Abstract
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Obesity is one of the primary clinical features of Bardet–Biedl Syndrome (BBS), a genetically heterogeneous disorder that is usually inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. It has been suggested that heterozygous carriers of BBS are predisposed to obesity. We set out to identify the common mutation in BBS1 families from southwest Newfoundland and to examine the relationship between this mutation and obesity in the general population.
METHODS AND SUBJECTS: We genotyped BBS1 families from Newfoundland to determine the nature of the mutation causing BBS in this population. We then screened 200 obese individuals (average body mass index (BMI)=37.9 kg/m2; average waist to hip ratio=0.935; average waist=113.8 cm) and 200 ethnically matched, unrelated, controls (average BMI=25.0 kg/m2; average waist to hip ratio=0.896; average waist=86.9 cm) from the same geographic region for the presence of this mutation.
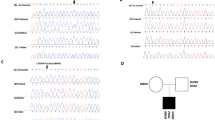
RESULTS: All affected members of the six Newfoundland BBS1 families were homozygous for the most common BBS1 mutation (M390R). This mutation was found in the heterozygous state in three of the 200 obese individuals and also in three of the 200 matched controls.
CONCLUSIONS: The high frequency of BBS1 in Newfoundland appears to be the result of a founder event. Our data do not support the hypothesis that the M390R BBS1 mutation plays a significant role in the frequency of obesity in the general public in Newfoundland.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Green JS, Parfrey PS, Harnett JD, Farid NR, Cramer BC, Johnson G, Heath O, McManamon PJ, O'Leary E, Pryse-Phillips W . The cardinal manifestations of Bardet–Biedl Syndrome, a form of Laurence–Moon–Biedl Syndrome. N Engl J Med 1989; 321: 1002–1009.
Beales PL, Elcioglu N, Woolf AS, Parker D, Flinter FA . New criteria for improved diagnosis of Bardet–Biedl syndrome: results of a population survey. J Med Genet 1999; 36: 437–446.
Katsanis N, Beales PL, Woods MO, Lewis RA, Green JS, Parfrey PS, Ansley SJ, Davidson WS, Lupski JR . Mutations in MKKS cause obesity, retinal dystrophy and renal malformations associated with Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Nat Genet 2000; 26: 67–70.
Slavotinek AM, Stone EM, Mykytyn K, Heckenlively JR, Green JS, Heon E, Musarella MA, Parfrey PS, Sheffield VC, Biesecker LG . Mutations in MKKS cause Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Nat Genet 2000; 26: 15–16.
Nishimura DY, Searby CC, Carmi R, Elbedour K, Van Maldergem L, Fulton AB, Lam BL, Powell BR, Swiderski RE, Bugge KE, Haider NB, Kwitek-Black AE, Ying L, Duhl DM, Gorman SW, Heon E, Iannaccone A, Bonneau D, Biesecker LG, Jacobson SG, Stone EM, Sheffield VC . Positional cloning of a novel gene on chromosome 16q causing Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS2). Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 865–874.
Mykytyn K, Braun T, Carmi R, Haider NB, Searby CC, Shastri M, Beck G, Wright AF, Iannaccone A, Elbedour K, Riise R, Baldi A, Raas-Rothschild A, Gorman SW, Duhl DM, Jacobson SG, Casavant T, Stone EM, Sheffield VC . Identification of the gene that, when mutated, causes the human obesity syndrome BBS4. Nat Genet 2001; 28: 188–191.
Mykytyn K, Nishimura DY, Searby CC, Shastri M, Yen HJ, Beck JS, Braun T, Streb LM, Cornier AS, Cox GF, Fulton AB, Carmi R, Luleci G, Chandrasekharappa SC, Collins FS, Jacobson SG, Heckenlively JR, Weleber RG, Stone EM, Sheffield VC . Identification of the gene (BBS1) most commonly involved in Bardet–Biedl syndrome, a complex human obesity syndrome. Nat Genet 2002; 31: 435–438.
Badano JL, Ansley SJ, Leitch CC, Lewis RA, Lupski JR, Katsanis N . Identification of a novel Bardet–Biedl syndrome protein, BBS7, that shares structural features with BBS1 and BBS2. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 72: 650–658.
Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Blacque OE, Hill J, Hoskins BE, Leitch CC, Chul Kim J, Ross AJ, Eichers ER, Teslovich TM, Mah AK, Johnsen RC, Cavender JC, Lewis RA, Leroux MR, Beales PL, Katsanis N . Basal body dysfunction is a likely cause of pleiotropic Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Nature 2003; 425: 628–633.
Sheffield VC, Carmi R, Kwitek-Black A, Rokhlina T, Nishimura D, Duyk GM, Elbedour K, Sunden SL, Stone EM . Identification of a Bardet–Biedl syndrome locus on chromosome 3 and evaluation of an efficient approach to homozygosity mapping. Hum Mol Genet 1994; 3: 1331–1335.
Young TL, Penney L, Woods MO, Parfrey PS, Green JS, Hefferton D, Davidson WS . A fifth locus for Bardet–Biedl syndrome maps to chromosome 2q31. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 64: 900–904.
Katsanis N, Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Eichers ER, Lewis RA, Hoskins BE, Scambler PJ, Davidson WS, Beales PL, Lupski JR . Triallelic inheritance in Bardet–Biedl syndrome, a Mendelian recessive disorder. Science 2001; 293: 2256–2259.
Katsanis N, Eichers ER, Ansley SJ, Lewis RA, Kayserili H, Hoskins BE, Scambler PJ, Beales PL, Lupski JR . BBS4 is a minor contributor to Bardet–Biedl syndrome and may also participate in triallelic inheritance. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 22–29.
Beales PL, Badano JL, Ross AJ, Ansley SJ, Hoskins BE, Kirsten B, Mein CA, Froguel P, Scambler PJ, Lewis RA, Lupski JR, Katsanis N . Genetic interaction of BBS1 mutations with alleles at other BBS loci can result in non-Mendelian Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 72: 1187–1199.
Burghes AH, Vaessin HE, de la Chapelle A . Genetics. The land between Mendelian and multifactorial inheritance. Science 2001; 293: 2213–2214.
Dekaban AS, Parks JS, Ross GT . Laurence–Moon syndrome: evaluation of endocrinological function and phenotypic concordance and report of cases. Med Ann Dist Columbia 1972; 41: 687–694.
Bauman ML, Hogan GR . Laurence–Moon–Biedl syndrome. Report of two unrelated children less than 3 years of age. Am J Dis Child 1973; 126: 119–126.
Hrynchak PK . Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Optom Vis Sci 2000; 77: 236–243.
O'Dea D, Parfrey PS, Harnett JD, Hefferton D, Cramer BC, Green JS . The importance of renal impairment in the natural history of Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 1996; 27: 776–783.
Croft JB, Swift M . Obesity, hypertension, and renal disease in relatives of Bardet–Biedl syndrome sibs. Am J Med Genet 1990; 36: 37–42.
Croft JB, Morrel D, Chase CL, Swift M 1995 Obesity in heterozygous carriers of the gene for Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Am J Med Genet 1995; 55: 12–15.
Beales PL, Warner AM, Hitman GA, Thakker R, Flinter FA . Bardet–Biedl syndrome: a molecular and phenotypic study of 18 families. J Med Genet 1997; 34: 92–98.
Klein D, Amman F . The syndrome of Laurence–Moon–Bardet–Biedl and allied disease in Switzerland. Clinical, genetic and epidemiological studies. J Neurol Sci 1969; 9: 479–513.
Parfrey PS, Davidson WS, Green JS . Clinical and genetic epidemiology of inherited renal disease in Newfoundland. Kidney Int 2002; 61: 1925–1934.
Woods MO, Young TL, Parfrey PS, Hefferton D, Green JS, Davidson WS . Genetic heterogeneity of Bardet–Biedl syndrome in a distinct Canadian population: evidence for a fifth locus. Genomics 1999; 55: 2–9.
Young TL, Woods MO, Parfrey PS, Green JS, Hefferton D, Davidson WS . A founder effect in the Newfoundland population reduces the Bardet–Biedl syndrome I (BBS1) interval to 1 cM. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 65: 1680–1687.
Young TL, Woods MO, Parfrey PS, Green JS, O'Leary E, Hefferton D, Davidson WS . Canadian Bardet–Biedl syndrome family reduces the critical region of BBS3 (3p) and presents with a variable phenotype. Am J Med Genet 1998; 78: 461–467.
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF . A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 1988; 16: 1215.
Mykytyn K, Nishimura DY, Searby CC, Beck G, Bugge K, Haines HL, Cornier AS, Cox GF, Fulton AB, Carmi R, Iannaccone A, Jacobson SG, Weleber RG, Wright AF, Riise R, Hennekam RC, Luleci G, Berker-Karauzum S, Biesecker LG, Stone EM, Sheffield VC . Evaluation of complex inheritance involving the most common Bardet–Biedl syndrome locus (BBS1). Am J Hum Genet 2003; 72: 429–437.
Barsh GS, Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S . Genetics of body-weight regulation. Nature 2000; 404: 644–651.
Chagnon YC, Rankinen T, Snyder EE, Weisnagel SJ, Perusse L, Bouchard C . The human obesity gene map: the 2002 update. Obes Rev 2003; 11: 313–367.
Katsanis N, Lupski JR, Beales PL . Exploring the molecular basis of Bardet–Biedl Syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 2293–2299.
Davidson WS, Fan Y, Parfrey PS, Dicks E, Moore SJ, Green JS . Genetics of Bardet–Biedl Syndrome: obesity and the Newfoundland population. In: Medeiros-Neto G, Halpern A, Bouchard C (eds) Progress in Obesity Research 9: Proceedings of the Ninth International Congress on Obesity. Libbey: Esher; 2003. pp 324–327.
Rahman P, Jones A, Curtis J, Bartlett SE, Peddle L, Fernandez BA, Freimer NB . The Newfoundland population: a unique resource for genetics investigation of disease. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: R167–R172.
Horikawa Y, Oda N, Cox NJ, Li X, Orho-Melander M, Hara M, Hinokio Y, Lindner TH, Mashima H, Schwarz PE, del Bosque-Plata L, Horikawa Y, Oda Y, Yoshiuchi I, Colilla S, Polonsky KS, Wei S, Concannon P, Iwasaki N, Schulze J, Baier LJ, Bogardus C, Groop L, Boerwinkle E, Hanis CL, Bell GI . Genetic variation in the gene encoding calpain-10 is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet 2000; 26: 163–175.
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of the BBS families and the volunteers who participated in this study. Financial support for this project was provided by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Janeway Foundation, Memorial University Opportunities Fund, the Arthritis Society of Canada and Newfound Genomics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Rahman, P., Peddle, L. et al. Bardet–Biedl syndrome 1 genotype and obesity in the Newfoundland population. Int J Obes 28, 680–684 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802601
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802601
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
BBS4 directly affects proliferation and differentiation of adipocytes
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2014)
-
Autosomal recessive Bardet–Biedl syndrome: first-degree relatives have no predisposition to metabolic and renal disorders
Kidney International (2009)
-
Pitfalls of homozygosity mapping: an extended consanguineous Bardet–Biedl syndrome family with two mutant genes (BBS2, BBS10), three mutations, but no triallelism
European Journal of Human Genetics (2006)
-
The Human Obesity Gene Map: The 2004 Update
Obesity Research (2005)
-
Linkage disequilibrium mapping in the Newfoundland population: a re-evaluation of the refinement of the Bardet?Biedl syndrome 1 critical interval
Human Genetics (2005)