Abstract
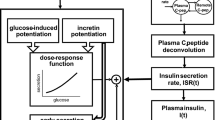
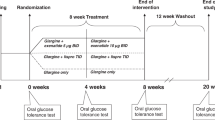
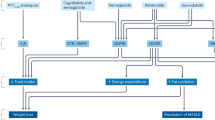
Type 2 diabetes is characterised by a progressive deterioration of the prandial insulin response, in a situation of continuing insulin resistance. Early phase insulin release is attenuated and delayed and there is a consequent failure to suppress glucagon secretion and curtail hepatic glucose production and gluconeogenesis. Postprandial plasma glucose concentration rises to pathological levels and fails to return to normal before the patient consumes their next meal, creating a problem of continuous daytime hyperglycaemia. Although late insulin secretion is preserved it does not rectify the hyperglycaemia. The pathology of excessive prandial glucose excursions and continual daytime hyperglycaemia can be normalised, at least in part, if early-phase insulin availability is restored through pharmacologic intervention. Initially, the feasibility of this approach was demonstrated experimentally with the use of carefully controlled insulin infusions or insulin analogue injections. More recently, the availability of the rapid or early augmentor of insulin secretion—repaglinide—provides a means for restoring prandial glucose regulation with oral therapy. Placebo-controlled and oral hypoglycaemic agent (OHA) comparative studies of repaglinide have established its antidiabetic efficacy and flexible mealtime/dosing studies have confirmed the importance of the prandial approach to treatment. Prandial glucose regulation with repaglinide has also been demonstrated to provide synergies when used as combination therapy with insulin sensitising agents. As a strategy, prandial glucose regulation has a number of theoretical advantages over the use of fixed doses of conventional insulin secretagogues, and these have been borne out in clinical trials. As well as offering a more flexible approach to treatment, prandial repaglinide is associated with a reduced risk of severe hypoglycaemia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garber, A. The importance of early insulin secretion and its impact on glycaemic regulation. Int J Obes 24 (Suppl 3), S32–S37 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801423
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801423