Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access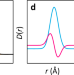 Multivariate analysis of disorder in metal–organic frameworks
Multivariate analysis of disorder in metal–organic frameworks
Structural disorder in materials is challenging to characterise. Here, the authors use multivariate analysis of atomic pair distribution functions to study structural collapse and melting of metal–organic frameworks, revealing powerful mechanistic and kinetic insight.
- Adam F. Sapnik
- , Irene Bechis
- & Thomas D. Bennett
-
Comment
| Open Access Analysing the relationship between the fields of thermo- and electrocatalysis taking hydrogen peroxide as a case study
Analysing the relationship between the fields of thermo- and electrocatalysis taking hydrogen peroxide as a case study
Research in thermo- and electrocatalysis have often preceded in isolation, even for similar reactions. Here, the authors compare current trends in both fields and elaborate on the commonalities and differences with a specific focus on the production of hydrogen peroxide.
- Guilherme V. Fortunato
- , Enrico Pizzutilo
- & Marc Ledendecker
-
Article
| Open Access Doubly linked chiral phenanthrene oligomers for homogeneously π-extended helicenes with large effective conjugation length
Doubly linked chiral phenanthrene oligomers for homogeneously π-extended helicenes with large effective conjugation length
Helically twisted conductive nanocarbon materials are applicable to optoelectronic and electromagnetic molecular devices but the design of nanocarbons with an absorption edge in the low energy region is challenging. Here, the authors report the synthesis of a helically fused oligophenanthrenes and demonstrate an increased effective conjugation length leading to an absorption edge in the NIR region.
- Yusuke Nakakuki
- , Takashi Hirose
- & Kenji Matsuda
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic structure of a seed-sized gold nanoprism
Atomic structure of a seed-sized gold nanoprism
The formation pathway of shape-anisotropic nanoparticles is difficult to characterize and not well understood. The authors synthesize a prismatic-shaped Au56 nanocluster as possible seed of a prismatic nanoparticle and characterize the structure and ligand bonding motifs, providing insight into the formation and surface protection mechanisms.
- Yongbo Song
- , Yingwei Li
- & Rongchao Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Massive interstitial solid solution alloys achieve near-theoretical strength
Massive interstitial solid solution alloys achieve near-theoretical strength
Interstitials can substantially strengthen metals. Here the authors show a massive interstitial solid solution (MISS) approach enabling a model multicomponent alloy to achieve near-theoretical strength together with large deformability.
- Chang Liu
- , Wenjun Lu
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article
| Open Access Unprecedentedly high activity and selectivity for hydrogenation of nitroarenes with single atomic Co1-N3P1 sites
Unprecedentedly high activity and selectivity for hydrogenation of nitroarenes with single atomic Co1-N3P1 sites
Modulating the atomic coordination structure has emerged as a promising strategy to further improve catalytic performance. Here, the authors report an atomic Co1/NPC catalyst with unsymmetrical single Co1N3P1 sites that displays high activity and chemoselectivity for hydrogenation of functionalized nitroarenes.
- Hongqiang Jin
- , Peipei Li
- & Changyan Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Polyamide-based membranes with structural homogeneity for ultrafast molecular sieving
Polyamide-based membranes with structural homogeneity for ultrafast molecular sieving
Thin-film composite membranes formed by conventional interfacial polymerization generally suffer from depth heterogeneity of the polyamide layer. Here, authors investigate salt-mediated polymerization approaches to achieve membranes with tuneable structural homogeneity.
- Liang Shen
- , Ruihuan Cheng
- & Yan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial compatibility critically controls Ru/TiO2 metal-support interaction modes in CO2 hydrogenation
Interfacial compatibility critically controls Ru/TiO2 metal-support interaction modes in CO2 hydrogenation
Supports can largely affect the catalytic performance of metal nanoparticles, but the underlying principles are not yet fully understood. Here the authors demonstrate that metal-support interfacial compatibility of Ru/TiO2 can critically control the metal-support interaction modes and the catalytic performances in CO2 hydrogenation.
- Jun Zhou
- , Zhe Gao
- & Leyu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization and validation of twin nucleation and early-stage growth in magnesium
Visualization and validation of twin nucleation and early-stage growth in magnesium
The origins of deformation twins in Mg have remained unclear in the past. Here the authors, by combining in situ experimental observations and atomistic simulations, capture the rapid twinning phenomena in Mg crystals and show that twinning occurs through pure atomic shuffle.
- Lin Jiang
- , Mingyu Gong
- & Julie M. Schoenung
-
Article
| Open Access Twinning-assisted dynamic adjustment of grain boundary mobility
Twinning-assisted dynamic adjustment of grain boundary mobility
Grain boundary can change its structure upon deformation. Here, the authors show that during this process, grain boundary mobility can be tuned dynamically via a self-stimulated twinning process.
- Qishan Huang
- , Qi Zhu
- & Jiangwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A reasonable approach for the generation of hollow icosahedral kernels in metal nanoclusters
A reasonable approach for the generation of hollow icosahedral kernels in metal nanoclusters
The origin of the hollow icosahedral M12 kernel in metal nanoclusters is under debate. Here the authors demonstrate the Au alloying-induced kernel collapse from small-sized nano-building blocks as a viable approach for the generation of hollow icosahedral M12 kernel in metal nanoclusters.
- Xi Kang
- , Xiao Wei
- & Manzhou Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access A class of organic cages featuring twin cavities
A class of organic cages featuring twin cavities
The preparation of nanocages with unprecedented architectures may lead to new functions. Here the authors report the self-assembly of organic cages featuring twin cavities; the geometry and pocket size determine the molecular packing and the proton conductivity performance.
- Zhenyu Yang
- , Chunyang Yu
- & Shaodong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Reaching silicon-based NEMS performances with 3D printed nanomechanical resonators
Reaching silicon-based NEMS performances with 3D printed nanomechanical resonators
NEMS devices, nano-electro-mechanical systems, by virtue of their minute size, offer ultra-high sensitivity, though at the expense of manufacturing complexity. Here, Stassi et al succeed in manufacturing high quality factor NEMS devices using high resolution 3D printing.
- Stefano Stassi
- , Ido Cooperstein
- & Carlo Ricciardi
-
Article
| Open Access Out-of-equilibrium processes in crystallization of organic-inorganic perovskites during spin coating
Out-of-equilibrium processes in crystallization of organic-inorganic perovskites during spin coating
Complex phenomena are prevalent during the formation of materials, and they affect the processing structure-function relationship. Here the authors elucidate the stochastic transformation processes happening during the spin coating of perovskite colloidal precursors by multimodal characterization.
- Shambhavi Pratap
- , Finn Babbe
- & Peter Müller-Buschbaum
-
Article
| Open Access Grain-growth mediated hydrogen sorption kinetics and compensation effect in single Pd nanoparticles
Grain-growth mediated hydrogen sorption kinetics and compensation effect in single Pd nanoparticles
Grains are the building blocks of crystalline solids. Here the authors show how hydrogen-sorption induced grain-growth in Pd nanoparticles slows down the hydrogen sorption kinetics and constitutes the physical origin of corresponding kinetic compensation.
- Svetlana Alekseeva
- , Michal Strach
- & Christoph Langhammer
-
Article
| Open Access Stiff and tough PDMS-MMT layered nanocomposites visualized by AIE luminogens
Stiff and tough PDMS-MMT layered nanocomposites visualized by AIE luminogens
Fine tuning of mechanical properties in elastomers is important for application of elastomers in flexible devices and biomedical field. Here, the authors prepare a nacre inspired PDMS-montmorrillonite composite with good mechanical properties and demonstrate crack tracing using aggregation-induced emission luminogens.
- Jingsong Peng
- , Antoni P. Tomsia
- & Qunfeng Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access X-ray studies bridge the molecular and macro length scales during the emergence of CoO assemblies
X-ray studies bridge the molecular and macro length scales during the emergence of CoO assemblies
The understanding of nucleation and growth of nanostructures plays a key role in complex materials design. Here, the authors illustrate how X-ray in situ studies link transformation at the molecular- and macro- length scales during the emergence of cobalt oxide assemblies.
- Lukas Grote
- , Cecilia A. Zito
- & Dorota Koziej
-
Article
| Open Access Polymer cyclization for the emergence of hierarchical nanostructures
Polymer cyclization for the emergence of hierarchical nanostructures
Synthetic polymer nano-objects with well-defined hierarchical structures are important for a wide range of applications such as nanomaterial synthesis, catalysis, and therapeutics. Here the authors demonstrate the strategy of fabricating controlled hierarchical structures through self-assembly of folded synthetic polymers.
- Chaojian Chen
- , Manjesh Kumar Singh
- & Tanja Weil
-
Article
| Open Access The origin of the high electrochemical activity of pseudo-amorphous iridium oxides
The origin of the high electrochemical activity of pseudo-amorphous iridium oxides
The origins of the superior catalytic activity of poorly crystallized Ir-based oxide material for the OER in acid is still under debate. Here, authors synthesize porous IrMo oxides to deconvolute the effect of Ir oxidation state from short-range ordering and show the latter to be a key factor.
- Marine Elmaalouf
- , Mateusz Odziomek
- & Jennifer Peron
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature oxygen vacancy migration induced reversible phase transformation during the anelastic deformation in CuO
Room-temperature oxygen vacancy migration induced reversible phase transformation during the anelastic deformation in CuO
The effect of point defects on mechanical behaviour of materials is generally considered at high temperatures. This work reports a reversible stress-induced migration of point defects during anelastic deformation in CuO nanowires at room temperature resulting from heterogeneous strain distribution.
- Lei Li
- , Guoxujia Chen
- & Jianbo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Converting copper sulfide to copper with surface sulfur for electrocatalytic alkyne semi-hydrogenation with water
Converting copper sulfide to copper with surface sulfur for electrocatalytic alkyne semi-hydrogenation with water
Highly selective electrocatalytic semi-hydrogenation of alkynes over a noble-metal-free catalyst is highly desirable. Here, authors synthesize sulfur-containing copper nanowire sponges for selective electrocatalytic alkyne semi-hydrogenation using water as the hydrogen source.
- Yongmeng Wu
- , Cuibo Liu
- & Bin Zhang
-
Comment
| Open Access Correlating advanced microscopies reveals atomic-scale mechanisms limiting lithium-ion battery lifetime
Correlating advanced microscopies reveals atomic-scale mechanisms limiting lithium-ion battery lifetime
The longevity of a lithium-ion battery is limited by cathode degradation. Combining atom probe tomography and scanning transmission electron microscopy reveals that the degradation results from atomic-scale irreversible structural changes once lithium leaves the cathode during charging, thereby inhibiting lithium intercalation back into the cathode as the battery discharges. This information unveils possible routes for improving the lifetime of lithium-ion batteries.
- Baptiste Gault
- & Jonathan D. Poplawsky
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing composition and structure dependent deep-level defect in antimony trisulfide photovoltaics
Revealing composition and structure dependent deep-level defect in antimony trisulfide photovoltaics
Antimony trisulfide emerges as a suitable candidate for light-harvesting due to its good stability and abundance, yet the defect properties are not well-understood. Here, by means of deep-level transient spectroscopy, Lian et al. find that there are three kinds of deep-level defects depending on the chemical composition.
- Weitao Lian
- , Chenhui Jiang
- & Tao Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Printable homocomposite hydrogels with synergistically reinforced molecular-colloidal networks
Printable homocomposite hydrogels with synergistically reinforced molecular-colloidal networks
Composites which are made up of a single polymer, and yet allow modulation of the mechanical properties of the matrix without stress concentration, are challenging to fabricate. Here, the authors design a selfreinforced homocomposite alginate hydrogel with enhanced mechanical properties incorporating soft dendritic alginate colloids in the matrix and demonstrate its application in extrusion printing.
- Austin H. Williams
- , Sangchul Roh
- & Orlin D. Velev
-
Article
| Open Access Unique reactivity of nanoporous cellulosic materials mediated by surface-confined water
Unique reactivity of nanoporous cellulosic materials mediated by surface-confined water
The efficiency of chemical reactions in biological systems is often connected to the properties of confined water, but the developments and applications of artificial mimicking systems are impeded by the complexity of the biological systems. Here, the authors show how surface bound water in nanoporous cellulosic fibers can increase the reaction rate of surface acetylation reactions and enable regioselectivity of the reaction
- Marco Beaumont
- , Paul Jusner
- & Thomas Rosenau
-
Article
| Open Access SMART transfer method to directly compare the mechanical response of water-supported and free-standing ultrathin polymeric films
SMART transfer method to directly compare the mechanical response of water-supported and free-standing ultrathin polymeric films
Intrinsic mechanical properties of sub-100 nm thin films are markedly difficult to obtain, yet an ever-growing necessity for emerging fields such as soft organic electronics. Here, the authors present a shear motion assisted transfer technique for fabricating free-standing sub-100 nm thin films and measuring their inherent structural–mechanical properties.
- Luke A. Galuska
- , Eric S. Muckley
- & Xiaodan Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving atomic SAPO-34/18 intergrowth architectures for methanol conversion by identifying light atoms and bonds
Resolving atomic SAPO-34/18 intergrowth architectures for methanol conversion by identifying light atoms and bonds
The micro-structures of zeolite catalysts affect their macroarchitectures and catalytic performances. Here, the different SAPO-34/18 intergrowth catalysts are atomically resolved, and the correlation between synthesis conditions and zeolite structures is revealed to further enhance their performances in methanol conversion.
- Boyuan Shen
- , Xiao Chen
- & Fei Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Unusual hydrogen implanted gold with lattice contraction at increased hydrogen content
Unusual hydrogen implanted gold with lattice contraction at increased hydrogen content
Hydrogen can be absorbed into various metals, but generally causes the metals to expand. Here the authors show that when hydrogen is dynamically bound to the lattice, as in dilute Au:H solutions, the gold contracts accordingly.
- Khac Thuan Nguyen
- , Van Hiep Vuong
- & Nam Nhat Hoang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrarobust, tough and highly stretchable self-healing materials based on cartilage-inspired noncovalent assembly nanostructure
Ultrarobust, tough and highly stretchable self-healing materials based on cartilage-inspired noncovalent assembly nanostructure
Strong self-healing materials with high healing efficiency are of great use in many fields but their fabrication is extremely challenging. Here, the authors present a robust self-healing material by incorporating high density noncovalent bonds at the interfaces between dentritic tannic acid-modified tungsten disulfide nanosheets and a polyurethane matrix to collectively produce a strong interfacial interaction.
- Yuyan Wang
- , Xin Huang
- & Xinxing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access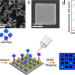 A digital single-molecule nanopillar SERS platform for predicting and monitoring immune toxicities in immunotherapy
A digital single-molecule nanopillar SERS platform for predicting and monitoring immune toxicities in immunotherapy
There is a clinical need to monitor immune-related toxicities of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Here, the authors develop a digital SERS platform for multiplexed single cytokine counting to track immune-toxicities and demonstrate the ability to use pre-screening to identify patients at higher risk.
- Junrong Li
- , Alain Wuethrich
- & Matt Trau
-
Article
| Open Access Functional and versatile superhydrophobic coatings via stoichiometric silanization
Functional and versatile superhydrophobic coatings via stoichiometric silanization
Artificial superhydrophobic coatings that are simple to prepare and practical to use are sought after. Here, the authors create versatile, complete-waterproof coatings based on a single-step, stoichiometrically controlled reaction of organosilanes with water.
- Lishen Zhang
- , Alvin G. Zhou
- & Hua-Zhong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Unusual solute segregation phenomenon in coherent twin boundaries
Unusual solute segregation phenomenon in coherent twin boundaries
Segregation of solute atoms at interfaces affects the properties of alloys and needs to be understood to allow their rational design. Here the authors report an unusual solute segregation phenomenon in a group of Mg alloys, driven by chemical bonding, where solute atoms larger than Mg segregate to compression sites of specific fully coherent twin boundary.
- Cong He
- , Zhiqiao Li
- & Jian-Feng Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Distilling nanoscale heterogeneity of amorphous silicon using tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) via multiresolution manifold learning
Distilling nanoscale heterogeneity of amorphous silicon using tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) via multiresolution manifold learning
Short range atomic ordering quantification and nanoscale spatial resolution over a large area for amorphous materials is crucial for accelerating technology development but remain challenges. Here, the authors explore nanoscale heterogeneity of amorphous silicon by tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy via multiresolution manifold learning.
- Guang Yang
- , Xin Li
- & Jagjit Nanda
-
Article
| Open Access Non-equilibrium metal oxides via reconversion chemistry in lithium-ion batteries
Non-equilibrium metal oxides via reconversion chemistry in lithium-ion batteries
The charging of Fe and Mn oxide anodes in lithium-ion batteries are believed to form rocksalt phases via reconstructive conversion reactions. Here, the authors show that MxOy (M = Fe, Mn) transform into non-native body-centred cubic FeO and zincblende MnO via topotactic displacement-like pathways.
- Xiao Hua
- , Phoebe K. Allan
- & Andrew L. Goodwin
-
Article
| Open Access Adsorption separation of heavier isotope gases in subnanometer carbon pores
Adsorption separation of heavier isotope gases in subnanometer carbon pores
Separation of isotopes of heavier gases than hydrogen or helium is essential for biomedical applications, but current methods are very energy and time consuming. Here the authors report cryogenic separation of oxygen and methane isotopes through adsorption in nanoporous materials, based on a collective nuclear quantum effect.
- Sanjeev Kumar Ujjain
- , Abhishek Bagusetty
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
Article
| Open Access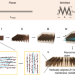 Controlling nanochannel orientation and dimensions in graphene-based nanofluidic membranes
Controlling nanochannel orientation and dimensions in graphene-based nanofluidic membranes
Vertically stacked graphene oxide sheets are promising structures for molecular sieving technologies. By folding large planar sheets in an accordion-like manner, Liu et al. fabricate a thin robust filter with near-vertically aligned nanochannels geared towards commercial separation membranes.
- Muchun Liu
- , Paula J. Weston
- & Robert H. Hurt
-
Article
| Open Access Light-directed trapping of metastable intermediates in a self-assembly process
Light-directed trapping of metastable intermediates in a self-assembly process
Knowledge about kinetically favored intermediate states in self-assembly processes can provide information about the self-assembly process but trapping these states without changing the reaction conditions is challenging. Here, the authors report a method for trapping metastable intermediates in self-assembly processes that is based on a photopolymerization strategy.
- Joonsik Seo
- , Joonyoung F. Joung
- & Jong-Man Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved in situ visualization of the structural response of zeolites during catalysis
Time-resolved in situ visualization of the structural response of zeolites during catalysis
Study of structural inhomogeneities in zeolites is important but limited by conventional techniques. Here the authors employ in situ free-electron-laser-based time-resolved coherent X-ray diffraction imaging to visualize the effect of these inhomogeneities during catalytic deoxygenation of NOx.
- Jinback Kang
- , Jerome Carnis
- & Hyunjung Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional strain dynamics govern the hysteresis in heterogeneous catalysis
Three-dimensional strain dynamics govern the hysteresis in heterogeneous catalysis
Direct visualisation of site-specific strain variations of catalysts is needed to better understand catalytic properties. Here, the authors determine with attojoule precision that the well-known catalytic hysteresis phenomenon occurs at single particle level and involves three-dimensional strain field.
- Aline R. Passos
- , Amélie Rochet
- & Florian Meneau
-
Article
| Open Access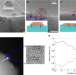 Atomic-scale phase separation induced clustering of solute atoms
Atomic-scale phase separation induced clustering of solute atoms
Dealloying usually relies on chemical dissolution of an alloy component. By contrast, the authors demonstrate an atomic-scale phase separation process that differs completely from the chemical dealloying mechanism and thus represents a significant departure from the well-known Hume-Rothery rules.
- Lianfeng Zou
- , Penghui Cao
- & Guangwen Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Structural order in plasmonic superlattices
Structural order in plasmonic superlattices
Superlattices of nanoparticles promise new properties emerging from the periodic order. Here, the authors describe the synthesis of superlattices of plasmonic gold nanoparticles with high crystallinity and demonstrate how new plasmon-polariton modes appear in the structures.
- Florian Schulz
- , Ondřej Pavelka
- & Holger Lange
-
Article
| Open Access Heterophase fcc-2H-fcc gold nanorods
Heterophase fcc-2H-fcc gold nanorods
The crystal phase-based heterostructures of noble metal nanomaterials are of interest for various applications. Here, the authors report the wet-chemical synthesis of gold nanorods with a well-defined fcc-2H-fcc heterophase, which possess unique optical and catalytic properties.
- Zhanxi Fan
- , Michel Bosman
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Metallic nanocrystals with low angle grain boundary for controllable plastic reversibility
Metallic nanocrystals with low angle grain boundary for controllable plastic reversibility
Improving the reversible plastic deformability and damage tolerance of nanosized metals remains challenging. Here, the authors custom-design low angle grain boundaries in metallic bicrystals to achieve controllable plastic reversibility via fully conservative grain boundary migration.
- Qi Zhu
- , Qishan Huang
- & Jiangwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access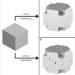 Hardening in Au-Ag nanoboxes from stacking fault-dislocation interactions
Hardening in Au-Ag nanoboxes from stacking fault-dislocation interactions
Fabricating and mechanically testing nanoarchitected materials remains a challenge. Here, the authors use colloidal synthesis to fabricate Au-Ag hollow nanoboxes and investigate the effect of either a rough or a smooth nanobox surface on the mechanical properties.
- Radhika P. Patil
- , David Doan
- & X. Wendy Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Achieving micron-scale plasticity and theoretical strength in Silicon
Achieving micron-scale plasticity and theoretical strength in Silicon
Silicon is thought to be brittle, which limits its mechanical application in devices. Here, the authors lithographically fabricate silicon and show its superior surface quality leads to near ideal strength and micron-scale plasticity.
- Ming Chen
- , Laszlo Pethö
- & Jeffrey M. Wheeler
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous crystalline graphene papers with gigapascal strength by intercalation modulated plasticization
Continuous crystalline graphene papers with gigapascal strength by intercalation modulated plasticization
Strong but flexible graphene tends to wrinkle, which compromises some properties. Here the authors report a solid plasticization method to prepare continuous graphene papers with high crystalline order, achieving high strength, stiffness, electrical and thermal conductivities.
- Peng Li
- , Mincheng Yang
- & Chao Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Unstable twin in body-centered cubic tungsten nanocrystals
Unstable twin in body-centered cubic tungsten nanocrystals
Body-centred cubic metals rarely show twinning during deformation. Here, the authors use high resolution transmission electron microscopy to show tungsten, a body-centred cubic metal, spontaneously undergoes detwinning when unloaded.
- Xiang Wang
- , Jiangwei Wang
- & Scott X. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of dual-step twinning nucleation in hexagonal close-packed crystals
Direct observation of dual-step twinning nucleation in hexagonal close-packed crystals
Aspects of twinning in hexagonal-close-packed crystals remain elusive. Here, the authors directly image twinning in rhenium nanocrystals and show the process is mediated by disconnections on Prismatic│Basal interfaces as the twin initially deviates from its ideal orientation before it is corrected.
- Yang He
- , Bin Li
- & Scott X. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Dual heterogeneous structures lead to ultrahigh strength and uniform ductility in a Co-Cr-Ni medium-entropy alloy
Dual heterogeneous structures lead to ultrahigh strength and uniform ductility in a Co-Cr-Ni medium-entropy alloy
Improving both strength and ductility simultaneously in structural metals and alloys remains a challenge. Here, the authors design a heterogeneous structure in a Co-Cr-Ni alloy that results in ultrahigh strength and significant uniform elongation.
- X. H. Du
- , W. P. Li
- & E. W. Huang

 Ultrahigh strength and shear-assisted separation of sliding nanocontacts studied in situ
Ultrahigh strength and shear-assisted separation of sliding nanocontacts studied in situ