News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Explaining fast ejections of plasma and exotic X-ray emission from the solar corona
Explaining fast ejections of plasma and exotic X-ray emission from the solar corona
Sudden bursts of charged particles emitted from the surface of the Sun can disrupt the satellites orbiting Earth. However, the mechanisms that drive these so-called coronal mass ejections remain unclear. An advanced computer model now establishes a link between the onset of an ejection and the emergence of magnetic flux into the solar atmosphere.
- Ilia I. Roussev
- , Klaus Galsgaard
- & Jun Lin
-
News & Views |
 Where did all the electrons go?
Where did all the electrons go?
Geomagnetic storms driven by the solar wind can cause the flux of high-energy electrons in the Earth's Van Allen belts to rapidly fall. Analysis of data obtained during one such event from multiple spacecraft located at different altitudes in the magnetosphere reveals just where these electrons go.
- Mary K. Hudson
-
Letter |
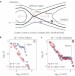 Large-scale electron acceleration by parallel electric fields during magnetic reconnection
Large-scale electron acceleration by parallel electric fields during magnetic reconnection
Magnetic reconnection is a process by which the field lines of a magnetized plasma undergo dramatic realignment, releasing large amounts of energy. Large-scale simulations of reconnection events in the Earth’s magnetosphere suggest that this process takes place over much greater distances than previously expected.
- J. Egedal
- , W. Daughton
- & A. Le
-
Letter |
 Explaining sudden losses of outer radiation belt electrons during geomagnetic storms
Explaining sudden losses of outer radiation belt electrons during geomagnetic storms
Geomagnetic storms driven by the solar wind can cause a dramatic drop in the flux of high-energy electrons in the Earth’s outer Van Allen belt. Analysis of data obtained during such an event by three different sets of spacecraft suggests that these electrons are directed into space rather than lost to the atmosphere.
- Drew L. Turner
- , Yuri Shprits
- & Vassilis Angelopoulos

 The birth of a solar eruption
The birth of a solar eruption