Abstract
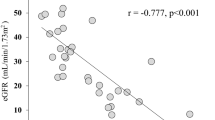
This study documents the determinants and plasma levels of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) among hypertensive and normotensive subjects in a multi-ethnic population in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). We obtained demographic, anthropometric and clinical data, together with fasting NT-proBNP and biochemical indices from 128 hypertensive patients and 138 normotensive subjects matched for age, gender and ethnicity. Plasma NT-proBNP levels were significantly (P<0.001), and several-fold higher among hypertensives (median 5.92, inter quartile range (IQR): 1.79–18.48 pmol/l) than normotensives (median 1.78, IQR: 0.59–4.32 pmol/l) in the total study population, and the same was true for the ethnic groups separately. Similarly, plasma levels of glucose, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine, but not insulin, were significantly (P<0.05) higher among hypertensives than normotensives. For all subjects combined, log NT-proBNP correlated positively and significantly with age (P<0.01), log glucose (P<0.05), systolic blood pressure (SBP, P<0.001), log BUN (P<0.001) and log creatinine (P<0.001). Multivariate regression analysis showed that NT-proBNP levels were independently and positively correlated with SBP, age, gender, log BUN, Emirati and South East Asian ethnic groups and inversely associated with current exercise. In conclusion, we found circulating levels of NT-proBNP to be significantly increased in hypertensive versus normotensive subjects in the UAE and independently related to SBP, age, gender, indices of renal function and possibly exercise. Our results further suggest a possible modulating effect of ethnicity on NT-proBNP levels.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis M, Espiner E, Richards G, Billings J, Town I, Neill A et al. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide in assessment of acute dyspnoea. Lancet 1994; 343: 440–444.
Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P et al. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 161–167.
Mueller C, Scholer A, Laule-Kilian K, Martina B, Schindler C, Buser P et al. Use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the evaluation and management of acute dyspnea. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 647–654.
Lainchbury JG, Campbell E, Frampton CM, Yandle TG, Nicholls MG, Richards AM . Brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of heart failure in patients with acute shortness of breath. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003; 42: 728–735.
Richards AM, Nicholls MG, Yandle TG, Frampton C, Espiner EA, Turner JG et al. Plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and adrenomedullin: new neurohormonal predictors of left ventricular function and prognosis after myocardial infarction. Circulation 1998; 97: 1921–1929.
de Lemos JA, Morrow DA, Bentley JH, Omland T, Sabatine MS, McCabe CH et al. The prognostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 1014–1021.
Troughton RW, Frampton CM, Yandle TG, Espiner EA, Nicholls MG, Richards AM . Treatment of heart failure guided by plasma aminoterminal brain natriuretic peptide (N-BNP) concentrations. Lancet 2000; 355: 1126–1130.
Sagnella GA, Markandu ND, Shore AC, MacGregor GA . Raised circulating levels of atrial natriuretic peptides in essential hypertension. Lancet 1986; 1: 179–181.
Takeda T, Kohno M . Brain natriuretic peptide in hypertension. Hypertens Res 1995; 18: 259–266.
Nilsson P, Lindholm L, Schersten B, Horn R, Melander A, Hesch RD . Atrial natriuretic peptide and blood pressure in a geographically defined population. Lancet 1987; 2: 883–885.
Abdulle AM, Nagelkerke NJ, Abouchacra S, Pathan JY, Adem A, Obineche EN . Under-treatment and under diagnosis of hypertension: a serious problem in the United Arab Emirates. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2006; 6: 24.
Belluardo P, Cataliotti A, Bonaiuto L, Giuffre′ E, Maugeri E, Noto P et al. Lack of activation of the molecular forms of the BNP system in human grade 1 hypertension and relationship to cardiac hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2006; 291: 1529–1535.
Uusimaa P, Tokola H, Ylitalo A, Vuolteenaho O, Ruskoaho H, Risteli J et al. Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide reflects left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic function in hypertension. Int J Cardiol 2004; 97: 251–256.
Conen D, Zeller A, Pfisterer M, Martina B . Usefulness of B-type natriuretic peptide and C-reactive protein in predicting the presence or absence of left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol 2006; 97: 249–252.
Yamamoto K, Burnett Jr JC, Jougasaki M, Nishimura RA, Bailey KR, Saito Y et al. Superiority of brain natriuretic peptide as a hormonal marker of ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction and ventricular hypertrophy. Hypertension 1996; 28: 988–994.
Struthers AD, Davies J . B-type natriuretic peptide: a simple new test to identify coronary artery disease? QJM 2005; 98: 765–769.
Abdullah SM, Khera A, Das SR, Stanek HG, Canham RM, Chung AK et al. Relation of coronary atherosclerosis determined by electron beam computed tomography and plasma levels of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in a multiethnic population-based sample (The Dallas Heart Study). Am J Cardiol 2005; 96: 1284–1289.
Rana BS, Davies JI, Band MM, Pringle SD, Morris A, Struthers AD . B-type natriuretic peptide can detect silent myocardial ischaemia in asymptomatic type 2 diabetes. Heart 2006; 92: 916–920.
Redfield MM, Rodeheffer RJ, Jacobsen SJ, Mahoney DW, Bailey KR, Burnett Jr JC . Plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration: impact of age and gender. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002; 40: 976–982.
Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Leip EP, Benjamin EJ, Wilson PW et al. Impact of age and sex on plasma natriuretic peptide levels in healthy adults. Am J Cardiol 2002; 90: 254–258.
Raymond I, Groenning BA, Hildebrandt PR, Nilsson JC, Baumann M, Trawinski J et al. The influence of age, sex and other variables on the plasma level of N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide in a large sample of the general population. Heart 2003; 89: 745–751.
Clerico A, Emdin M . Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic relevance of the measurement of cardiac natriuretic peptides: a review. Clin Chem 2004; 50: 33–50.
Mottram PM, Haluska BA, Marwick TH . Response of B-type natriuretic peptide to exercise in hypertensive patients with suspected diastolic heart failure: correlation with cardiac function, hemodynamics, and workload. Am Heart J 2004; 148: 365–370.
Neumayr G, Pfister R, Mitterbauer G, Eibl G, Hoertnagl H . Effect of competitive marathon cycling on plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and cardiac troponin T in healthy recreational cyclists. Am J Cardiol 2005; 96: 732–735.
Meredith IT, Jennings GL, Esler MD, Dewar EM, Bruce AM, Fazio VA et al. Time-course of the antihypertensive and autonomic effects of regular endurance exercise in human subjects. J Hypertens 1990; 8: 859–866.
Luchner A, Schunkert H . Interactions between the sympathetic nervous system and the cardiac natriuretic peptide system. Cardiovasc Res 2004; 63: 443–449.
Passino C, Severino S, Poletti R, Piepoli MF, Mammini C, Clerico A et al. Aerobic exercise decreases B-type natriuretic peptide expression and adrenergic activation in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006; 47: 1835–1839.
Amine EK, Samy M . Obesity among female medical students in the United Arab Emirates. J R Soc Health 1996; 116: 91–96.
Henry CJK, Lightowler HJ, Al-Hourani H . Physical activity and levels of inactivity in adolescent females ages 11–16 years in the United Arab Emirates. Am J Human Biol 2004; 16: 346–353.
Sabri S, Bener A, Eapen V, Abu Zeid MS, Al-Mazrouei AM, Singh J . Some risk factors for hypertension in the United Arab Emirates. East Mediterr Health J 2004; 10: 610–619.
Das SR, Drazner MH, Dries DL, Vega GL, Stanek HG, Abdullah SM et al. Impact of body mass and body composition on circulating levels of natriuretic peptides. Results from the Dallas Heart Study. Circulation 2005; 112: 2163–2168.
Maisel AS, Clopton P, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE et al. Impact of age, race, and sex on the ability of B-type natriuretic peptide to aid in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure: results from the Breathing Not Properly (BNP) multinational study. Am Heart J 2004; 147: 1078–1084.
Kohno M, Minami M, Kano H, Yasunari K, Maeda K, Hanehira T et al. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor on left ventricular parameters and circulating brain natriuretic peptide in elderly hypertensives with left ventricular hypertrophy. Metabolism 2000; 49: 1356–1360.
Dahlof B, Zanchetti A, Diez J, Nicholls MG, Yu CM, Barrios V et al. For the REGAAL Study Investigators. Effects of losartan and atenolol on left ventricular mass and neurohormonal profile in patients with essential hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy. J Hypertens 2002; 20: 1855–1864.
Deary AJ, Schumann AL, Murfet H, Haydock S, Foo RS, Brown MJ . Influence of drugs and gender on the arterial pulse wave and natriuretic peptide secretion in untreated patients with essential hypertension. Clin Sci 2002; 103: 493–499.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge generous financial support from UAE University Research Affairs (Grant: 01.50.08-11/05), and the Sheikh Hamdan Bin Rashid Al Maktoum Awards for Medical Sciences (Grant: MRG 18/1-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdulle, A., Nagelkerke, N., Adem, A. et al. Plasma N terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide levels and its determinants in a multi-ethnic population. J Hum Hypertens 21, 647–653 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002210
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002210
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Obesity, kidney dysfunction and hypertension: mechanistic links
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2019)