Featured
-
-
Review
| Open Access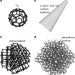 Therapeutic applications of low-toxicity spherical nanocarbon materials
Therapeutic applications of low-toxicity spherical nanocarbon materials
Various spherical nanocarbon materials, including fullerenes, carbon nanohorn aggregates, nanodiamonds etc., have shown potential anti-cancer effects. Fullerenes and metallofullerenes possess outstanding ROS-scavenging capability, as well as other biological effects like immunity enhancement etc., affording promising tumor suppression potential. Carbon nanohorn aggregates and nanodiamond particles have demonstrated effective drug delivery ability for cancer therapy. Moreover, it is noteworthy that these spherical nanocarbon materials show positive toxicological evaluation results, encouraging possible practical usage for biomedical applications.
- Jing Wang
- , Zhongbo Hu
- & Yuliang Zhao
-
Original Article
| Open Access Significant increase in the water dispersibility of zinc phthalocyanine nanowires and applications in cancer phototherapy
Significant increase in the water dispersibility of zinc phthalocyanine nanowires and applications in cancer phototherapy
Water-dispersed nanowires for phototherapy: Without passivation of any water-friendly functional groups in its backbone, one-dimensional zinc phthalocyanine nanowires show remarkably increased dispersibility in water. Upon irradiation with near infrared light, the zinc phthalocyanine nanowires exhibit dual photodynamic and photothermal properties, which enhance the cytotoxic efficiency against tumor cells.
- Hye Kyung Moon
- , Minhyeok Son
- & Hee Cheul Choi
-
Research Highlight |
 Cancer nanotechnology: Smoldering nanoparticles
Cancer nanotechnology: Smoldering nanoparticles
Optimizing the conversion of electromagnetic energy into heat allows the production of nanoparticles that can destroy cancer cells.
-
Research Highlight |
 Drug delivery: Micelle-wrapped
Drug delivery: Micelle-wrapped
The encapsulation of nanoparticles in protective micelles with controlled structures could improve the delivery of therapeutic drugs.
-
Research Highlight |
 Nanomedicine: Controlled relief
Nanomedicine: Controlled relief
Ultrasmall acid-decomposable lids regulate the release of an antitumor drug into target cells for low-toxicity chemotherapy.
-
Research Highlight |
 Nanomedicine: Multiplying the possibilities
Nanomedicine: Multiplying the possibilities
Tiny bright fluorescent spheres promise to simultaneously provide diagnosis and treatment for multiple targets.
-
Research Highlight |
 Nanomedicine: ‘Self-diagnosing’ therapy
Nanomedicine: ‘Self-diagnosing’ therapy
Acid-sensitive nanocarriers simultaneously diagnose tumors and release chemotherapy drugs to target cancer cells
-
Research Highlight |
 Nanomedicine: Smart delivery
Nanomedicine: Smart delivery
An electrochemically responsive membrane promises improved treatments for chronic diseases.

 Aptamer-conjugated nanomaterials for specific cancer cell recognition and targeted cancer therapy
Aptamer-conjugated nanomaterials for specific cancer cell recognition and targeted cancer therapy