Collection |
Collections
Filters
-
Collection Type
-
-
Focus |
 Covid-19: The Molecular Mechanism and Drug Research
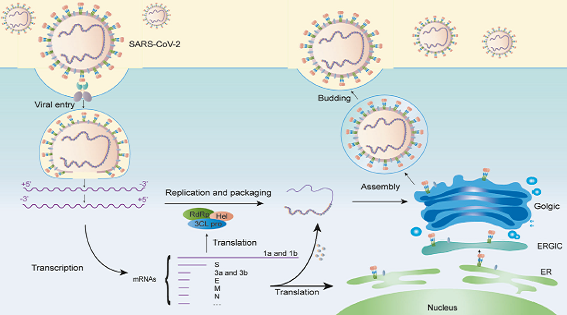
Covid-19: The Molecular Mechanism and Drug Research
In this collection, we provide a broad overview of recent advances for anti-Covid-19 treatment. We hope it will deepen our understanding about the molecular mechanisms and development of antivirus drugs targeting Covid-19.
-
Focus |
 Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
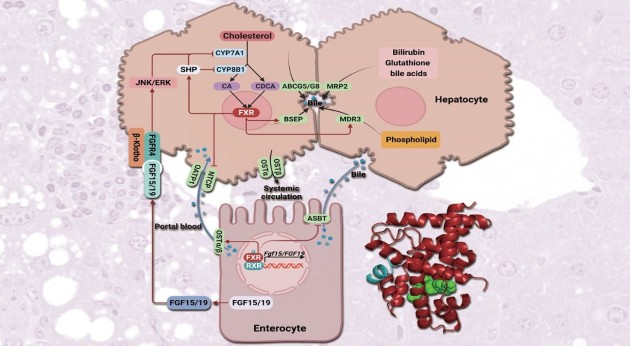
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
In this special issue, we invite 10 articles into the challenges and opportunities of NASH drug discovery. We hope that it will provide valuable insights into NASH biology, drug targets, diagnosis and regulatory issues.
-
Focus |
 40 years of APS
40 years of APS
We celebrate the 40th anniversary of Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (APS) with a series of specially commissioned Reviews and Articles across the diverse areas of the journal’s scope, highlighting the advances made in pharmacological research.
-
Focus |
 Nanomedicine and Cancer Immunotherapy
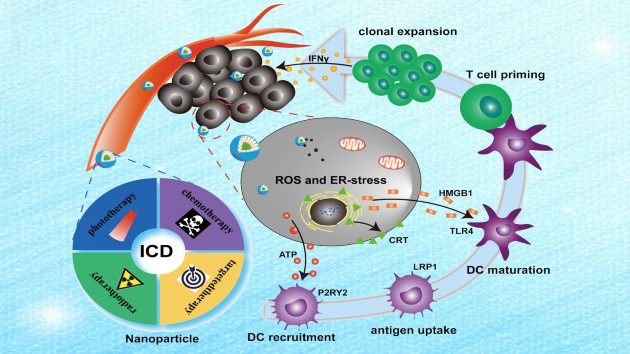
Nanomedicine and Cancer Immunotherapy
In this special issue, we provide a broad overview of recent advances of nanomedicine for cancer immunotherapy. We hope this fruitful collection of articles will deepen our understanding about how nanomedicine can be used to reprogram the tumor microenvironment, and the challenges of nanomedicine approaches for cancer immunotherapy.
-
Focus |
 Drug Research and Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease
Drug Research and Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases. The special feature of APS published in April, 2020 is focused on Drug Research and Diagnosis on Parkinson's Disease (PD) in which we collected 6 Reviews and 4 Research Articles with broad coverage from PD drug discovery, imaging probe, mitochondrial functions, synaptic plasticity, non-dopaminergic system to animal model and psychosis in PD.
-
Focus |
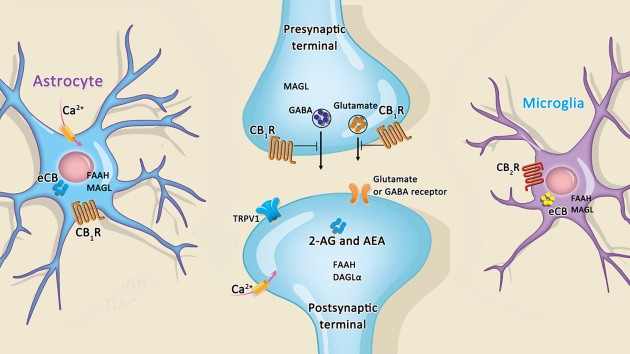 Cannabis, cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoid system
Cannabis, cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoid system
In this collection of articles, we provide a broad perspective on current advances in cannabinoid studies involving a great variety of experimental techniques.
-
Focus |
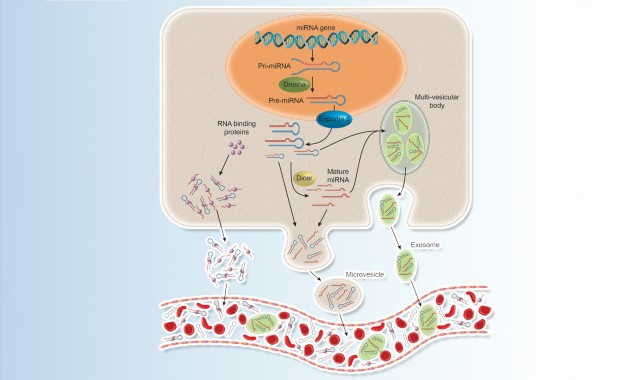 Circulating Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Diseases
Circulating Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) remain the No. 1 killer in industrial countries and a main reason for frequent re-hospitalization. Biomarker testing may play a central role in promoting improved clinical outcome, better quality of life, and alleviated socio-economic burden of CVD. Even in this post-cTn (cardiac troponin) and post-BNP (B-type natriuretic peptide) era, there are still significant gaps and demands for more reliable and innovative biomarker-based tools for diagnosis and evidence-guided management of CVD. This Special Issue of Acta Pharmacologica Sinica consists of 18 original research or review articles authored by 108 scientists from 15 countries to showcase recent advances in translational and clinical investigations focusing on biomarkers that are released from injured cardiovascular tissues into circulation during various CVD events, such as acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, aortic aneurysms, carotid restenosis, pulmonary hypertension, and cardiac amyloidosis. These collective efforts can benefit future technological development of novel tests for CVD biomarkers.
-
Focus |
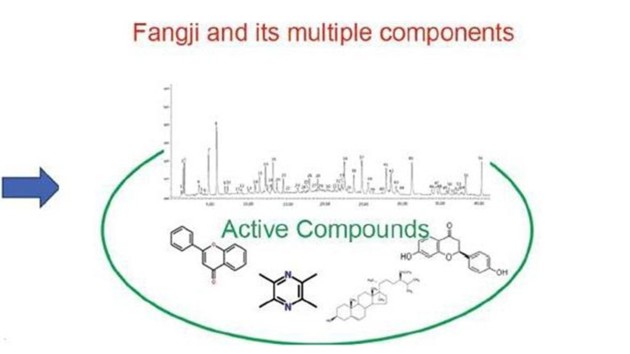 Fangjiomics
Fangjiomics
In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), the main therapeutics is the unique TCM medicinal formula, so called Fangji, which is usually composed of multiple herbs and medical materials with integrated multiple therapeutic objects. The modern pharmacological approach to the study of Fangji, however, has been focusing on the isolation and identification of individual active components within a Fangji for cellular and molecular targets. This not only has led to the misinterpretations of mechanisms of Fangji’s therapeutic actions and clinical effectiveness but also has seriously hampered the scientific research and development of TCM in general. Clearly, new omic/systematic and networking paradigms are urgently needed for deep understanding of the unique composition theories and mechanisms of effective combination therapy through TCM Fangji. In this special issue, we continued to introduce Fangjiomics-based combination therapy applications to the discovery of rational combination therapy and precision medicine.
-
Focus |
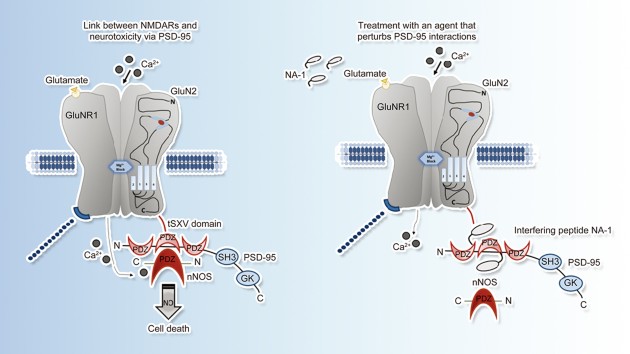 Frontier in Medical Research and Drug Development
Frontier in Medical Research and Drug Development
This special issue attributes to the 2017 China-Canada-USA Pharmacology/Physiology Conference (CCUPPC), one of the largest initiatives promoting scientific exchanges and research collaborations in the field of pharmacology, physiology and drug development. Specifically, this special issue features review and original articles highlighting the most recent innovations in drug discovery and drug delivery in stroke, mental health, and neurodegenerative disorders; potential mechanisms of novel endogenous peptides, and natural products broadly used in metabolic, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disorders; and organ preservation, etc. The conference brought scientists from China, Canada, and USA together, and created a new platform for international interaction and collaboration. The conference took place at the University of Toronto, known as the birthplace for insulin, the alma mater of Dr. Norman Bethune, and one of the world’s top research-intensive universities.
-
Focus |
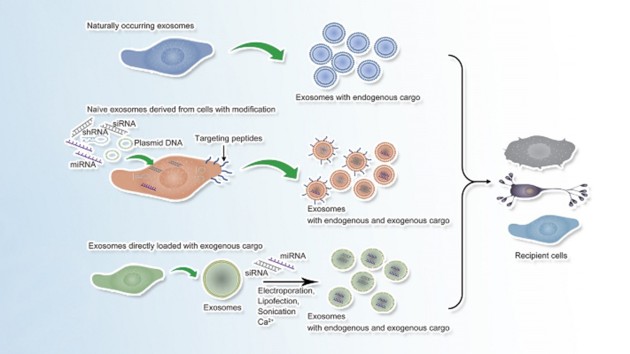 Exosomes
Exosomes
Extracellular microvesicles (MVs) and exosomes (EXs) are the major types of extracellular vesicles (EVs) which can carry and transfer molecular messages (proteins, mRNAs and microRNAs,etc). Thereby, EVs could serve to mark the changes of the producing cells and to function on the recipient cells. These features deem EVs as potential biomarkers and pharmacological targets for various diseases including metabolic, vascular and neurological diseases and tumors. The current special feature provides reviews and original research articles on novel pharmacological studies of MVs and EXs.
-
Focus |
 Cancer Nanobiotechnology
Cancer Nanobiotechnology
Nanobiotechnology plays a more and more important role in combating cancer. Ideal delivery should maximize drug accumulation at tumors while minimize the unwanted drug exposure to the normal tissues, thus executing cytotoxicity specifically in cancer cells and sparing the healthy cells. Nanotechnology-based targeting delivery has been generally believed as the most promising method to achieve this ultimate goal of pharmacotherapy. Nano drug delivery systems can improve the pharmacokinetics profiles and tumor biodistribution of the antitumor drugs, and enhance their intracellular delivery as well; in addition, the drug instability and water insolubility problems can be solved by encapsulation into nano carriers.

 Celebrating the 90th Anniversary of SIMM
Celebrating the 90th Anniversary of SIMM