Abstract
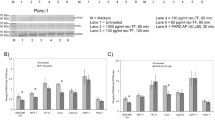
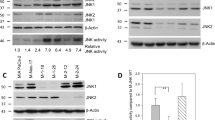
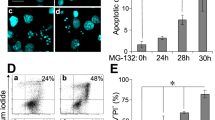
Nerve growth factor (NGF) treatment of Chinese hamster ovary fibroblast (CHO) cells exogenously expressing 2.5–105 TrkA receptors (CHO/TrkA) results in inhibition of serum and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) stimulated cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, NGF does not stimulate [3H]thymidine incorporation and inhibits IGF-I mediated DNA synthesis in CHO/TrkA cells. NGF and IGF-I induce extracellular-signal regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) and ERK2 activation, but NGF is able to stimulate a higher and more sustained activation of these enzymes compared with IGF-I. Cotreatment with NGF and IGF-I yields an ERK1/2 activity profile similar to that of NGF treatment alone. While pretreatment with mitogen activated protein kinase kinase (MKK) inhibitor PD98059 (30 μM) results in 100% inhibition of IGF-I stimulated MAPK phosphorylation (IC50<1 μM), NGF mediated MAPK phosphorylation is only decreased by 50% (IC50=3 μM). NGF, but not IGF-I, stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of PLC-γ1 which can be inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) inhibitor U73122 (IC50=4 μM). Pretreatment with U73122 (IC50=7 μM) results in an 87% inhibition of NGF mediated MAPK phosphorylation, while cotreatment with PD98059 and U73122 results in 97% inhibition. U73122 pretreatment has no effect on NGF stimulated Akt activation. NGF, but not IGF-I, stimulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of Suc1-associated neurotrophic factor-induced tyrosine phosphorylation target (SNT-1)/fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 (FRS2) which can be completely prevented by pretreatment with 10 μM U73122. Finally, inhibition of PI-PLC results in NGF's ability to stimulate DNA synthesis in the absence and presence of IGF-I.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT and Saltiel AR. . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 27489–27494.
Anderson NG, Maller JL, Tonks NK and Sturgill TW. . 1990 Nature 343: 651–653.
Andjelkovic M, Suidan HS, Meier R, Frech M, Alessi DR and Hemmings BA. . 1998 Eur. J. Biochem. 251: 195–200.
Berridge MJ. . 1987 Ann. Rev. Biochem. 56: 159–193.
Billon N, van Grunsven LA and Rudkin BB. . 1996 Oncogene 13: 2047–2054.
Burgering BM and Coffer PJ. . 1995 Nature 376: 599–602.
Chen P, Xie H and Wells A. . 1996 Mol. Biol. Cell 7: 871–88
Cordon-Cardo C, Tapley P, Jing SQ, Nanduri V, O'Rourke, Lamballe F, Kovary K, Klein R, Jones KR, Reichardt LF, Barbacid M. . 1991 Cell 66: 173–183.
Decker SJ. . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 30841–30844.
Dent P, Haser W, Haystead TA, Vincent LA, Roberts TM and Sturgill TW. . 1992 Science 257: 1404–1407.
Dikic I, Schlessinger J and Lax I. . 1994 Curr. Biol. 4: 702–708.
Dobashi Y, Kudoh T, Matsumine A, Toyoshima K and Akiyama T. . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 23031–23037.
Downward J, Graves JD, Warne PH, Rayter S and Cantrell DA. . 1990 Nature 346: 719–723.
Duckworth BC and Cantley LC. . 1997 J. Biol. Chem. 272: 27665–27670.
Gille H, Kortenjann M, Thomae O, Moomaw C, Slaughter C, Cobb MH and Shaw PE. . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 951–962.
Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, Kim JW, Machesky LM, Rhee SG and Pollard TD. . 1991 Science 251: 1231–1233.
Greene LA and Tischler AS. . 1976 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73: 2424–2428.
Griendling KK, Rittenhouse SE, Brock TA, Ekstein LS, Gimbrone MA and Alexander RW. . 1986 J. Biol. Chem. 261: 5901–5906.
Janknecht R, Ernst WH, Pingoud V and Nordheim A. . 1993 EMBO J. 12: 5097–5104.
Janmey PA. . 1991 Methods Enzymol. 196: 92–99.
Kim UH, Fink DJ, Kim HS, Park DJ, Contreras ML, Guroff G and Rhee SG. . 1991 J. Biol. Chem. 266: 1359–1362.
Kolch W, Heidecker G, Kochs G, Hummel R, Vahidi H, Mischak H, Finkenzeller G, Marme D and Rapp UR. . 1993 Nature 364: 249–252.
Kouhara H, Hadari YR, Spivak-Kroizman T, Schilling J, Bar-Sagi D, Lax I and Schlessinger J. . 1997 Cell 89: 693–702.
Kowenz-Leutz E, Twamley G, Ansieau S and Leutz A. . 1994 Genes Dev. 8: 2781–2791.
Kyriakis JM, App H, Zhang XF, Banerjee P, Brautigan DL, Rapp UR and Avruch J. . 1992 Nature 358: 417–421.
Loeb DM, Stephens RM, Copeland T, Kaplan DR and Greene LA. . 1994 J. Biol. Chem. 269: 8901–8910.
Marais R, Wynne J and Treisman R. . 1993 Cell 73: 381–393.
Marshall CJ. . 1995 Cell 80: 179–185.
Nguyen TT, Scimeca JC, Filloux C, Peraldi P, Carpentier JL and Van Obberghen E. . 1993 J. Biol. Chem. 268: 9803–9810.
Nishizuka Y. . 1988 Nature 334: 661–665.
Obermeier A, Halfter H, Wiesmuller KH, Jung G, Schlessinger J and Ullrich A. . 1993 EMBO J. 12: 933–941.
Ohmichi M, Decker SJ, Pang L and Saltiel AR. . 1991a J. Biol. Chem. 266: 14858–14861.
Ohmichi M, Decker SJ, Pang L and Saltiel AR. . 1991b Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 179: 217–223.
Pang L, Sawada T, Decker SJ and Saltiel AR. . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 13585–13588.
Payne DM, Rossomando AJ, Martino P, Erickson AK, Her JH, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Weber MJ and Sturgill TW. . 1991 EMBO J. 10: 885–892.
Pumiglia KM and Decker SJ. . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 448–452.
Rabin SJ, Cleghon V and Kaplan DR. . 1993 Mol. Cell Biol. 13: 2203–2213.
Seth A, Alvarez E, Gupta S and Davis RJ. . 1991 J. Biol. Chem. 266: 23521–23524.
Smith RJ, Sam LM, Justen JM, Bundy GL, Bala GA and Bleasdale JE. . 1990 J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 253: 688–697.
Songyang Z, Shoelson SE, Chaudhuri M, Gish G, Pawson T, Haser WG, King F, Roberts T, Ratnofsky S, Lechleider RJ, Neel BG, Birge RB, Fajardo JE, Chou MM, Hanafusa H, Schaffhausen B and Cantley LC. . 1993 Cell 72: 767–778.
Stephens RM, Loeb DM, Copeland TD, Pawson T, Greene LA and Kaplan DR. . 1994 Neuron 12: 691–705.
Stephens RM, Sithanandam G, Copeland TD, Kaplan DR, Rapp UR and Morrison DK. . 1992 Mol. Cell Biol. 12: 3733–3742.
Traverse S, Gomez N, Paterson H, Marshall C and Cohen P. . 1992 Biochem. J. 288: 351–355.
Traverse S, Seedorf K, Paterson H, Marshall C, Cohen P and Ullrich A. . 1994 Curr. Biol. 4: 694–701.
Ulrich E, Duwel A, Kauffmann-Zeh A, Gilbert C, Lyon D, Rudkin B, Evan G and Martin-Zanca D. . 1998 Oncogene 16: 825–832.
Valius M and Kazlauskas A. . 1993 Cell 73: 321–334.
van Grunsven LA, Billon N, Savatier P, Thomas A, Urdiales JL and Rudkin BB. . 1996 Oncogene 12: 1347–1356.
Vetter ML, Martin-Zanca D, Parada LF, Bishop JM and Kaplan DR. . 1991 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 5650–5654.
Wadman IA, Hsu HL, Cobb MH and Baer R. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 3713–3716.
Wen Z, Zhong Z and Darnell JE. . 1995 Cell 82: 241–250.
Xu H, Lee KW and Goldfarb M. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 17987–17990.
Yan GZ and Ziff EB. . 1995 J. Neurosci. 15: 6200–6212.
Yan GZ and Ziff EB. . 1997 J. Neurosci. 17: 6122–6132.
Yang BS, Hauser CA, Henkel G, Colman MS, Van Beveren C, Stacey KJ, Hume DA, Maki RA and Ostrowski MC. . 1996 Mol. Cell Biol. 16: 538–547.
Zapf-Colby A and Olefsky JM. . 1998 Endocrinology 139: 3232–3240.
Zhang J, Zhang F, Ebert D, Cobb MH and Goldsmith EJ. . 1995 Structure 3: 299–307.
Acknowledgements
We thank M Chao for generously providing pDM69 and are grateful to A Saltiel for kindly donating PD98059. This work was supported by a predoctoral fellowship (to A Zapf-Colby) from NIH institutional training grant 5 T32 AG 00216-05, by NIH grant DK-33651 (to JM Olefsky), by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) (to J Eichhorn), and by a Merit Review Award from the Department of Veterans Affairs and a Diabetes Research Center Grant jointly funded by the VA and the Juvenile Diabetes Foundation (to NJG Webster). These studies were performed in partial fullfilment of a Ph.D. degree (A Zapf-Colby) in the Biomedical Sciences Graduate Program at the University of California, San Diego.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zapf-Colby, A., Eichhorn, J., Webster, N. et al. Inhibition of PLC-γ1 activity converts nerve growth factor from an anti-mitogenic to a mitogenic signal in CHO cells. Oncogene 18, 4908–4919 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202861
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202861
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multiple Gi Proteins Participate in Nerve Growth Factor-Induced Activation of c-Jun N-terminal Kinases in PC12 Cells
Neurochemical Research (2009)