News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Terahertz field-induced nonlinear coupling of two magnon modes in an antiferromagnet
Terahertz field-induced nonlinear coupling of two magnon modes in an antiferromagnet
Magnons—quanta of spin waves—have potential applications in signal processing technology. But it is challenging to obtain coupling between different magnons. Now a study achieves this by demonstrating nonlinear magnon mixing in an antiferromagnet.
- Zhuquan Zhang
- , Frank Y. Gao
- & Keith A. Nelson
-
Article |
 Terahertz-field-driven magnon upconversion in an antiferromagnet
Terahertz-field-driven magnon upconversion in an antiferromagnet
Inducing coherent interactions between distinct magnon modes—collective excitations of magnetic order—has been challenging. A canted antiferromagnet has demonstrated coherent magnon upconversion induced by terahertz laser pulses.
- Zhuquan Zhang
- , Frank Y. Gao
- & Keith A. Nelson
-
News & Views |
 Stronger pairs with resonant excitation
Stronger pairs with resonant excitation
Understanding the mechanism underlying light-induced superconductivity could help manifest it at higher temperatures. Experiments now show that the excitation of a specific phonon leads to a resonant enhancement of this effect in K3C60.
- Jingdi Zhang
-
Article |
 A Hubbard exciton fluid in a photo-doped antiferromagnetic Mott insulator
A Hubbard exciton fluid in a photo-doped antiferromagnetic Mott insulator
Hole and particle-like quasiparticles of a Mott insulator can pair into excitonic bound states. Now, time-resolved measurements of Sr2IrO4 show signs of an excitonic fluid forming from a photo-excited population of quasiparticles.
- Omar Mehio
- , Xinwei Li
- & David Hsieh
-
Article
| Open Access Critical slowing down near a magnetic quantum phase transition with fermionic breakdown
Critical slowing down near a magnetic quantum phase transition with fermionic breakdown
YbRh2Si2 has a quantum phase transition between an antiferromagnetic phase and a so-called heavy-Fermi-liquid state. Measurements of critical slowing down suggest that the heavy-fermion quasiparticles break down at the transition.
- Chia-Jung Yang
- , Kristin Kliemt
- & Shovon Pal
-
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling of terahertz light with nanometre-wavelength magnon modes via spin–orbit torque
Coupling of terahertz light with nanometre-wavelength magnon modes via spin–orbit torque
Engineering of the spin–orbit interactions in a magnetic multilayered structure makes it possible to coherently generate coherent spin waves using terahertz radiation, which could benefit the development of spintronic devices.
- Ruslan Salikhov
- , Igor Ilyakov
- & Sergey Kovalev
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum coherence tomography of light-controlled superconductivity
Quantum coherence tomography of light-controlled superconductivity
Multidimensional coherent spectroscopy measurements in iron-based superconductors demonstrate how the coupling between a superconductor and strong light pulses can drive the transition into a non-equilibrium superconducting state with distinct collective modes.
- L. Luo
- , M. Mootz
- & J. Wang
-
Research Briefing |
 Experimentally confirming the special relativistic properties of Coulomb fields
Experimentally confirming the special relativistic properties of Coulomb fields
The spatiotemporal profile of the electric field around a high-energy electron beam was visualized using an ultrafast technique based on electro-optic sampling. By investigating the formation of the Coulomb field it was possible to experimentally confirm the validity of the predictions of special relativity regarding electromagnetic fields.
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast visualization of an electric field under the Lorentz transformation
Ultrafast visualization of an electric field under the Lorentz transformation
The Lorentz transformation of electromagnetic potentials is confirmed in experiments with a highly energetic electron beam. This provides another test of the predictions of special relativity.
- Masato Ota
- , Koichi Kan
- & Makoto Nakajima
-
Article
| Open Access Band transport by large Fröhlich polarons in MXenes
Band transport by large Fröhlich polarons in MXenes
The charge transport mechanism in MXenes—an emerging class of layered materials—is not yet fully understood. A combination of terahertz spectroscopy and transport measurements shows that the formation of large polarons play a crucial role.
- Wenhao Zheng
- , Boya Sun
- & Mischa Bonn
-
Article |
 Cyclotron resonance overtones and near-field magnetoabsorption via terahertz Bernstein modes in graphene
Cyclotron resonance overtones and near-field magnetoabsorption via terahertz Bernstein modes in graphene
Electrons in an external magnetic field absorb electromagnetic radiation via cyclotron resonance. Deviations from this behaviour in the form of overtone resonances due to ultraslow magnetoplasmonic excitations are now reported for graphene.
- D. A. Bandurin
- , E. Mönch
- & S. D. Ganichev
-
Perspective |
 Engineering crystal structures with light
Engineering crystal structures with light
The interaction between light and the crystal lattice of a quantum material can modify its properties. Utilizing nonlinear interactions allows this to be done in a controlled way to design specific non-equilibrium functionalities.
- Ankit S. Disa
- , Tobia F. Nova
- & Andrea Cavalleri
-
Letter |
 Ultrafast switching to an insulating-like metastable state by amplitudon excitation of a charge density wave
Ultrafast switching to an insulating-like metastable state by amplitudon excitation of a charge density wave
Ultrafast optical excitation of a charge density wave leads to the formation of a metastable gapped state that synchronizes with the underlying correlated phase.
- Naotaka Yoshikawa
- , Hiroki Suganuma
- & Ryo Shimano
-
Article |
 Ultrafast spin current generated from an antiferromagnet
Ultrafast spin current generated from an antiferromagnet
Spin currents are generated from an antiferromagnet/heavy-metal heterostructure using optical excitation on picosecond timescales. This will have applications in antiferromagnetic spintronics.
- Hongsong Qiu
- , Lifan Zhou
- & Peiheng Wu
-
Article |
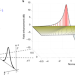 Subcycle squeezing of light from a time flow perspective
Subcycle squeezing of light from a time flow perspective
A general theoretical picture regarding the generation and the detection of extremely short pulses of squeezed vacuum light is provided, allowing the treatment of arbitrary wavepackets of quantum light intrinsically in the time domain.
- Matthias Kizmann
- , Thiago Lucena de M. Guedes
- & Guido Burkard
-
Letter |
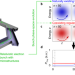 Stable coherent terahertz synchrotron radiation from controlled relativistic electron bunches
Stable coherent terahertz synchrotron radiation from controlled relativistic electron bunches
A feedback loop based on chaos control theory permits the generation of stable and coherent terahertz radiation from relativistic electron bunches in synchrotron light sources.
- C. Evain
- , C. Szwaj
- & S. Bielawski
-
Letter |
 Far out-of-equilibrium spin populations trigger giant spin injection into atomically thin MoS2
Far out-of-equilibrium spin populations trigger giant spin injection into atomically thin MoS2
Efficient spin injection across ferromagnet/semiconductor interfaces is a major goal for future spintronic approaches. Ultrafast spectroscopy now reveals strong spin currents to be inducible in monolayer MoS2 by ultralow-intensity laser pulses.
- Liang Cheng
- , Xinbo Wang
- & Elbert E. M. Chia
-
Letter |
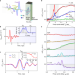 Leggett mode controlled by light pulses
Leggett mode controlled by light pulses
There has latterly been a renewed interest in collective excitations in condensed matter systems. Now, spectroscopic evidence for the so-called Leggett mode is revealed in the superconductor MgB2.
- Flavio Giorgianni
- , Tommaso Cea
- & Lara Benfatto
-
Article |
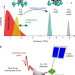 Terahertz-driven phonon upconversion in SrTiO3
Terahertz-driven phonon upconversion in SrTiO3
A spectroscopic study of strontium titanate provides a method for transferring the vibrational energy of a low-frequency phonon mode to higher-frequency modes, with the potential to access elusive ‘silent’ modes.
- M. Kozina
- , M. Fechner
- & M. C. Hoffmann
-
Article |
 Magneto-transport controlled by Landau polariton states
Magneto-transport controlled by Landau polariton states
A polariton is a hybrid excitation resulting from strong light–matter coupling. The magneto-transport measurements have now revealed the crucial role played by its electronic component.
- Gian L. Paravicini-Bagliani
- , Felice Appugliese
- & Jérôme Faist
-
Letter |
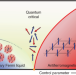 Time-resolved collapse and revival of the Kondo state near a quantum phase transition
Time-resolved collapse and revival of the Kondo state near a quantum phase transition
Using terahertz pulses, the quasiparticle dynamics of the heavy-fermion compound CeCu6−xAu are investigated in the vicinity of its quantum critical point.
- C. Wetli
- , S. Pal
- & M. Fiebig
-
Letter |
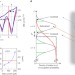 Light-induced electron localization in a quantum Hall system
Light-induced electron localization in a quantum Hall system
Picosecond pulses of terahertz radiation induce non-equilibrium electron dynamics in a GaAs quantum Hall system, suppressing the longitudinal resistivity, and giving rise to a quantized transverse component.
- T. Arikawa
- , K. Hyodo
- & K. Tanaka
-
Article |
 Ultrafast terahertz control of extreme tunnel currents through single atoms on a silicon surface
Ultrafast terahertz control of extreme tunnel currents through single atoms on a silicon surface
Controlling electric currents on the atomic scale requires being able to handle the ultrafast timescales involved. Now, experiments have demonstrated the feasibility of terahertz scanning tunnelling microscopy as a method for doing just that.
- Vedran Jelic
- , Krzysztof Iwaszczuk
- & Frank A. Hegmann
-
Letter |
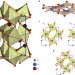 An effective magnetic field from optically driven phonons
An effective magnetic field from optically driven phonons
Light can be used to directly excite phonon modes in condensed matter. Simultaneously exciting several modes in an antiferromagnetic rare-earth orthoferrite drives behaviour that mimics the application of a magnetic field.
- T. F. Nova
- , A. Cartella
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Letter |
 Parametric amplification of a superconducting plasma wave
Parametric amplification of a superconducting plasma wave
Josephson plasma waves — electromagnetic waves propagating between layered superconductors — lie at the basis of a broad variety of phenomena. Now, parametric amplification of such waves has been shown by tuning the phase between pump and seed waves.
- S. Rajasekaran
- , E. Casandruc
- & A. Cavalleri
-
News & Views |
 Light-induced superconductivity
Light-induced superconductivity
Intense light pulses irradiating a sample of K3C60 result in dramatic changes of its high-frequency (terahertz) conductivity. Could these be signatures of fleeting superconductivity at 100 K and beyond?
- Jure Demsar
-
Letter |
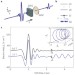 Coherent cyclotron motion beyond Kohn’s theorem
Coherent cyclotron motion beyond Kohn’s theorem
Kohn’s theorem states that the electron cyclotron resonance is unaffected by many-body interactions in a static magnetic field. Yet, intense terahertz pulses do introduce Coulomb effects between electrons—holding promise for quantum control of electrons.
- T. Maag
- , A. Bayer
- & M. Kira
-
Letter |
 Terahertz control of nanotip photoemission
Terahertz control of nanotip photoemission
Nanoscale metallic tips are a useful source of electrons for material characterization. It is now shown how terahertz radiation can provide precision control and enhancement of photoelectron emission from these sources. The approach can shape the spectrum of the electron pulse, which could pave the way to improvements in ultrafast electron diffraction and transmission electron microscopy.
- L. Wimmer
- , G. Herink
- & C. Ropers

 Terahertz magnon algebra
Terahertz magnon algebra Band build-up
Band build-up