Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Insulin is thought to be an important regulator of leptin secretion. However, increasing evidence suggests that insulin-mediated glucose uptake rather than insulin per se regulates circulating leptin concentration. Here, we hypothesised that a reduction of insulin sensitivity, ie insulin resistance, will diminish the stimulatory effect of insulin on leptin secretion as a consequence of decreased insulin-mediated glucose uptake.
DESIGN: Changes in serum leptin concentration during 30 hyperinsulinaemic–hypoglycaemic clamps were studied after induction of different levels of insulin resistance in normal-weight men. In 15 subjects insulin sensitivity was reduced by exposing them to a 2.5 h antecedent hypoglycaemia (3.1 mmol/l) induced by a high rate of insulin infusion (15.0 mU/min/kg) on the day before the proper experiment (‘ante-hypo’ condition). In the other 15 subjects no antecedent hypoglycaemia was induced (‘control’ condition). The proper experiment on both conditions was a 6 h stepwise hypoglycaemic clamp induced by a constant rate of insulin infusion (1.5 mU/min/kg).
SUBJECTS: Experiments were carried out in 30 lean healthy subjects (age, mean±s.e.m., 26±1 y; body mass index, 23.1±0.6 kg/m2).
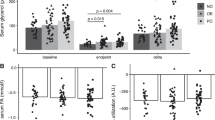
RESULTS: As expected, glucose demand during the clamp was lower in the ante-hypo condition than in the control condition (gram of glucose infused per kilogram body weight, 1.52±0.16 vs 2.01±0.17 g/kg; P<0.05). During the clamp, leptin levels increased by 25.4±4.3% in the control condition (P<0.05), but not in the ante-hypo condition (+4.8±4.5%; P>0.25). Thus, serum leptin response to the clamp significantly differed between the two conditions (P<0.01). Across both conditions, the increase of leptin levels during the clamp was correlated with the amount of glucose infused (r=0.37; P<0.05).
CONCLUSION: Considering that insulin concentrations were identical during both clamp conditions, the data indicate that experimentally-induced insulin resistance diminishes the stimulatory effect of insulin on leptin secretion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trayhurn P, Hoggard N, Mercer JG, Rayner DV . Leptin: fundamental aspects Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23(Suppl 1): 22–28.
Ho SC, Tai ES, Eng PH, Ramli A, Tan CE, Fok AC . A study in the relationships between leptin, insulin, and body fat in Asian subjects Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 246–252.
Zimmet PZ, Collins VR, de Courten MP, Hodge AM, Collier GR, Dowse GK, Alberti KG, Tuomilehto J, Hemraj F, Gareeboo H, Chitson P, Fareed D . Is there a relationship between leptin and insulin sensitivity independent of obesity? A population-based study in the Indian Ocean nation of Mauritius. Mauritius NCD Study Group Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 171–177.
Havel PJ, Kasim Karakas S, Mueller W, Johnson PR, Gingerich RL, Stern JS . Relationship of plasma leptin to plasma insulin and adiposity in normal weight and overweight women: effects of dietary fat content and sustained weight loss J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996 81: 4406–4413.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephans TW, Nyce M, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL, Caro JF . Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans New Engl J Med 1996 334: 292–295.
Saladin R, De Vos P, Guerre Millo M, Leturque A, Girard J, Staels B, Auwerx J . Transient increase in obese gene expression after food intake or insulin administration Nature 1995 377: 527–529.
Wabitsch M, Jensen PB, Blum WF, Christoffersen CT, Englaro P, Heinze E, Rascher W, Teller W, Tornqvist H, Hauner H . Insulin and cortisol promote leptin production in cultured human fat cells Diabetes 1996 45: 1435–1438.
Pagano C, Englaro P, Granzotto M, Blum WF, Sagrillo E, Ferretti E, Federspil G, Vettor R . Insulin induces rapid changes of plasma leptin in lean but not in genetically obese (fa/fa) rats Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1997 21: 614–618.
Utriainen T, Malmstrom R, Makimattila S, Yki Jarvinen H . Supraphysiological hyperinsulinemia increases plasma leptin concentrations after 4 h in normal subjects Diabetes 1996 45: 1364–1366.
Malmstrom R, Taskinen MR, Karonen SL, Yki Jarvinen H . Insulin increases plasma leptin concentrations in normal subjects and patients with NIDDM Diabetologia 1996 39: 993–996.
Saad MF, Khan A, Sharma A, Michael R, Riad Gabriel MG, Boyadjian R, Jinagouda SD, Steil GM, Kamdar V . Physiological insulinemia acutely modulates plasma leptin Diabetes 1998 47: 544–549.
Schmitz O, Fisker S, Orskov L, Hove KY, Nyholm B, Moller N . Effects of hyperinsulinaemia and hypoglycaemia on circulating leptin levels in healthy lean males Diabetes Metab 1997 23: 80–83.
Mueller WM, Gregoire FM, Stanhope KL, Mobbs CV, Mizuno TM, Warden CH, Stern JS, Havel PJ . Evidence that glucose metabolism regulates leptin secretion from cultured rat adipocytes Endocrinology 1998 139: 551–558.
Wang J, Liu R, Hawkins M, Barzilai N, Rossetti L . A nutrient-sensing pathway regulates leptin gene expression in muscle and fat Nature 1998 393: 684–688.
Wellhoener P, Fruehwald-Schultes B, Kern W, Dantz D, Kerner W, Born J, Fehm HL, Peters A . Glucose metabolism rather than insulin is a main determinant of leptin secretion in humans J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000 85: 1267–1271.
Clore JN, Brennan JR, Gebhart SP, Newsome HH, Nestler JE, Blackard WG . Prolonged insulin resistance following insulin-induced hypoglycaemia Diabetologia 1987 30: 851–858.
Fowelin J, Attvall S, Von Schenck H, Smith U, Lager I . Combined effect of growth hormone and cortisol on late posthypoglycemic insulin resistance in humans Diabetes 1989 38: 1357–1364.
Peters A, Rohloff F, Kerner W . Preserved counterregulatory hormone release and symptoms after short term hypoglycemic episodes in normal men J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995 80: 2894–2898.
Tuominen JA, Ebeling P, Stenman UH, Heiman ML, Stephens TW, Koivisto VA . Leptin synthesis is resistant to acute effects of insulin in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 381–382.
Saad MF, Damani S, Gingerich RL, Riad Gabriel MG, Khan A, Boyadjian R, Jinagouda SD, el Tawil K, Rude RK, Kamdar V . Sexual dimorphism in plasma leptin concentration J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 579–584.
Haffner SM, Stern MP, Miettinen H, Wei M, Gingerich RL . Leptin concentrations in diabetic and nondiabetic Mexican-Americans Diabetes 1996 45: 822–824.
Fruehwald-Schultes B, Peters A, Kern W, Beyer J, Pfutzner A . Influence of sex differences in subcutaneous fat mass on serum leptin concentrations Diabetes Care 1998 21: 1204–1205.
Fruehwald-Schultes B, Peters A, Kern W, Beyer J, Pfutzner A . Serum leptin is associated with serum uric acid concentrations in humans Metabolism 1999 48: 677–680.
Kahn CR . Insulin resistance: a common feature of diabetes mellitus New Engl J Med 1986 315: 252–254.
Kolaczynski JW, Goldstein BJ, Considine RV . Dexamethasone, OB gene, and leptin in humans; effect of exogenous hyperinsulinemia J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 3895–3897.
Papaspyrou Rao S, Schneider SH, Petersen RN, Fried SK . Dexamethasone increases leptin expression in humans in vivo J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 1635–1637.
Larsson H, Ahren B . Short-term dexamethasone treatment increases plasma leptin independently of changes in insulin sensitivity in healthy women J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996 81: 4428–4432.
Kosaki A, Yamada K, Kuzuya H . Reduced expression of the leptin gene (ob) by catecholamine through a G(S) protein-coupled pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes Diabetes 1996 45: 1744–1749.
Pinkney JH, Coppack SW, Mohamed Ali V . Effect of isoprenaline on plasma leptin and lipolysis in humans Clin Endocrinol Oxf 1998 48: 407–411.
Mitrakou A, Ryan C, Veneman T, Mokan M, Jenssen T, Kiss I, Durrant J, Cryer P, Gerich J . Hierarchy of glycemic thresholds for counterregulatory hormone secretion, symptoms, and cerebral dysfunction Am J Physiol 1991 260: E67–74.
Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros C, Qu D, Lowell B, Maratos Flier E, Flier JS . Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting Nature 1996 382: 250–252.
Licinio J, Mantzoros C, Negrao AB, Cizza G, Wong ML, Bongiorno PB, Chrousos GP, Karp B, Allen C, Flier JS, Gold PW . Human leptin levels are pulsatile and inversely related to pituitary-adrenal function Nature Med 1997 3: 575–579.
Bornstein SR, Licinio J, Tauchnitz R, Engelmann L, Negrao AB, Gold P, Chrousos GP . Plasma leptin levels are increased in survivors of acute sepsis: associated loss of diurnal rhythm, in cortisol and leptin secretion J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998 83: 280–283.
Heiman ML, Ahima RS, Craft LS, Schoner B, Stephens TW, Flier JS . Leptin inhibition of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in response to stress Endocrinology 1997 138: 3859–3863.
Bornstein SR, Uhlmann K, Haidan A, Ehrhart Bornstein M, Scherbaum WA . Evidence for a novel peripheral action of leptin as a metabolic signal to the adrenal gland: leptin inhibits cortisol release directly Diabetes 1997 46: 1235–1238.
Acknowledgements
We thank Christiane Zinke for her expert and invaluable laboratory assistance and Anja Otterbein for her organisational work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fruehwald-Schultes, B., Oltmanns, K., Kern, W. et al. The effect of experimentally induced insulin resistance on the leptin response to hyperinsulinaemia. Int J Obes 26, 510–516 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801942
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801942
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Insulin determines leptin responses during a glucose challenge in fed and fasted rats
International Journal of Obesity (2005)
-
Insulin resistance induces hyperleptinemia, cardiac contractile dysfunction but not cardiac leptin resistance in ventricular myocytes
International Journal of Obesity (2003)