Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Nestin regulates cellular redox homeostasis in lung cancer through the Keap1–Nrf2 feedback loop
Nestin regulates cellular redox homeostasis in lung cancer through the Keap1–Nrf2 feedback loop
Loss of Nestin sensitizes non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) to oxidative stress. Here, the authors report a feedback loop between Nestin and Nrf2 wherein Nestin competes with Nrf2 for Keap1 binding, preventing Nrf2 degradation, and show the Nestin–Keap1–Nrf2 axis to regulate redox homeostasis in NSCLC.
- Jiancheng Wang
- , Qiying Lu
- & Andy Peng Xiang
-
Article
| Open Access HCMV-encoded US7 and US8 act as antagonists of innate immunity by distinctively targeting TLR-signaling pathways
HCMV-encoded US7 and US8 act as antagonists of innate immunity by distinctively targeting TLR-signaling pathways
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) has evolved several mechanisms to evade the host immune response. Here, Park et al. show that HCMV-encoded US7 and US8 proteins bind TLR3 and TLR4 and facilitate TLR degradation by distinct mechanisms, including ER-associated and lysosomal degradation.
- Areum Park
- , Eun A. Ra
- & Boyoun Park
-
Article
| Open Access USP7 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling through promoting stabilization of Axin
USP7 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling through promoting stabilization of Axin
Axin is a scaffolding protein known for its role in Wnt signalling that can be marked with a variety of post-translational modifications. Here, Cong et al. demonstrate that USP7 de-ubiquinates Axin and that canonical Wnt signaling output can be increased with USP7 inhibitors.
- Lei Ji
- , Bo Lu
- & Feng Cong
-
Article
| Open Access Cyclin A2 degradation during the spindle assembly checkpoint requires multiple binding modes to the APC/C
Cyclin A2 degradation during the spindle assembly checkpoint requires multiple binding modes to the APC/C
During the spindle assembly checkpoint, the activity of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is repressed, yet cyclin A2 evades the checkpoint and is targeted for degradation. Here, the authors define the underlying mechanism and reveal that cyclin A2 engages the APC/C in multiple binding modes.
- Suyang Zhang
- , Thomas Tischer
- & David Barford
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure and substrate-induced activation of ADAMTS13
Crystal structure and substrate-induced activation of ADAMTS13
The plasma metalloprotease ADAMTS13 regulates the platelet-tethering function of von Willebrand factor (VWF) in a shear-dependent manner. Here the authors present the ADAMTS13 crystal structure of the 70kDa N-terminal metalloprotease to spacer domains, and using kinetic measurements they identify a substrate binding induced allosteric mechanism for ADAMTS13, where VWF functions both as an activating cofactor and substrate.
- Anastasis Petri
- , Hyo Jung Kim
- & James T. B. Crawley
-
Article
| Open Access GIGANTEA recruits the UBP12 and UBP13 deubiquitylases to regulate accumulation of the ZTL photoreceptor complex
GIGANTEA recruits the UBP12 and UBP13 deubiquitylases to regulate accumulation of the ZTL photoreceptor complex
The daily accumulation of the ZEITLUPE (ZTL) photoreceptor/E3 ubiquitin ligase relies on a light-dependent interaction with GIGANTEA (GI). Here the authors show that GI recruits two deubiquitylases to help stabilize the ZTL-GI complex during the day and likely counterbalance the activity of ZTL.
- Chin-Mei Lee
- , Man-Wah Li
- & Joshua M. Gendron
-
Article
| Open Access Arkadia/RNF111 is a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase with preference for substrates marked with SUMO1-capped SUMO2/3 chain
Arkadia/RNF111 is a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase with preference for substrates marked with SUMO1-capped SUMO2/3 chain
The cellular functions of poly-SUMO chains of different compositions are not fully understood. Here, the authors characterize Arkadia/RNF111 as a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase that recognizes proteins with hybrid SUMO1-capped SUMO2/3 chains and targets them for proteasomal degradation.
- Annie M. Sriramachandran
- , Katrin Meyer-Teschendorf
- & R. Jürgen Dohmen
-
Article
| Open Access WWP2 regulates pathological cardiac fibrosis by modulating SMAD2 signaling
WWP2 regulates pathological cardiac fibrosis by modulating SMAD2 signaling
Pathological cardiac fibrosis is a hallmark of diseases leading to heart failure. Here, the authors used systems genetics to identify a pro-fibrotic gene network regulated by WWP2, a E3 ubiquitin ligase, which orchestrates the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and transcriptional activity of SMAD2 in the diseased heart.
- Huimei Chen
- , Aida Moreno-Moral
- & Enrico Petretto
-
Article
| Open Access Degron-tagged reporters probe membrane topology and enable the specific labelling of membrane-wrapped structures
Degron-tagged reporters probe membrane topology and enable the specific labelling of membrane-wrapped structures
Visualising certain organelles and their dynamics is challenging in living cells. Here the authors co-opt selective degradation to label membrane-bound compartments in worm embryos and mammalian cells, revealing membrane topology during cell division.
- Katharina B. Beer
- , Gholamreza Fazeli
- & Ann M. Wehman
-
Article
| Open Access Small molecule degraders of the hepatitis C virus protease reduce susceptibility to resistance mutations
Small molecule degraders of the hepatitis C virus protease reduce susceptibility to resistance mutations
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) is a promising strategy for drug development. In this proof-of-concept study, the authors use telaprevir, which binds hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3/4A protease, to target the protease for protein degradation, and show inhibition of wildtype as well as drug resistant HCV.
- Mélissanne de Wispelaere
- , Guangyan Du
- & Priscilla L. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into E1 recognition and the ubiquitin-conjugating activity of the E2 enzyme Cdc34
Structural insights into E1 recognition and the ubiquitin-conjugating activity of the E2 enzyme Cdc34
The E2 enzyme Cdc34 plays a critical role in cell cycle progression but the structural bases for its activities are unknown. Here, the authors present crystal structures of Cdc34 alone, in complex with E1, and in complex with Ub that provide insights into the mechanism of Cdc34 activity in the cell.
- Katelyn M. Williams
- , Shuo Qie
- & Shaun K. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access SPRTN protease and checkpoint kinase 1 cross-activation loop safeguards DNA replication
SPRTN protease and checkpoint kinase 1 cross-activation loop safeguards DNA replication
Cells deficient in SPRTN protease activity exhibit severe DNA-protein crosslink induced replication stress and genome instability. Here the author reveal a functional link between the SPRTN protease and the CHK1 kinase during physiological DNA replication.
- Swagata Halder
- , Ignacio Torrecilla
- & Kristijan Ramadan
-
Article
| Open Access AWD regulates timed activation of BMP signaling in intestinal stem cells to maintain tissue homeostasis
AWD regulates timed activation of BMP signaling in intestinal stem cells to maintain tissue homeostasis
Regeneration after injury in the Drosophila intestine involves early activation of intestinal stem cells (ISCs) and subsequent return to quiescence. Here the authors show that return to quiescence by ISCs involves BMP Type I receptor Tkv protein stabilization along with AWD mediated internalization into endocytic vesicles.
- Xiaoyu Tracy Cai
- , Hongjie Li
- & Heinrich Jasper
-
Article
| Open Access Feedback inhibition of cAMP effector signaling by a chaperone-assisted ubiquitin system
Feedback inhibition of cAMP effector signaling by a chaperone-assisted ubiquitin system
How intracellular cAMP activate PKA is well-characterized, but PKA inactivation remains poorly understood. Here, Rinaldi et al. show that CHIP/HSP70 ubiquitinates the catalytic subunit of PKA, with implications for the human disease spinocerebellar ataxia 16, as patients often have CHIP mutations.
- Laura Rinaldi
- , Rossella Delle Donne
- & Antonio Feliciello
-
Article
| Open Access SAGA DUBm-mediated surveillance regulates prompt export of stress-inducible transcripts for proteostasis
SAGA DUBm-mediated surveillance regulates prompt export of stress-inducible transcripts for proteostasis
Stress-inducible transcripts are quickly exported to preserve cell survival when cells are under stress. Here, the authors suggest that Sgf73p of the SAGA deubiquitylating module monitors messenger ribonucleoprotein biogenesis to regulate non-canonical export of stress-inducible transcripts.
- Minhoo Kim
- , Yoonjung Choi
- & Daeyoup Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Vps11 and Vps18 of Vps-C membrane traffic complexes are E3 ubiquitin ligases and fine-tune signalling
Vps11 and Vps18 of Vps-C membrane traffic complexes are E3 ubiquitin ligases and fine-tune signalling
Endosomal fusion depends on the HOPS and CORVET complexes but whether and how their subunits modulate signal transduction is not fully understood. Here, the authors show that the HOPS/CORVET subunits Vps11 and Vps18 are E3 ubiquitin ligases that are involved in the regulation of ERα signalling.
- Gregory Segala
- , Marcela A. Bennesch
- & Didier Picard
-
Article
| Open Access Co-translational assembly of mammalian nuclear multisubunit complexes
Co-translational assembly of mammalian nuclear multisubunit complexes
Genes encoding protein complex subunits are often dispersed in the genome of eukaryotes, raising the question how these protein complexes assemble. Here, the authors provide evidence that mammalian nuclear transcription complexes are formed co-translationally to ensure specific and functional interactions.
- Ivanka Kamenova
- , Pooja Mukherjee
- & László Tora
-
Article
| Open Access KIBRA controls exosome secretion via inhibiting the proteasomal degradation of Rab27a
KIBRA controls exosome secretion via inhibiting the proteasomal degradation of Rab27a
Exosomes are intercellular signaling vesicles created by fusion of multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and the plasma membrane (PM), but secretory regulation is ill-defined. Song et al. show that KIBRA controls exosome secretion by protecting Rab27a from proteasomal degradation, promoting MVB-PM docking.
- Lin Song
- , Shi Tang
- & Yifeng Du
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering the complex role of thrombospondin-1 in glioblastoma development
Deciphering the complex role of thrombospondin-1 in glioblastoma development
Thrombospondin-1 (THSB1) is a component of the ECM with a role in regulating cancer development and tumour vasculature. Here, the authors show that TGF-beta-induced THBS1 expression contributes to the invasive behaviour of GBM cells and promotes resistance to antiangiogenic therapy partially through interaction with CD47.
- Thomas Daubon
- , Céline Léon
- & Andréas Bikfalvi
-
Article
| Open Access Secreted metalloproteases ADAMTS9 and ADAMTS20 have a non-canonical role in ciliary vesicle growth during ciliogenesis
Secreted metalloproteases ADAMTS9 and ADAMTS20 have a non-canonical role in ciliary vesicle growth during ciliogenesis
Ciliogenesis is a complex process requiring hundreds of molecules, although few secreted proteins have been implicated. Here, the authors show that the secreted metalloproteases ADAMTS9 and ADAMTS20 intracellularly regulate ciliogenesis from unique periciliary vesicles with proteolytic activity.
- Sumeda Nandadasa
- , Caroline M. Kraft
- & Suneel S. Apte
-
Article
| Open Access Gigaxonin E3 ligase governs ATG16L1 turnover to control autophagosome production
Gigaxonin E3 ligase governs ATG16L1 turnover to control autophagosome production
Membrane elongation is fundamental to autophagy and is controlled by an ubiquitin-conjugating cascade orchestrated by ATG16L1. Here, the authors identify that the E3 ligase Gigaxonin regulates autophagosome formation by controlling ATG16L1 turnover.
- Aurora Scrivo
- , Patrice Codogno
- & Pascale Bomont
-
Article
| Open Access PTEN self-regulates through USP11 via the PI3K-FOXO pathway to stabilize tumor suppression
PTEN self-regulates through USP11 via the PI3K-FOXO pathway to stabilize tumor suppression
PTEN is a lipid phosphatase that functions as a dose-dependent tumor suppressor through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Here the authors describe a signaling feedback mechanism where PTEN stability is regulated through transcriptional upregulation of X-linked ubiquitin-specific protease 11 (USP11) via the PI3K/FOXO pathway.
- Mi Kyung Park
- , Yixin Yao
- & Min Sup Song
-
Article
| Open Access Usp7 regulates Hippo pathway through deubiquitinating the transcriptional coactivator Yorkie
Usp7 regulates Hippo pathway through deubiquitinating the transcriptional coactivator Yorkie
Hippo signaling leads to the phosphorylation of the key transcriptional effector, Yap/Yki, although how Yap/Yki stability is regulated has remained unclear. Here, Sun et al. identify HAUSP/Usp7 as a conserved and clinically relevant regulator of the Hippo pathway that increases Yap/Yki stability.
- Xiaohan Sun
- , Yan Ding
- & Zizhang Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct adaptive mechanisms drive recovery from aneuploidy caused by loss of the Ulp2 SUMO protease
Distinct adaptive mechanisms drive recovery from aneuploidy caused by loss of the Ulp2 SUMO protease
Transient aneuploidy enables cells to survive sudden environmental changes before longterm cellular adaptations are established. Here, the authors show that yeast cells respond to the acute loss of Ulp2 SUMO protease by rapid induction of aneuploidy, and reveal predictable long-term adaptation mechanisms that restore euploidy.
- Hong-Yeoul Ryu
- , Francesc López-Giráldez
- & Mark Hochstrasser
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism of a covalent allosteric inhibitor of SUMO E1 activating enzyme
Molecular mechanism of a covalent allosteric inhibitor of SUMO E1 activating enzyme
Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifiers such as SUMO play important roles in several cellular pathways that can become deregulated in cancer. Here the authors describe the structural basis for inhibition of SUMO E1 ligase by the small molecule COH000.
- Zongyang Lv
- , Lingmin Yuan
- & Shaun K. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access A quaternary tetramer assembly inhibits the deubiquitinating activity of USP25
A quaternary tetramer assembly inhibits the deubiquitinating activity of USP25
USP25 is a deubiquitinating enzyme and a positive regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Here the authors present the crystal structure of USP25 in a tetrameric inactive state and their biochemical and kinetic assays support an USP25 autoinhibitory mechanism that is mediated through a dimer to tetramerization transition.
- Bing Liu
- , Marta Sureda-Gómez
- & David Reverter
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome-wide analysis of USP14 substrates revealed its role in hepatosteatosis via stabilization of FASN
Proteome-wide analysis of USP14 substrates revealed its role in hepatosteatosis via stabilization of FASN
Ubiquitin-specific protease 14 (USP14) is a proteasome-associated deubiquitinating enzyme with known roles in physiology and disease. Here the authors show that fatty acid synthase (FASN) is a substrate of USP14, and that by stabilizing FASN, it plays a role in hepatosteatosis.
- Bin Liu
- , Shangwen Jiang
- & Minjia Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic ubiquitylation of Sox2 regulates proteostasis and governs neural progenitor cell differentiation
Dynamic ubiquitylation of Sox2 regulates proteostasis and governs neural progenitor cell differentiation
Sox2 regulates pluripotency in neural progenitor cells (NPC) but how protein stability affects this is unclear. Here, the authors identify changes in ubiquitylation of Sox2 (by CUL4A-DET1-COP1 ligase and OTUD7B deubiquitylase) as controlling protein stability and so the differentiation state of NPCs.
- Chun-Ping Cui
- , Yuan Zhang
- & Lingqiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access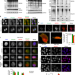 NEDDylation promotes nuclear protein aggregation and protects the Ubiquitin Proteasome System upon proteotoxic stress
NEDDylation promotes nuclear protein aggregation and protects the Ubiquitin Proteasome System upon proteotoxic stress
Protein NEDDylation increases upon proteotoxic stress but the function of this response remains to be elucidated. Here, the authors show that NEDDylation contributes to the cellular defence against proteotoxicity by promoting nuclear protein aggregation and protecting the ubiquitin proteasome system.
- Chantal M. Maghames
- , Sofia Lobato-Gil
- & Dimitris P. Xirodimas
-
Article
| Open Access SMYD2 glutathionylation contributes to degradation of sarcomeric proteins
SMYD2 glutathionylation contributes to degradation of sarcomeric proteins
Ischemic reperfusion or nutrient deprivation that produces reactive oxygen species can lead to a loss of muscle contractile function. Here the authors show that glutathionylation of the lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 contributes to degradation or disassembly of sarcomeres.
- Dhanushka N. P. Munkanatta Godage
- , Garrett C. VanHecke
- & Young-Hoon Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access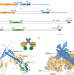 A bidentate Polycomb Repressive-Deubiquitinase complex is required for efficient activity on nucleosomes
A bidentate Polycomb Repressive-Deubiquitinase complex is required for efficient activity on nucleosomes
The Polycomb Repressive-Deubiquitinase (PR-DUB) complex is responsible for the removal of the ubiquitin epigenetic modification from Histone 2A. Here the authors describe the structure of the Drosophila PR-DUB complex, providing new insight into its regulation and how cancer-associated mutations disrupt PR-DUB activity.
- Martina Foglizzo
- , Adam J. Middleton
- & Peter D. Mace
-
Article
| Open Access ER-associated ubiquitin ligase HRD1 programs liver metabolism by targeting multiple metabolic enzymes
ER-associated ubiquitin ligase HRD1 programs liver metabolism by targeting multiple metabolic enzymes
HRD1 is an E3 ligase known to play a role in targeting degradation of misfolded proteins in the ER. Here the authors show that HRD1 interacts with metabolic enzymes and its liver specific deficiency results in lower body weight, blood glucose and plasma lipids during high fat diet in mice.
- Juncheng Wei
- , Yanzhi Yuan
- & Deyu Fang
-
Article
| Open Access The structure of the ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10 reveals an alternative targeting mechanism for proteasomal degradation
The structure of the ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10 reveals an alternative targeting mechanism for proteasomal degradation
The ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10 is composed of two ubiquitin-like domains (UBDs). Here the authors present the FAT10 UBD structures and show that the unstructured FAT10 N-terminal heptapeptide together with the poor stability of FAT10 facilitate the rapid proteasomal targeting of FAT10 along with its substrates.
- Annette Aichem
- , Samira Anders
- & Silke Wiesner
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into degradation mechanism of N-end rule substrates by p62/SQSTM1 autophagy adapter
Insights into degradation mechanism of N-end rule substrates by p62/SQSTM1 autophagy adapter
The autophagy adapter p62/SQSTM1 plays a key role in selective autophagy and also recognizes N-end rule substrates. Here the authors provide molecular insights into p62 N-end rule substrate recognition by solving the structures of the p62 ZZ-domain in complex with various type 1 and type 2 degrons and also show the pH dependent oligomerization of p62.
- Do Hoon Kwon
- , Ok Hyun Park
- & Hyun Kyu Song
-
Article
| Open Access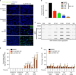 The ubiquitin ligase UBR5 suppresses proteostasis collapse in pluripotent stem cells from Huntington’s disease patients
The ubiquitin ligase UBR5 suppresses proteostasis collapse in pluripotent stem cells from Huntington’s disease patients
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) suppress the aggregation of Huntington’s disease (HD) polyQ-expanded huntingtin (HTT). Here the authors show that proteasome activity determines the levels of mutant HTT in HD-iPSCs and find that UBR5 is a modulator of super-vigilant proteostasis of iPSCs.
- Seda Koyuncu
- , Isabel Saez
- & David Vilchez
-
Article
| Open Access Rpn11-mediated ubiquitin processing in an ancestral archaeal ubiquitination system
Rpn11-mediated ubiquitin processing in an ancestral archaeal ubiquitination system
Ubiquitin modification also occurs in archaea. Here, the authors characterize an archaeal ancestral ubiquitination system, present the crystal structure of the archaeal deubiquitinase Rpn11 from Caldiarchaeum subterraneum bound to ubiquitin and provide insights into evolutionary relationships.
- Adrian C. D. Fuchs
- , Lorena Maldoner
- & Jörg Martin
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational switching in the coiled-coil domains of a proteasomal ATPase regulates substrate processing
Conformational switching in the coiled-coil domains of a proteasomal ATPase regulates substrate processing
Proteasomal ATPases contain functionally important coiled-coil (CC) domains, the mechanistic role of which is not fully understood. Here, the authors provide evidence for three distinct CC conformations, showing that CC conformational changes enable ATPases to switch between active and resting states.
- Aaron Snoberger
- , Evan J. Brettrager
- & David M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Vms1p is a release factor for the ribosome-associated quality control complex
Vms1p is a release factor for the ribosome-associated quality control complex
The ribosome-associated quality control complex (RQC) functions to disassemble stalled ribosomes. Here the authors find that the tRNA hydrolase Vms1 is involved in the release of nascent peptide from stalled ribosomes.
- Olga Zurita Rendón
- , Eric K. Fredrickson
- & Jared Rutter
-
Article
| Open Access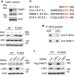 Methylated DNMT1 and E2F1 are targeted for proteolysis by L3MBTL3 and CRL4DCAF5 ubiquitin ligase
Methylated DNMT1 and E2F1 are targeted for proteolysis by L3MBTL3 and CRL4DCAF5 ubiquitin ligase
Lysine methylation is increasingly being implicated in the modification of non-histone proteins. Here the authors find that the methylation of DNMT1 and E2F1 are recognized by the protein L3MBTL3 and the ubiquitin E3 ligase CRL4DCAF5, which cooperatively target these methylated proteins for ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis.
- Feng Leng
- , Jiekai Yu
- & Hui Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access TRIM11 activates the proteasome and promotes overall protein degradation by regulating USP14
TRIM11 activates the proteasome and promotes overall protein degradation by regulating USP14
The proteasome-bound ubiquitinase USP14 plays an important role in determining proteasome activity and substrate specificity. Here the authors show that TRIM11, a member of the mammalian tripartite motif family, regulates USP14 and is an important activator of the proteasome.
- Liang Chen
- , Guixin Zhu
- & Xiaolu Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A family of unconventional deubiquitinases with modular chain specificity determinants
A family of unconventional deubiquitinases with modular chain specificity determinants
Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) are essential to modulate ubiquitin signaling. While known DUBs can be grouped into six families, the authors here present biochemical and structural evidence for a seventh DUB family, defining determinants of substrate specificity for two representative enzymes.
- Thomas Hermanns
- , Christian Pichlo
- & Kay Hofmann
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic analysis of protein turnover in primary cells
Systematic analysis of protein turnover in primary cells
The proteome-wide characterization of proteostasis depends on robust approaches to determine protein half-lives. Here, the authors improve the accuracy and precision of mass spectrometry-based quantification, enabling reliable protein half-life determination in several non-dividing cell types.
- Toby Mathieson
- , Holger Franken
- & Mikhail M. Savitski
-
Article
| Open Access Ub-ProT reveals global length and composition of protein ubiquitylation in cells
Ub-ProT reveals global length and composition of protein ubiquitylation in cells
Ubiquitylation is a dynamic post-translational modification involved in the regulation of numerous cellular processes. Here the authors describe Ub-ProT: a method to measure the length of substrate-attached ubiquitin chains in biological samples, and demonstrate a critical role for chain length in directing substrates to specific cellular pathways.
- Hikaru Tsuchiya
- , Daocharad Burana
- & Yasushi Saeki
-
Article
| Open Access UFD-2 is an adaptor-assisted E3 ligase targeting unfolded proteins
UFD-2 is an adaptor-assisted E3 ligase targeting unfolded proteins
The U-box ubiquitin ligase UFD-2 is one of the most abundant components of the ubiquitin proteasome system in muscle cells. Here the authors perform in vitro and in vivo experiments and show that UFD-2 has E3 ligase activity and that it ubiquitinates unfolded myosin using the C. elegans myosin chaperone UNC-45 as an adaptor protein.
- Doris Hellerschmied
- , Max Roessler
- & Tim Clausen
-
Article
| Open Access Whole proteome analysis of human tankyrase knockout cells reveals targets of tankyrase-mediated degradation
Whole proteome analysis of human tankyrase knockout cells reveals targets of tankyrase-mediated degradation
Tankyrase 1 and 2 are poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases that mark proteins for degradation, but there is a current lack of knowledge about their distinct functions and substrates. Here, the authors elucidate the cellular roles and substrates of these polymerases using comparative functional and proteomics analyses of tankyrase knockout cell lines.
- Amit Bhardwaj
- , Yanling Yang
- & Susan Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Estrogen-related receptor γ causes osteoarthritis by upregulating extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes
Estrogen-related receptor γ causes osteoarthritis by upregulating extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes
The pathogenesis of osteoarthritis is unclear. The authors show that estrogen-related receptor gamma is upregulated in cartilage from patients and mouse models, where it drives production of matrix-degrading MMPs in chondrocytes, and that its downregulation ameliorates pathology in mice.
- Young-Ok Son
- , Seulki Park
- & Jang-Soo Chun
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation of LAMP2A by p38 MAPK couples ER stress to chaperone-mediated autophagy
Phosphorylation of LAMP2A by p38 MAPK couples ER stress to chaperone-mediated autophagy
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and lysosome are central to cellular stress responses, but it is unclear how ER stress is signaled to lysosomes. Here the authors show that ER stress activates chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) via direct phosphorylation of the CMA receptor LAMP2A by the lysosomal p38 MAPK.
- Wenming Li
- , Jinqiu Zhu
- & Zixu Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of adaptor-mediated protein degradation by the tail-specific PDZ-protease Prc
Structural basis of adaptor-mediated protein degradation by the tail-specific PDZ-protease Prc
MepS is a peptidoglycan (PG) cross-link specific hydrolase needed for cell wall expansion and its cellular levels must be tightly regulated. Here the authors present the structure of the MepS degrading protease Prc bound to its adaptor NlpI and propose a model how the NlpI-Prc complex mediates MepS degradation.
- Ming-Yuan Su
- , Nilanjan Som
- & Chung-I Chang
-
Article
| Open Access RNF8/UBC13 ubiquitin signaling suppresses synapse formation in the mammalian brain
RNF8/UBC13 ubiquitin signaling suppresses synapse formation in the mammalian brain
Ubiquitin ligases play critical roles in neuronal connectivity in the brain. Here, Valnegri and colleagues show that ubiquitin ligase RNF8 and ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBC13 regulate synapse number in cerebellar granule neurons and rodent cerebellar learning.
- Pamela Valnegri
- , Ju Huang
- & Azad Bonni

 Structural insights into ubiquitin recognition and Ufd1 interaction of Npl4
Structural insights into ubiquitin recognition and Ufd1 interaction of Npl4