Abstract
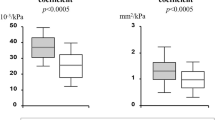
In subjects with essential hypertension, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition increases arterial diameter, compliance and distensibility of peripheral muscular arteries in association with blood pressure reduction. Whether pulse pressure amplification is modified by ACE inhibition and whether changes in compliance and distensibility are due to a drug effect on the arterial wall, to the blood pressure reduction or to a combination of both factors, is largely ignored. In a randomised, double-blind crossover trial, we used the ACE inhibitor quinapril as a marker to evaluate the changes in: pulse pressure amplification (applanation tonometry), carotid compliance and distensibility (echo-tracking technique), and aortic distensibility (measured from pulse wave velocity). Quinapril decreased in the same extent carotid and brachial pulse pressure, thus causing a resetting of pulse pressure amplification toward normal values. Carotid compliance and distensibility as well as aortic distensibility increased significantly. Based on three-way analysis of variance, it was shown that, whereas the changes in carotid stiffness were exclusively due to blood pressure reduction and not to a drug-induced relaxation of the arterial wall, the changes in aortic distensibility were due to the combination of both factors. Thus, using an atraumatic non-invasive procedure, it was possible to show that: (i) ACE inhibition is able to maintain pulse pressure amplification, an important factor contributing to reduce the afterload of the heart; and (ii) ACE inhibition alters the hypertensive arterial wall in a very heterogeneous manner, with a maximal drug effect on muscular large arteries like the abdominal aorta, and not on elastic arteries like the carotid artery and the thoracic aorta.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topouchian, J., Brisac, A., Pannier, B. et al. Assessment of the acute arterial effects of converting enzyme inhibition in essential hypertension: a double-blind, comparative and crossover study. J Hum Hypertens 12, 181–187 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000581
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000581
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Optimal Blood Pressure Control Improves Left Ventricular Torsional Deformation and Vascular Function in Newly Diagnosed Hypertensives: a 3-Year Follow-up Study
Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research (2020)
-
Future Treatment of Hypertension: Shifting the Focus from Blood Pressure Lowering to Arterial Stiffness Modulation?
Current Hypertension Reports (2015)
-
Acute effects of renin-angiotensin system blockade on arterial function in hypertensive patients
Journal of Human Hypertension (2007)