Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structure sensitivity of Cu and CuZn catalysts relevant to industrial methanol synthesis
Structure sensitivity of Cu and CuZn catalysts relevant to industrial methanol synthesis
The dependence of the Cu-catalysed methanol synthesis on the structure of the Cu surface is a matter of debate. Here the authors show that activity falls for Cu and Cu-Zn particles below 8 nm and propose this is due to the absence of certain atomic configurations on the smaller particle surfaces.
- Roy van den Berg
- , Gonzalo Prieto
- & Krijn P. de Jong
-
Article
| Open Access Super-elastic and fatigue resistant carbon material with lamellar multi-arch microstructure
Super-elastic and fatigue resistant carbon material with lamellar multi-arch microstructure
Low-density compressible materials often suffer from fatigue-induced failure or limited elasticity. Here, the authors create a hierarchical multi-arch carbon material that achieves high compressibility, superior elasticity and fatigue resistance simultaneously, inspired by properties of arches in daily life.
- Huai-Ling Gao
- , Yin-Bo Zhu
- & Shu-Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Structural lubricity under ambient conditions
Structural lubricity under ambient conditions
Structural lubricity—referring to ultralow levels of friction between atomically flat, incommensurate surfaces—has previously been observed under ultrahigh vacuum. Here, the authors report structural lubricity at gold-graphite interfaces under ambient conditions and on mesoscopic scales.
- Ebru Cihan
- , Semran İpek
- & Mehmet Z. Baykara
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional shape memory graphene oxide
Two-dimensional shape memory graphene oxide
When reducing the size of shape memory materials to the nanoscale regime, the memory effect tends to diminish. Here, the authors report a theoretical proposal of a shape memory graphene oxide with ordered epoxy groups retaining excellent programmability and actuation capabilities.
- Zhenyue Chang
- , Junkai Deng
- & Jefferson Zhe Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-scale disproportionation in amorphous silicon monoxide
Atomic-scale disproportionation in amorphous silicon monoxide
Amorphous silicon monoxide is known to undergo disproportionation to silicon- and silicon dioxide-like regions, however direct observation of the atomic-scale heterogeneity is still missing. Here, the authors use angstrom-beam electron diffraction to reveal precise structural details of this unusual material.
- Akihiko Hirata
- , Shinji Kohara
- & Mingwei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic mechanism of polarization-controlled surface reconstruction in ferroelectric thin films
Atomic mechanism of polarization-controlled surface reconstruction in ferroelectric thin films
Miniature of electronic devices is attractive yet challenging due to structural variation at nanoscale. Here, Gao et al. report atomic imaging of reconstruction and unusual domain walls on Pb(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3surfaces, providing possibilities to engineer nanoscale structural change.
- Peng Gao
- , Heng-Jui Liu
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Structural control of mixed ionic and electronic transport in conducting polymers
Structural control of mixed ionic and electronic transport in conducting polymers
Conducting polymers are promising materials for applications including bioelectronics and soft robotics, but little is known about how morphology affects mixed conduction. Here, the authors show how bulk ionic/electronic transport is affected by changes in nano- and meso-scale structure in PEDOT:PSS films.
- Jonathan Rivnay
- , Sahika Inal
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Article
| Open Access A low-cost hierarchical nanostructured beta-titanium alloy with high strength
A low-cost hierarchical nanostructured beta-titanium alloy with high strength
Lightweight materials with high strength are desirable for applications where they could reduce energy consumption. Here, the authors develop a low cost beta-titanium alloy that uses a hierarchical nanostructure of precipitates with different sizes to achieve high strength.
- Arun Devaraj
- , Vineet V. Joshi
- & Curt Lavender
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleation of amorphous shear bands at nanotwins in boron suboxide
Nucleation of amorphous shear bands at nanotwins in boron suboxide
Grain boundaries affect the physical properties of metals but their influence on covalent solids is less well established. Here, the authors use scanning transmission electron microscopy and quantum mechanics to understand deformation mechanisms in perfect and twinned boron suboxide crystals.
- Qi An
- , K. Madhav Reddy
- & William A. Goddard III
-
Article
| Open Access A three-dimensional actuated origami-inspired transformable metamaterial with multiple degrees of freedom
A three-dimensional actuated origami-inspired transformable metamaterial with multiple degrees of freedom
Typically, most structures and devices that can be reconfigured are designed with application specific requirements. Inspired by modular origami ideas, Overveldeet al. present a mechanical metamaterial enabling the design of three-dimensional structures of arbitrary architecture with tunable shape, volume and stiffness.
- Johannes T.B. Overvelde
- , Twan A. de Jong
- & Katia Bertoldi
-
Article
| Open Access Multiscale deformations lead to high toughness and circularly polarized emission in helical nacre-like fibres
Multiscale deformations lead to high toughness and circularly polarized emission in helical nacre-like fibres
The mechanical properties and hierarchical structure of nacre have been widely investigated as a biomimetic template for applications. Here, the authors demonstrate that nacre-like fibres made from nanoplatelets and polymers show exceptional stretchability and toughness.
- Jia Zhang
- , Wenchun Feng
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
Article
| Open Access Nanotwin-governed toughening mechanism in hierarchically structured biological materials
Nanotwin-governed toughening mechanism in hierarchically structured biological materials
As a natural biocomposite, Strombus gigas, commonly known as the giant pink queen conch shell, exhibits outstanding mechanical properties such as fracture toughness. Here, the authors show that these properties can be partially attributed to nanoscale twin boundaries in the basic building block of the shell.
- Yoon Ah Shin
- , Sheng Yin
- & Sang Ho Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Structural complexity of simple Fe2O3 at high pressures and temperatures
Structural complexity of simple Fe2O3 at high pressures and temperatures
Fe2O3is known to undergo a series of structural, electronic and magnetic transformations at high pressures and temperatures but these are poorly understood due to a lack of structural data. Here, the authors perform experiments to elucidate the transformations and relationships between them.
- E. Bykova
- , L. Dubrovinsky
- & V. Prakapenka
-
Article
| Open Access Monolayer-to-bilayer transformation of silicenes and their structural analysis
Monolayer-to-bilayer transformation of silicenes and their structural analysis
Two dimensional forms of silicon offer different conductive properties to that of the bulk material, promising applications in new electronic technologies. Here, the authors report the fabrication of bilayer silicenes which, unlike their monolayer form, are indirect bandgap semiconductors.
- Ritsuko Yaokawa
- , Tetsu Ohsuna
- & Hideyuki Nakano
-
Article
| Open Access Non-random walk diffusion enhances the sink strength of semicoherent interfaces
Non-random walk diffusion enhances the sink strength of semicoherent interfaces
Materials resistant to radiation damage could improve the safety, efficiency and sustainability of nuclear energy. Here, the authors suggest that some materials and interfaces may be effective sinks for defects caused by this damage and propose that elastic interactions enhance sink strength.
- A. Vattré
- , T. Jourdan
- & M. J. Demkowicz
-
Article
| Open Access Structure sensitivity in the nonscalable regime explored via catalysed ethylene hydrogenation on supported platinum nanoclusters
Structure sensitivity in the nonscalable regime explored via catalysed ethylene hydrogenation on supported platinum nanoclusters
Ethylene hydrogenation often serves as an example of a structure insensitive reaction. Here, the authors study the reaction, catalyzed by a range of size-selected platinum nanocatalysts, and demonstrate that in the sub-nanometer regime particle size can be used to tune hydrogenation activity and selectivity.
- Andrew S. Crampton
- , Marian D. Rötzer
- & Uzi Landman
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling the structural arrangements responsible for the atomic dynamics in metallic glasses during physical aging
Unveiling the structural arrangements responsible for the atomic dynamics in metallic glasses during physical aging
Glass aging is one of unsolved problems during glass processing and annealing, partly due to the lack of the mechanistic understanding on microscales. Here, the authors show how local stresses and their evolution affect structural relaxation at an atomic level in a metallic glass system.
- V. M. Giordano
- & B Ruta
-
Article
| Open Access Quasi one-dimensional band dispersion and surface metallization in long-range ordered polymeric wires
Quasi one-dimensional band dispersion and surface metallization in long-range ordered polymeric wires
Polymerization on surfaces is an emerging approach for producing graphene nanoribbons with a tunable bandgap, a promising material for carbon-based electronics. Here, Vasseur et al.show quasi-one-dimensional band structure of a model semiconducting polymer synthesized directly on a supporting surface.
- Guillaume Vasseur
- , Yannick Fagot-Revurat
- & Dmitrii F. Perepichka
-
Article
| Open Access Structural diversity in binary superlattices self-assembled from polymer-grafted nanocrystals
Structural diversity in binary superlattices self-assembled from polymer-grafted nanocrystals
Binary nanocrystal superlattice metamaterials are arousing significant interest due to their potential for use in functional devices. Here, the authors endow the nanoparticles with polymer brushes which enable control over their spacings and thus mesoscale structure and properties.
- Xingchen Ye
- , Chenhui Zhu
- & A. Paul Alivisatos
-
Article
| Open Access Determination of band alignment in the single-layer MoS2/WSe2 heterojunction
Determination of band alignment in the single-layer MoS2/WSe2 heterojunction
The alignment of the bandgap of adjacent materials in a heterostructure largely determines the electronic properties of a device. Here, the authors measure the conduction and valance band offsets at the interface between two two-dimensional materials: molybdenum disulphide and tungsten diselenide.
- Ming-Hui Chiu
- , Chendong Zhang
- & Lain-Jong Li
-
Article
| Open Access The surface structure of silver-coated gold nanocrystals and its influence on shape control
The surface structure of silver-coated gold nanocrystals and its influence on shape control
Nanocrystal surface structure affects many properties but is tough to determine for halide-adsorbed materials. Here, the authors combine X-ray absorption measurements and computational modelling to elucidate the chloride metal surface structures for silver-coated gold nanocrystals with controlled shapes.
- J. Daniel Padmos
- , Michelle L. Personick
- & Peng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Complex structural dynamics of nanocatalysts revealed in Operando conditions by correlated imaging and spectroscopy probes
Complex structural dynamics of nanocatalysts revealed in Operando conditions by correlated imaging and spectroscopy probes
Studying a catalyst during reaction (operando conditions) can give significant insights into the changes a catalyst undergoes. Here, the authors use an operandoapproach to correlate X-ray spectroscopy and electron based imaging techniques to measure the dynamic changes in Pt nanoparticles during the catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene.
- Y. Li
- , D. Zakharov
- & A.I. Frenkel
-
Article
| Open Access Damage-tolerant nanotwinned metals with nanovoids under radiation environments
Damage-tolerant nanotwinned metals with nanovoids under radiation environments
Materials that are tolerant to radiation damage are important for use in nuclear reactors or the storage of nuclear materials. Here, the authors show that pre-introduced nanovoids in nanotwinned copper improve self-healing of the material and therefore enhance its radiation tolerance.
- Y. Chen
- , K Y. Yu
- & X. Zhang
-
Article |
 Narrowband light detection via internal quantum efficiency manipulation of organic photodiodes
Narrowband light detection via internal quantum efficiency manipulation of organic photodiodes
There is a growing interest in the development of narrowband photodiodes for full-color imaging and visible-blind near-infrared detection. Armin et al.show a sub-100 nm response by tuning the spectral bandwidth through regulating the charge collection efficiency in a thick organic bulk heterojunction.
- Ardalan Armin
- , Ross D. Jansen-van Vuuren
- & Paul Meredith
-
Article
| Open Access The 3D-architecture of individual free silver nanoparticles captured by X-ray scattering
The 3D-architecture of individual free silver nanoparticles captured by X-ray scattering
The occurrence of thermodynamically metastable nanoparticles determines the particle growth in nature, but capturing them is experimentally challenging. Barke et al. identify the three-dimensional shape of metastable silver nanoparticles in gas phase, characterized by X-ray free-electron laser.
- Ingo Barke
- , Hannes Hartmann
- & Thomas Möller
-
Article |
 Redox response of actinide materials to highly ionizing radiation
Redox response of actinide materials to highly ionizing radiation
Understanding the degradation of materials subject to energetic radiation is important for the development of technologies based on nuclear fission. Here, the authors show that redox reactions of actinide compounds play an important role in their response to energetic radiation and their radiation tolerance.
- Cameron L. Tracy
- , Maik Lang
- & Rodney C. Ewing
-
Article
| Open Access Dislocation-mediated relaxation in nanograined columnar palladium films revealed by on-chip time-resolved HRTEM testing
Dislocation-mediated relaxation in nanograined columnar palladium films revealed by on-chip time-resolved HRTEM testing
Nanostructured metallic materials involve a high rate sensitivity usually resulting from grain boundary related mechanisms. Here, the authors report mechanical tests on freestanding Pd thin films and show that creep is associated with dislocations rather than grain boundaries.
- M. -S. Colla
- , B. Amin-Ahmadi
- & T. Pardoen
-
Article |
 Low-density three-dimensional foam using self-reinforced hybrid two-dimensional atomic layers
Low-density three-dimensional foam using self-reinforced hybrid two-dimensional atomic layers
Low-density foams offer a number of attractive properties as compared to bulk materials. Here, the authors report a three-dimensional foam structure composed of stacked graphene oxide layers reinforced by hexagonal boron nitride, causing enhanced mechanical integrity.
- Soumya Vinod
- , Chandra Sekhar Tiwary
- & Pulickel M. Ajayan
-
Article
| Open Access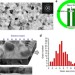 Grain rotation mediated by grain boundary dislocations in nanocrystalline platinum
Grain rotation mediated by grain boundary dislocations in nanocrystalline platinum
Grain rotation is proposed as an active deformation mechanism in nanocrystalline metals at room temperature. Here, during in-situatomic scale experimentation, the authors observe that grains with a size <6 nm deform by coordinated rotation of multiple grains, associated with dislocation climb at grain boundaries.
- Lihua Wang
- , Jiao Teng
- & Xiaodong Han
-
Article
| Open Access A critical analysis of calcium carbonate mesocrystals
A critical analysis of calcium carbonate mesocrystals
The term mesocrystal describes three-dimensional crystals formed by oriented assembly and that exhibit nanoparticle substructures. Here, the authors perform detailed structural analyses on synthetic calcium carbonate/polymer crystals, and show that common signatures used to assign mesocrystals may be unreliable.
- Yi-Yeoun Kim
- , Anna S. Schenk
- & Fiona C. Meldrum
-
Article |
 Tablet-level origin of toughening in abalone shells and translation to synthetic composite materials
Tablet-level origin of toughening in abalone shells and translation to synthetic composite materials
The mechanism responsible for the toughness of nacre, the hierarchical iridescent material in seashells, is still unknown. Espinosa and colleagues show that the waviness of its tablets leads to interfacial hardening, and ultimately to energy dissipation, when the material is stressed.
- Horacio D. Espinosa
- , Allison L. Juster
- & Pablo D. Zavattieri
-
Article |
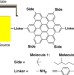 Gate-controlled electron transport in coronenes as a bottom-up approach towards graphene transistors
Gate-controlled electron transport in coronenes as a bottom-up approach towards graphene transistors
Graphene sheets used to build electronic devices have defects that limit performance. As a possible bottom-up route towards better devices, Diez-Perez and co-workers build large polyaromatic molecules with precisely defined structures which show good performance as field-effect transistors.
- Ismael Diez-Perez
- , Zhihai Li
- & Nongjian Tao

 Unveiling the pentagonal nature of perfectly aligned single-and double-strand Si nano-ribbons on Ag(110)
Unveiling the pentagonal nature of perfectly aligned single-and double-strand Si nano-ribbons on Ag(110)