Abstract
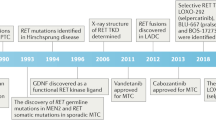
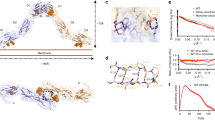
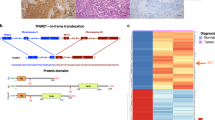
Mutations of the RET gene, encoding a receptor tyrosine kinase, have been associated with the inherited cancer syndromes MEN 2A and MEN 2B. They have also further been associated with both familial and sporadic medullary thyroid carcinomas. Missense mutations affecting cysteine residues within the extracellular domain of the receptor causes constitutive tyrosine kinase activation through the formation of disulfide-bonded homodimers. We have recently reported that a somatic 6 bp in-frame deletion, originally coding for Glu632-Leu633, potently activates the RET gene. This activation is increased with respect to the frequent MEN 2A-associated missense mutation Cys634Arg. This finding specifically correlated to the clinic behavior of the corresponding tumor, which was characterized by an unusually aggressive progression with both multiple and recurrent metastases. By examining the possibility that this deletion acts in a manner similar to cysteine substitution, we have analysed the molecular mechanism by which this oncogenic activation occurs. Phosphorylated dimers of the deleted Ret receptor were detected in immunoprecipitates separated under non-reducing conditions. Like other Cys point mutations, this 6 bp deletion affecting two amino acid residues between two adjacent Cys, is capable of activating the transforming ability of Ret by promoting receptor dimerization. These results suggest that alteration to cysteine residue position or pairing is capable of inducing ligand independent dimerization. Furthermore, we present data demonstrating that the processing and sorting of the Ret membrane receptor to the cell surface is affected by mutation type.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander WS, Metcalf D and Dunn AR. . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 5569–5578.
Asai N, Iwashita T, Matsuyama M and Takahashi M. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 1613–1619.
Blaugrund JE, Johns MM, Eby JY, Ball DW, Baylin SB, Hruban RH and Sidransky D. . 1994 Hum. Mol. Genet. 3: 1895–1897.
Bolino A, Schuffenecker I, Luo Y, Seri M, Silengo M, Tocco T, Chabrier G, Houdent C, Murat A, Schlumberger M, Towniaire J, Senoir GM and Omeo G. . 1995 Oncogene 10: 2415–2419.
Bongarzone I, Monzini N, Borrello MG, Carcano C, Ferraresi G, Arighi E, Mondellini P, Della Porta G and Pierotti MA. . 1993 Mol. Cell. Biol. 13: 358–366.
Borrello MG, Alberti L, Arighi E, Bongarzone I, Battistini C, Bardelli A, Pasini B, Piutti C, Rizzetti MG, Mondellini P, Radice MT and Pierotti MA. . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 2151–2163.
Carlson KM, Dou S, Chi D, Scavarda NJ, Toshima K, Jackson CE, Wells Jr SA, Goodfellow P and Donis-Keller H. . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 1579–1583.
Ceccherini I, Pasini B, Pacini F, Gullo M, Bongarzone I, Romei C, Santamaria G, Matera I, Mondellini P, Scopsi L, Pinchera A, Pierotti MA and Romeo G. . 1997 Oncogene 14: 2609–2612.
Chappuis-Flament S. Pasini A, De Vita G, Segouffin-Cariou C, Fusco A, Attie T, Lenoir GM, Santoro M and Billaud M . 1998 Oncogene 17: 2851–2861.
Donis-Keller H, Dou S, Chi D, Carlson KM, Toshima K, Lairmore TC, Howe JR, Moley JF, Goodfellow P and Wells Jr SA. . 1993 Human Mol. Genet. 2: 851–856.
Eng C, Mulligan LM, Healey CS, Houghton C, Frilling A, Raue F, Thomas GA and Ponder BA. . 1996 Cancer Res. 56: 2167–2170.
Eng C, Smith DP, Mulligan LM, Healey CS, Zvelebil MJ, Stonehouse TJ, Ponder MA, Jackson CE, Waterfield MD and Ponder BAJ. . 1995a Oncogene 10: 509–513.
Eng C, Mulligan LM, Smith DP, Healey CS, Frilling A, Raue F, Neumann HPH, Pfragner R, Behmel A, Lorenzo MJ, Stonehouse TJ, Ponder MA and Ponder BAJ. . 1995b Genes Chrom. Cancer 12: 209–212.
Eng C, Smith DP, Mulligan LM, Nagai MA, Healey CS, Ponder MA, Gardner E, Scheumann GFW, Jackson CE, Tunnacliffe A and Ponder BAJ. . 1994 Human Mol. Genet. 3: 237–241.
Hofstra RM, Landsvater RM, Ceccherini I, Stulp RP, Stelwagen T, Luo Y, Pasini B, Hoppener JWM, Ploos van Hamstel HK, Romeo G, Lips CJM and Buys CHCM. . 1994 Nature 367: 375–376.
Hofstra RM, Stelwagen T, Stulp RP, De Jong D, Hulsbeek M, Kamsteeg EJ, van den Berg A, Landsvater RM, Vermey A, Molenaar WM, Lips CJ and Buys CH. . 1996 J. Clin. Endocrin. Metabol. 81: 2881–2884.
Hoppner W and Ritter MM. . 1997 Human Mol. Genet. 6: 587–590.
Isidoro C, Maggioni C, Demoz M, Pizzigalli A, Fra AM and Sitia R. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 26138–26142.
Kalinin V and Frilling A. . 1998 J. Mol. Med. (in press).
Komminoth P, Kunz EK, Matias-Guiu X, Hiort O, Christiansen G, Colomer A, Roth J and Heitz PU. . 1995 Cancer 76: 479–489.
Lotti LV, Lanfrancone L, Igliaccio E, Ompetta C, Elicci G, Alcini AE, Alini B, Elicci PG and Orrisi MR. . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 1946–1954.
Mulligan LM, Eng C, Attie T, Lyonnet S, Marsh DJ, Hyland VJ, Robinson BG, Frilling A, Verellen-Dumoulin C and Safar A. . 1994 Human Molec. Genet. 3: 2163–2167.
Mulligan LM, Kwok JBJ, Healey CS, Elsdon MJ, Eng C, Gardner E, Love DR, Mole SE, Moore JK, Papl L, Ponder MA, Telenlus H, Tunnacliffe A and Ponder BAJ. . 1993 Nature 363: 458–460.
Muragaki Y, Timothy N, Leight S, Hempstead BL, Chao MV, Trojanowski JQ and Lee VM. . 1995 J. Comparat. Neurol. 356: 387–397.
Romei C, Elisei R, Pinchera A, Ceccherini I, Molinaro E, Mancusi F, Martino E, Romeo G and Pacini F. . 1996 J. Clin. Endocrin. Metabol. 81: 1619–1622.
Siegel PM and Muller WJ. . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 8878–8883.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), Fondazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (FIRC), CNR (Biotecnologie) No. 97.01258.PF49, Project BIOMED2 No. BMH4-CT97-2157 and Istituto Superiore di Sanita’. The authors thank Dr. R Sitia for critical comments and suggestions on the manuscript. We also thank Cristina Mazzadi for secretarial help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bongarzone, I., Vigano, E., Alberti, L. et al. The Glu632-Leu633 deletion in cysteine rich domain of Ret induces constitutive dimerization and alters the processing of the receptor protein. Oncogene 18, 4833–4838 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202848
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202848