
April issue now live!
Our April issue includes a Comment on taking inspiration from epidemic modeling to improve wildfire resilience, and a Resource for high-resolution simulations of large and complex biological tissues.

Our April issue includes a Comment on taking inspiration from epidemic modeling to improve wildfire resilience, and a Resource for high-resolution simulations of large and complex biological tissues.




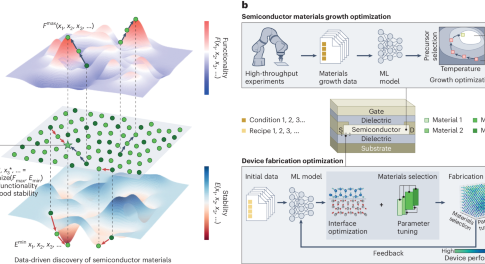
Discovering improved semiconductor materials is essential for optimal device fabrication. In this Perspective, data-driven computational frameworks for semiconductor discovery and device development are discussed, including the challenges and opportunities moving forward.