Abstract
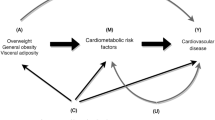
Hypothesis: The multi-faceted components of the metabolic syndrome now include markers of inflammation and endothelial activation. Despite this growing body of epidemiological data, standard statistical methods fail to evaluate the nature of these associations adequately. In this pilot study, we hypothesize that obesity may lead to endothelial activation which is in part mediated by dyslipidaemia and proinflammatory cytokines. These factors interact to give rise to hyperinsulinaemia, hypertension and an anti-fibrinolytic state. To test this hypothesis, we used confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modelling to fit these data to a model designed on theoretical grounds.
Methods: Metabolic syndrome variables, cytokines (IL6 and TNFα), markers of inflammation and endothelial activation were measured in 107 Caucasian non-diabetic subjects aged 40–75 y. Using confirmatory factor analysis, we identified six factors to represent composite measurements of blood pressure, obesity, dyslipidaemia, hyperinsulinaemia, endothelial activation and the anti-fibrinolytic state. We fitted these variables to two separate models, one using IL-6 and the other TNFα as the cytokine, and examined the inter-relationships (path analysis) amongst these variables, based on the above hypothesis.
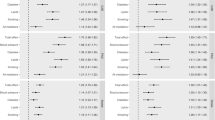
Results: Men were centrally more obese and had increased markers of endothelial activation, inflammation and the anti-fibrinolytic state as well as hyperinsulinaemia and dyslipidaemia, compared with women. Obesity indexes (both body mass index and waist–hip ratio) were strongly associated with multiple cardiovascular risk factors. Both IL6 and TNFα were correlated with age, male gender, obesity indexes and markers of endothelial activation. Only IL-6 was associated with smoking while TNFα was correlated with hyperinsulinaemia. In the TNFα model, 61% of the obesity variance was explained by male gender, 36% of TNFα variance by age and dyslipidaemia, 43% of dyslipidaemia variance by age and obesity, 33% of hyperinsulinaemia variance by dyslipidaemia and a non-smoking state, 29% of anti-fibrinolytic state variance by hyperinsulinaemia, 65% of endothelial activation variance by TNFα, dyslipidaemia and hyperinsulinaemia, 34% of blood pressure variance by hyperinsulinaemia and endothelial activation. In the IL-6 model, we observed similar relationships except that 23% of IL6 variance was explained by smoking and age.
Conclusions: Using confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modelling, we found that obesity, dyslipidemia and cytokines were the principal explanatory variables for the various components of the metabolic syndrome, with IL6 and TNFα having different explanatory variables and effects. These complex inter-relationships were in part mediated by hyperinsulinaemia and endothelial activation. While this hypothetical model was based on scientific evidence, supported by rigorous analysis, it requires further confirmation in large-scale prospective studies. Given the complexity of the biological system and its interactions with exogenous factors, structural equation modelling provides a useful scientific tool for hypothesis testing, complementary to the more traditional experimental and cohort studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reaven GM . Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Banting lecture 1988 Diabetes 1988 37: 1595–1607.
Modan M, Halkin H, Almog S, Lusky A, Shefi M . Hyperinsulinemia. A link between hypertension, obesity and glucose intolerance J Clin Invest 1985 75: 809–817.
Ferrannini E, Buzzigoli G, Bonadonna R, Giorico MA, Oleggini M, Graziadei L, Pedrinelli R, Brandi L, Bevilacqua S . Insulin resistance in essential hypertension New Engl J Med 1987 317: 350–357.
Kaplan NM . The deadly quartet: upper-body obesity, glucose intolerance, hypertriglyceridemia, and hypertension Arch Intern Med 1989 149: 1514–1520.
Bjórntorp P . Metabolic implications of body fat distribution Diabetes Care 1991 14: 1132–1143.
Frayn KN, Coppack SW . Insulin resistance, adipose tissue and coronary heart disease Clin Sci 1992 82: 1–8.
Boyko EJ, Leonetti DL, Bergstrom RW, Newell-Morris L, Fuji WY . Visceral adipostiy, fasting plasma insulin, and blood pressure in Japanese-Americans Diabetes Care 1995 18: 174–181.
Jaap AJ, Shore AC, Tooke JE . Relationship of insulin resistance to microvascular dysfunction in subjects with fasting hyperglycemia Diabetologia 1997 40: 238–243.
Enderle M-D, Benda N, Schmuelling R-M, Haering H, Pfohl M . Preserved endothelial function in IDDM patients, but not in NIDDM patients, compared with healthy subjects Diabetes Care 1998 21: 271–277.
Knock GA, McCarthy AL, Lowy C, Poston L . Association of gestational diabetes with abnormal maternal vascular endothelial function Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1997 104: 229–234.
Leeson CP, Whincup PH, Cook DG, Donald AE, Papacosta O, Lucas A, Deanfield JE . Flow mediated dilatation in 9 to 11 year old children: the influence of intrauterine and childhood factors Circulation 1997 96: 2233–2238.
Goodfellow J, Bellamy MF, Gorman ST, Brownlee M, Ramsey MW, Lewis MJ, Davies DP, Henderson AH . Endothelial function is impaired in fit young adults of low birth weight Cardiovasc Res 1998 40: 600–606.
Tan ES, Emmanuel SC, Chew SK, Tan BY, Tan CE . Isolated low HDL cholesterol: an insulin resistant state only in the presence of fasting hypertriglyceridemia Diabetes 1999 48: 1088–1092.
Vakkilainen J, Makimattila S, Seppala-Lindroos A, Vehkavaara S, Lahdenpera S, Groop PH, Taskinen MR, Yki-Järvinen H . Endothelial dysfunction in men with small dense LDL particles Circulation 2000 102: 716–721.
Tan KC, Ali VH, Chow WS, Chau MT, Leong L, Lam KS . Influence of low density lipoprotein (LDL) subfraction profile and LDL oxidation on endothelium-dependent and independent vasodilation in patients with type 2 diabetes J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999 84: 3212–3216.
Taskinen M-R . Quantitative and qualitative lipoprotein abnormalities in diabetes mellitus Diabetes 1992 41 (Suppl 2): 12–17.
Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC, Vague P . Thrombogenic and fibrinolytic factors and cardiovascular risk in non-insulin-dependent diabetes melltius Ann Med 1996 28: 371–380.
Juhan-Vague I, Pyke S, Alessi MC, Jespersen J, Haverkate F, Thompson SG . Myocardial ischemia/coronary artery vasoconstriction/thrombosis/myocardial infarction: fibrinolytic factors and the risk of myocardial infarction or sudden death in patients with angina pectoris Circulation 1996 94: 2057–2063.
Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE, Ridker PM . C-reactive protein, interleukin 6 and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus JAMA 2001 286: 327–334.
Schmidt MI, Duncan BB, Sharrett AR, Lindberg G, Savage PJ, Offenbacher S, Azanbuja MI, Tracy RP, Heiss C for the ARIC investigators. Markers of inflammation and prediction of diabetes mellitus in adults (atherosclerosis risks in communities study): a cohort study Lancet 1999 353: 1649–1652.
Thompson SG, Kienast J, Pyke SD, Haverkate F, van de Loo JC . Hemostatic factors and the risk of myocardial infarction or sudden death in patients with angina pectoris. European Concerted Action on Thrombosis and Disabilites Angina Pectoris Study Group New Engl J Med 1995 332: 635–641.
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracey RP, Hennekens CH . Inflammation, aspirin and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men New Engl J Med 1997 336: 973–979.
Jöreskog KG, Sörbom D . LISREL 8 user's reference guide Scientific Software: Chicago, IL 1993.
Jöreskog KG . Testing structural equation models In: Bollen KA, Long JS (eds) Testing structural equation models Sage: Newbury Park, CA 1993 294–316.
Chan JCN, Cheung JCK, Lau EMC, Woo J, Swaminathan R, Cockram CS . The Metabolic Syndrome in Hong Kong Chinese—the inter-relationships amongst its components analysed by structural equation modeling Diabetes Care 1996 19: 953–959.
DeFronzo RA . Pathogenesis of Type 2 diabetes: metabolic and molecular implications for identifying diabetes genes Diabetes Rev 1997 5: 177–269.
Facchini F, Chen YD, Clinkingbeard C, Jeppesen J, Reaven GM . Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and dyslipidemia in nonobese individuals with a family history of hypertension Am J Hypertens 1992 5: 694–699.
Williams B . Insulin resistance: the shape of things to come Lancet 1994 344: 521–524.
Saad MF, Lillioja S, Nyomba BL, Castillo C, Ferraro R, De Gregorio M, Ravussin E, Knowler WC, Bennett PH, Howard RV, Bogardus C . Racial differences in the relation between blood pressure and insulin resistance New Engl J Med 1991 324: 733–739.
Baron AD . Hemodynamic actions of insulin Am J Physiol 1994 267 (2 pt 1): E187–E202.
Rowe JW, Young JB, Minaker KL, Stevens AL, Pallotta J, Landsberg L . Effect of insulin and glucose infusion on sympathatic nervous system activity in normal man Diabetes 1981 30: 219–225.
Sawicki PT, Heinemann L, Starke A, Berger M . Hyperinsulinaemia is not linked with blood pressure elevation in patients with insulinoma Diabetologia 1992 35: 649–652.
Peiris AN, Stagner JI, Vogel RL, Nakagawa A, Samols E . Body fat distribution and peripheral insulin sensitivity in healthy men: Role of insulin pulsatility J Clin Endocinol Metab 1992 75: 290–293.
Fontbonne A, Thibult M, Eschwege E, Ducimetiere P . Body fat distribution and coronary heart disease mortality in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes mellitus: the Paris Prospective Study, a 15 year follow-up Diabetologia 1992 35: 464–468.
Bujalska IJ, Kumar S, Stewart PM . Does central obesity reflect ‘Cushing's disease of the omentum’? Lancet 1997 349: 1210–1213.
Lee ZSK, Chan JCN, Yeung VTF, Chow CC, Lau MSW, Ko GTC, Li JKY, Cockram CS, Critchley JAJH . Plasma insulin, growth hormone, cortisol and central obesity among young Chinese Type 2 diabetic patients Diabetes Care 1999 22: 1450–1457.
Bergman RN . New concepts in extracellular signalling for insulin action: the single gateway hypothesis Rec Prog Hormone Res 1997 52: 359–385.
Randle PJ, Hales CN, Garland PB, Newsholme EA . The glucose fatty-acid cycle: its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus Lancet 1963 ii: 785–789.
Mohamed-Ali V, Gould MM, Gillies S, Goubet S, Yudkin JS, Haines AP . Association of proinsulin-like molecules with lipids and fibrinogen in non-diabetic subjects—evidence against a modulating role for insulin Diabetologia 1995 38: 1110–1116.
Yudkin JS, Kumari M, Humphries SE, Mohamed-Ali V on behalf of the University College London Interleukin-6 Group. Inflammation, obesity, stress and coronary heart disease: is interleukin-6 the link? Athersclerosis 2000 209: 209–214.
Vallance P, Collier J, Bhagat K . Infection, inflammation and infarction: does acute endothelial dysfunction provide a link? Lancet 1997 349: 1391–1392.
Maseri A, Biasucci LM, Liuzzo G . Inflammation in ischaemic heart disease Br Med J 1996 312: 1049–1050.
Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Kundsin R, Shih J . Baseline IgG antibody titers to Chlamydia pneumoniae, Helicobacter pylori, herpes simplex virus, and cytomegalovirus and the risk for cardiovascular disease in women Ann Intern Med 2000 131: 573–577.
Tracy RP, Psaty BM, Macy E, Bovill EG, Cushman M, Cornell ES, Kuller LH . Lifetime smoking exposure affects the association of C-reactive protein with cardiovascular disease risk factors and subclinical disease in healthy elderly subjects Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1997 17: 2167–2176.
Björntorp P . Fatty acids, hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance: which comes first? Curr Opin Lipidol 1994 5: 166–174.
Libby P, Ridker PM . Novel inflammatory markers of coronary risk: theory versus practice Circulation 1999 100: 1148–1150.
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Increased adipose tissue expression of tumour necrosis factor α in human obesity and insulin resistance J Clin Invest 1995 95: 2409–2415.
Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CDA, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW . C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: association with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 972–978.
Foyle W-J, Carstensen E, Fernandez M, Yudkin JS . A longitudinal study of associations of microalbuminuria with the insulin resistance syndrome and sodium–lithium countertransport in non-diabetic subjects Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1995 15: 1330–1337.
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E . Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease Diabetes Care 1991 14: 173–194.
Frohlich M, Imhof A, Berg G, Hutchinson WL, Pepys MB, Boeing H, Muche R, Brenner H, Koenig W . Association between C-reactive protein and features of the Metabolic Syndrome Diabetes Care 2000 23: 1835–1839.
Hotamisligil GS, Spiegelman BM . Tumor necrosis factor α: a key component of the obesity-diabetes link Diabetes 1994 43: 1271–1278.
Pickup JC, Mattock MB, Chusney GD, Burt D . NIDDM as a disease of the innate immune system: association of acute-phase reactants and interleukin-6 with metabolic syndrome X Diabetologia 1997 40: 1286–1292.
Van Snick J . Interleukin-6: An overview A Rev Immunol 1990 8: 253–278.
Larsson B, Svardsudd K, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Björntorp P, Tibblin G . Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity, and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13 y follow up of participants in the study of men born in 1913 Br Med J 1984 288: 1401–1404.
Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC . PAI-I, obesity, insulin resistance and risk of cardiovascular events Thromb Haemost 1997 78: 656–660.
Valmadrid CT, Klein R, Moss SE, Klein BEK . The risk of cardiovascular disease mortality associated with microalbuminuria and gross proteinuria in persons with older-onset diabetes mellitus Ann Intern Med 2000 160: 1093–1100.
Imperatore G, Riccardi G, Lovine C, Rivellese AA, Vaccaro O . Plasma fibrinogen: a new factor of the metabolic syndrome population-based study Diabetes Care 1998 21: 649–654.
Tchernof A, Labrie F, Belanger A, Prud'homme D, Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Despres JP . Relationship between endogenous steroid hormone, sex hormone binding globulin and lipoprotein levels in men: contribution of visceral obesity, insulin levels and other metabolic variables Athersclerosis 1997 133: 235–244.
Marin P, Holmang S, Jonsson L, Sjostrom L, Kvist H, Holm G, Lindstedt G, Bjorntorp P . The effects of testosterone treatment on body composition and metabolism in middle-age obese men Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1992 16: 991–997.
Kelley DE, Mandarino LJ . Fuel selection in human skeletal muscle in insulin resistance: a reexamination Diabetes 2000 49: 677–683.
Goodpaster BH, Kelley DE . Role of muscle in triglyceride metabolism Curr Opin Lipidol 1998 9: 231–236.
Austin MA, Hokanson JE, Edwards KL . Hypertriglyceridemia as a cardiovascular risk factor Am J Cardiol 1998 81 (4A): 7B–12B.
Austin MA, Mykkanen L, Kuusisto J, Edwards KL, Nelson C, Haffner SM, Pyorala K, Laakso M . Prospective study of small LDLs as a risk factor for non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in elderly men and women Circulation 1995 92: 1770–1778.
Burke-Gaffney A, Hellewell PG . Tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced ICAM-1 expression in human vascular endothelial and lung epithelial cells: modulation by tyrosine kinase inhibitors Br J Pharmac 1996 119: 1149–1158.
Miki I, Kusano A, Ohta S, Hanai N, Otoshi M, Masaki S, Sato S, Ohmori K . Histamine enhanced the TNF-alpha-induced expression of E-selectin and ICAM-1 on vascular endothelial cells Cellular Immunol 1996 171: 285–288.
Bhunia AK, Arai T, Bulkley G, Chatterjee S . Lactosylceramide mediates tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression (ICAM1) and the adhesion of neutrophil in human umbilical vein endothelial cells J Biol Chem 1998 273: 34349–34357.
Ahima RS, Jeffery SF . Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ Trends Endocrinol Metab 2000 11: 327–332.
Hotamisligil GS, Peraldi P, Budavari A, Ellis R, White MF, Spiegelman BM . IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-α and obesity-induced insulin resistance Science 1996 271: 665–668.
Hotamisligil GS, Budavari A, Murray D, Spiegelman BM . Reduced tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor in obesity-diabetes J Clin Invest 1994 94: 1543–1549.
Tappia PS, Troughton KL, Langley-Evans SC, Grimble RF . Cigarette smoking influences cytokine production and antioxidant defences Clin Sci 1995 88: 485–489.
Mendall MA, Patel P, Asante M, Ballam L, Morris J, Strachan DP, Camm AJ, Northfield TC . Relation of serum cytokine concentrations to cardiovascular risk factors and coronary heart disease Heart 1997 78: 273–277.
Crabtree JE . Role of cytokines in pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori-induced mucosal damage Dig Dise Sci 1998 43 (Suppl 9): 46S–55S.
Watson C, Whittaker S, Smith N, Vora AJ, Dumonde DC, Brown KA . IL-6 acts on endothelial cells to preferentially increase their adherence for lymphocytes Clin Exp Immunol 1996 105: 112–119.
Romano M, Sironi M, Toniatti C, Polentarutti N, Fruscalla P, Ghezzi P, Faggioni R, Luini W, van Hinsbergh V, Sozzani S, Bussolino F, Poli V, Cillberto G, Mantovani A . Role of IL-6 and its soluble receptor in induction of chemokines and leukocyte recruitment Immunity 1997 6: 1–20.
Landsberg L . Diet, obesity and hypertension; a hypothesis involving insulin, the sympathetic nervous system, and adaptive thermogenesis Q J Med 1986 236: 1081–1090.
DeFronzo RA . The effect of insulin on renal sodium metabolism. A review with clinical implications Diabetologia 1981 21: 165–171.
Stout RW . Insulin and atheroma. 20 years perspective Diabetes Care 1990 13: 631–655.
Serne EH, Stehouwer CDA, ter Maaten JC, ter Wee PM, Rauwerda JA, Donker AJM, Gans ROB . Microvascular function relates to insulin sensitivity and blood pressure in normal subjects Circulation 1999 99: 896–602.
Baron AD . Cardiovascular actions of insulin in humans. Implications for insulin sensitivity and vascular tone Ballière's Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993 7: 961–985.
Julius S, Gudbrandsson T, Jamerson K, Andersson O . The interconnection between sympathetics, microcirculation, and insulin resistance in hypertension Blood Pressure 1992 1: 9–19.
Panahloo A, Yudkin JS . Diminished fibrinolysis in diabetes mellitus and its implication for diabetic vascular disease Coronary Artery Disease 1996 7: 723–731.
Juhan Vague I, Roul C, Alessi MC, Ardissone JP, Heim M, Vague P . Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor activity in non insulin dependent diabetic subjects: relationship with plasma insulin Thromb Haemostat 1989 61: 370–373.
Rimm EB, Chan J, Stampfer MJ et al. Prospective study of cigarette smoking, alcohol use and the risk of diabetes in man Br Med J 1995 310: 555–559.
Janzon L, Berntorp K, Hanson M, Lindell SE, Trell E . Glucose tolerance and smoking: a population study of oral and intravenous glucose tolerance test in middle-aged men Diabetologia 1983 25: 86–88.
Ko GTC, Cockram CS, Chan JCN . Smoking and diabetes in Chinese men Postgrad Med J 2000 77: 240–243.
Persson PG, Carlsson S, Svanstrom L, Ostenson CG, Efendic S, Grill V . Cigarette smoking, oral moist snuff use and glucose intolerance J Intern Med 2000 248: 103–110.
Corretti MC, Plotnick GD, Vogel R . Smoking correlates with flow mediated brachial artery vasoactivity but not cold pressor vasoactivity in men with coronary artery disease Int J Cardiac Imag 1998 14: 11–17.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the help of Mairi Gould for the work on the screening phase of the Goodinge Study and Maryam Fernández for work on the recall phase, to Dr John Griffin in performing the assays of cytokines and Dr Geoffrey Ridgway, Dr Nicola Brink and Dr John Holton for antibody titre assays. We thank Ms Christine Andrés for microalbumin and PAI-1 activity assays and Dr Vidya Mohamed-Ali for measurement of insulin and proinsulin-like molecules. We also thank Professor Melissa Austin for measuring the LDL-particle size. Aspects of this study were supported by grants from the Wellcome Trust (12441/1.5) and British Heart Foundation (PG92133) and a Program Grant from Diabetes UK. Dr Stehouwer is supported by a fellowship from the Diabetes Fonds Netherland and the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) and Dr Emeis by Grant 28-2623 from the Praeventiefonds. We thank Professor Melissa Austin for measuring the LDL particle size.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, J., Cheung, J., Stehouwer, C. et al. The central roles of obesity-associated dyslipidaemia, endothelial activation and cytokines in the Metabolic Syndrome—an analysis by structural equation modelling. Int J Obes 26, 994–1008 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802017
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802017
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Methionine adenosyltransferase 1a antisense oligonucleotides activate the liver-brown adipose tissue axis preventing obesity and associated hepatosteatosis
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Dietary influence on calcitropic hormones and adiposity in Caucasian and African American postmenopausal women assessed by structural equation modeling (SEM)
The journal of nutrition, health & aging (2016)
-
Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance in chronic kidney disease
Kidney International (2015)
-
Central Adiposity Rather Than Total Adiposity Measurements Are Specifically Involved in the Inflammatory Status from Healthy Young Adults
Inflammation (2011)
-
Disassociated relation between plasma tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6 and increased body weight in Amerindian women: A long-term prospective study of natural body weight variation and impaired glucose tolerance
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2010)