Abstract
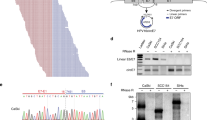
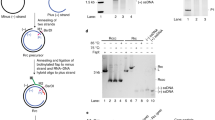
Full length cDNAs for p53 were made by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction of total RNA from two normal woodchuck livers. Two randomly chosen clones from each liver were sequenced and shown to be identical. This sequence revealed 80% or more identity with p53 sequences from human, monkey, and mouse. The cDNA was translated into a ∼55 kD protein in vitro that was immunoprecipitated by antibodies to p53. Cotranslation of woodchuck p53 with woodchuck hepatitis virus X antigen, followed by immunoprecipitation suggested X/p53 complex formation. Similar complexes were also immunoprecipitated from extracts of infected liver, but not from uninfected liver. The finding of X/p53 complexes in vivo and in vitro in the woodchuck hepadnavirus system, combined with analogous data with hepatitis B, suggests a common mechanism by which these viruses contribute to hepatocellular transformation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feitelson, M., Ranganathan, P., Clayton, M. et al. Partial characterization of the woodchuck tumor suppressor, p53, and its interaction with woodchuck hepatitis virus X antigen in hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene 15, 327–336 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201203
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201203