Abstract
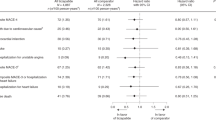
A meta-analysis was performed to compare the risk of serious adverse events associated with the use of all formulations of isradipine, when used as monotherapy in hypertension, to active drug or placebo controls. Eligible studies totalled 65 published and unpublished randomised controlled trials involving 9903 subjects and 10 675 treatment exposures: 4492 to isradipine, 1473 to isradipine sustained release, 2768 to other active drugs, and 1942 to placebo. Mortality, cardiovascular outcomes, other serious incident illnesses, such as cancer, and withdrawals were sought. Seventy-five per cent of the isradipine exposures were to standard-release formulations and 25% were to sustained-release formulations. Overall, isradipine therapy shows no difference in risk of major adverse events or withdrawals compared to other active controls or placebo (odds ratios [OR] 0.9; 95% CI 0.7–1.46 and 0.5; 95% CI 0.2–1.3). These major adverse events included angina, fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke and overall mortality. Isradipine sustained release could be compared only to placebo, based on available data, and shows a lower risk of withdrawals (OR 0.5; 95% CI 0.3–0.9), and a similar trend was observed for major adverse events, (OR 0.8; 95% CI 0.3–2.5). Published and unpublished randomised controlled trials were analysed in separate meta-analyses and later combined when this sensitivity analysis of risk showed no differences between the groups. In conclusion, we find no evidence for increased risk of serious adverse events in patients receiving isradipine as monotherapy for hypertension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ross, S., Kupelnick, B., Kumashiro, M. et al. Risk of serious adverse events in hypertensive patients receiving isradipine: a meta-analysis. J Hum Hypertens 11, 743–751 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000532
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000532
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Systematic review of methods used in meta-analyses where a primary outcome is an adverse or unintended event
BMC Medical Research Methodology (2012)
-
Has the role of calcium channel blockers in treating hypertension finally been defined?
Current Hypertension Reports (2003)