shaulian E, Vousden KH and Oren M. . 1995 Genes Dev. 9: 2170–2183.
Kapoor M and Lozano G. . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 2834–2837.
Ko LJ, Shieh SY, Chen X, Jayaraman L, Tamai K, Taya Y, Prives C and Pan ZQ. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 7220–7229.
Kubbutat MH and Vousden KH. . 1998 Trends Microbiol. 6: 173–175.
Lehmann AR. . 1995 Trends Biochem Sci. 20: 402–405.
Leveillard T, Andera L, Bissonnette N, Schaeffer L, Bracco L, Egly JM and Wasylyk B. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 1615–1624.
Levine AJ. . 1997 Cell 88: 323–331.
Lindahl T, Satoh MS, Poirier GG and Klungland A. . 1995 Trends Biochem Sci. 20: 405–411.
Lowe SW, Bodis S, McClatchey A, Remington L, Ruley HE, Fisher DE, Housman DE and Jacks T. . 1994 Science 266: 807–810.
Lu H, Fisher RP, Bailey P and Levine AJ. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 5923–5934.
Lu H, Taya Y, Ikeda M and Levine. . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 6399–6402.
Miyashita T and Reed JC. . 1995 Cell 80: 293–299.
Noda A, Ning Y, Venable SF, Pereira-Smith OM and Smith JR. . 1994 Exp. Cell. Res. 211: 90–98.
Prives C. . 1998 Cell 95: 5–8.
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM, Levine AJ and Howley PM. . 1990 Cell 63: 1129–1136.
Shah GM, Shah RG and Poirier GG. . 1996 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 229: 838–844.
Sheard MA, Vojtesek B, Janakova L, Kovarik J and Zaloudik J. . 1997 Int. J. Cancer 73: 757–762.
Sheikh MS, Burns TF, Huang Y, Wu GS, Amundson S, Brooks KS, Fornace AJ and el-Deiry WS. . 1998 Cancer Res. 58: 1593–1598.
Shieh SY, Ikeda M, Taya Y and Prives C. . 1997 Cell 91: 325–334.
Siliciano JD, Canman CE, Taya Y, Sakaguchi K, Appella E and Kastan. . 1997 Genes Dev. 11: 3471–3481.
Speth PA, van Hoesel QG and Haanen C. . 1988 Clin. Pharmacokinet. 15: 15–31.
Stary A and Sarasin A. . 1996 Cancer Surveys 26: 155–171.
Svejstrup JQ, Vichi P and Egly J-M. . 1996 Trends Biochem. Sci. 21: 346–350.
Taylor EM, Broughton BC, Botta E, Stefanini M, Sarasin A, Jaspers NG, Fawcett H, Harcourt SA, Arlett CF and Lehmann AR. . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 8658–8663.
Wang XW, Yeh H, Schaeffer L, Roy R, Moncollin V, Egly JM, Wang Z, Freidberg EC, Evans MK, Taffe BG, Bohr VA, Weeda G, Hoeijmakers JHJ, Forrester K and Harris CC. . 1995 Nat. Genet. 10: 188–195.
Wang XW, Vermeulen W, Coursen JD, Gibson M, Lupold SE, Forrester K, Xu G, Elmore L, Yeh H, Hoeijmakers JH and Harris CC. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 1219–1232.
Whitacre CM and Berger NA. . 1997 Cancer Res. 57: 2157–2163.
Wolf CM, Reynolds JE, Morana SJ and Eastman A. . 1997 Exp. Cell Res. 230: 22–27.
Yu Y and Little JB. . 1998 Cancer Res. 58: 4277–4281.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Kum Kum Khanna for providing the C3ABR cell line, Dr Denise Galloway for providing the HPV16 E6 retroviral vector, Dr AR Lehmann and Dr BC Broughton for their personal communication of XPD mutations, Mrs. Stacey Anderson for Flow Cytometry analysis, and Dr Steve Linke for critical revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robles, A., Wang, X. & Harris, C. Drug-induced apoptosis is delayed and reduced in XPD lymphoblastoid cell lines: possible role of TFIIH in p53-mediated apoptotic cell death. Oncogene 18, 4681–4688 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202862
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202862
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of XPD in cell apoptosis and viability and its relationship with p53 and cdk2 in hepatoma cells
Medical Oncology (2012)
-
Unexpected functional similarities between gatekeeper tumour suppressor genes and proto-oncogenes revealed by systems biology
Journal of Human Genetics (2011)
-
Impact of ERCC2 gene polymorphism on HIV-1 disease progression to AIDS among North Indian HIV patients
Molecular Biology Reports (2011)
-
DNA damage induced by the anthracycline cosmomycin D in DNA repair-deficient cells
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2010)
-
hHR23B is required for genotoxic-specific activation of p53 and apoptosis
Oncogene (2007)