Featured
-
-
Article |
 Neoantigen-directed immune escape in lung cancer evolution
Neoantigen-directed immune escape in lung cancer evolution
RNA sequencing data and tumour pathology observations of non-small-cell lung cancers indicate that the immune cell microenvironment exerts strong evolutionary selection pressures that shape the immune-evasion capacity of tumours.
- Rachel Rosenthal
- , Elizabeth Larose Cadieux
- & Andrew Kidd
-
Article |
 Necroptosis microenvironment directs lineage commitment in liver cancer
Necroptosis microenvironment directs lineage commitment in liver cancer
The tumour microenvironment determines which type of liver cancer develops, with transformed hepatocytes giving rise to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma or hepatocellular carcinoma depending or whether they are surrounded by cells undergoing necroptosis or apoptosis.
- Marco Seehawer
- , Florian Heinzmann
- & Lars Zender
-
Letter |
 RAP2 mediates mechanoresponses of the Hippo pathway
RAP2 mediates mechanoresponses of the Hippo pathway
The Ras-related GTPase RAP2 is a key intracellular signal transducer by which extracellular matrix rigidity controls mechanosensitive cellular activities through YAP and TAZ.
- Zhipeng Meng
- , Yunjiang Qiu
- & Kun-Liang Guan
-
Article |
 Leukaemia hijacks a neural mechanism to invade the central nervous system
Leukaemia hijacks a neural mechanism to invade the central nervous system
Expression of α6 integrin enables acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells to use neural migratory pathways to invade the central nervous system and metastasize to the brain.
- Hisayuki Yao
- , Trevor T. Price
- & Dorothy A. Sipkins
-
Article |
 IL-23 secreted by myeloid cells drives castration-resistant prostate cancer
IL-23 secreted by myeloid cells drives castration-resistant prostate cancer
IL-23 produced by myeloid-derived suppressor cells regulates castration resistance in prostate cancer by sustaining androgen receptor signalling.
- Arianna Calcinotto
- , Clarissa Spataro
- & Andrea Alimonti
-
Article |
 Identification of the tumour transition states occurring during EMT
Identification of the tumour transition states occurring during EMT
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in tumour cells occurs through distinct intermediate states, associated with different metastatic potential, cellular properties, gene expression, and chromatin landscape
- Ievgenia Pastushenko
- , Audrey Brisebarre
- & Cédric Blanpain
-
Letter |
 TGFβ drives immune evasion in genetically reconstituted colon cancer metastasis
TGFβ drives immune evasion in genetically reconstituted colon cancer metastasis
A combination of TGFβ inhibition and checkpoint-inhibition therapy provokes a potent cytotoxic response against metastatic tumours derived from colorectal cancers in mice.
- Daniele V. F. Tauriello
- , Sergio Palomo-Ponce
- & Eduard Batlle
-
Letter |
 TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells
TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells
In humans, TGFβ signalling is associated with lack of response to immunotherapy in immune-excluded tumours; in mouse models of this immune phenotype, robust tumour infiltration by T cells and tumour regression are observed only when checkpoint inhibition is combined with inhibition of TGFβ signalling.
- Sanjeev Mariathasan
- , Shannon J. Turley
- & Thomas Powles
-
Letter |
 Transcription elongation factors represent in vivo cancer dependencies in glioblastoma
Transcription elongation factors represent in vivo cancer dependencies in glioblastoma
An in vivo RNA interference screening strategy in glioblastoma enabled the identification of a host of epigenetic targets required for glioblastoma cell survival that were not identified by parallel standard screening in cell culture, including the transcription pause–release factor JMJD6, and could be a powerful tool to uncover new therapeutic targets in cancer.
- Tyler E. Miller
- , Brian B. Liau
- & Jeremy N. Rich
-
Letter |
 Mutual regulation of tumour vessel normalization and immunostimulatory reprogramming
Mutual regulation of tumour vessel normalization and immunostimulatory reprogramming
The cross-talk between immune cells and blood vessel endothelial cells promotes pericyte coverage and decreases hypoxia in mouse tumour models, and correlative evidence suggests that these processes influence cancer prognosis in humans.
- Lin Tian
- , Amit Goldstein
- & Xiang H.-F. Zhang
-
Letter |
 The ligand Sas and its receptor PTP10D drive tumour-suppressive cell competition
The ligand Sas and its receptor PTP10D drive tumour-suppressive cell competition
Wild-type Drosophila epithelial cells outcompete proto-oncogenic cells through translocation of the ligand Sas to the wild-type–tumour cell interface, where it binds the PTP10D receptor of the tumour cell, initiating pro-apoptotic signalling.
- Masatoshi Yamamoto
- , Shizue Ohsawa
- & Tatsushi Igaki
-
Letter |
 Microenvironmental autophagy promotes tumour growth
Microenvironmental autophagy promotes tumour growth
During early-stage tumour growth in Drosphila, tumour cells acquire necessary nutrients by triggering autophagy in surrounding cells in the tumour microenvironment.
- Nadja S. Katheder
- , Rojyar Khezri
- & Tor Erik Rusten
-
Letter |
 T-cell acute leukaemia exhibits dynamic interactions with bone marrow microenvironments
T-cell acute leukaemia exhibits dynamic interactions with bone marrow microenvironments
Here, leukaemia cells are followed by intravital microscopy as they infiltrate mouse bone marrow and respond to chemotherapy, revealing that at all stages analysed they are highly motile and do not display any associations with particular bone marrow sub-compartments.
- Edwin D. Hawkins
- , Delfim Duarte
- & Cristina Lo Celso
-
Article |
 Tumour hypoxia causes DNA hypermethylation by reducing TET activity
Tumour hypoxia causes DNA hypermethylation by reducing TET activity
- Bernard Thienpont
- , Jessica Steinbacher
- & Diether Lambrechts
-
Letter |
 Pancreatic stellate cells support tumour metabolism through autophagic alanine secretion
Pancreatic stellate cells support tumour metabolism through autophagic alanine secretion
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells drive autophagy in tumour microenvironment-associated stellate cells, which release alanine that is used by the cancer cells as a carbon source for a variety of metabolic processes in an otherwise nutrient-poor environment.
- Cristovão M. Sousa
- , Douglas E. Biancur
- & Alec C. Kimmelman
-
Article |
 Carcinoma–astrocyte gap junctions promote brain metastasis by cGAMP transfer
Carcinoma–astrocyte gap junctions promote brain metastasis by cGAMP transfer
A heterotypic cell interaction between astrocytes and tumour cells colonizing the brain is discovered; by establishing gap junctions, tumour cells trigger the activation of innate immune response signalling in astrocytes, which results in the secretion of factors that support growth and chemoresistance in brain metastatic cells.
- Qing Chen
- , Adrienne Boire
- & Joan Massagué
-
Letter |
 Neutrophils support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer cells
Neutrophils support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer cells
Neutrophils are shown to have a role in driving the metastasis of breast cancer cells to the lung, with neutrophil-derived leukotrienes promoting metastatic initiation in the lung by expanding the sub-pool of cancer cells with high tumorigenic potential.
- Stefanie K. Wculek
- & Ilaria Malanchi
-
Article |
 Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis
Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis
Exosomes originating from lung-, liver- and brain-tropic tumour cells are preferentially incorporated by specific resident cells of the target organs, thus preparing the site for metastasis; the expression of distinct combinations of exosomal integrin proteins determines the exosomal targeting to each of the three organs, and blocking these integrins reduces organotropic exosome uptake by the target organs, thereby reducing the likelihood of organotropic metastasis.
- Ayuko Hoshino
- , Bruno Costa-Silva
- & David Lyden
-
Letter |
 Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth
Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth
Expression of the tumour suppressor PTEN in disseminated primary tumour cells is lost after tumour cells metastasize to the brain, with downregulation instigated by microRNAs from astrocytes, which are transferred from cell to cell by exosomes; these findings reveal the dynamic nature of metastatic cancer cells when adapting to a new tissue environment.
- Lin Zhang
- , Siyuan Zhang
- & Dihua Yu
-
Letter |
 MET is required for the recruitment of anti-tumoural neutrophils
MET is required for the recruitment of anti-tumoural neutrophils
Whether neutrophils exert an anti- or pro-tumorigenic function has remained controversial; now, expression of the receptor molecule MET in neutrophils is shown to be required for their ability to restrict tumour growth in several mouse cancer models, with potential implications for human cancer therapy.
- Veronica Finisguerra
- , Giusy Di Conza
- & Massimiliano Mazzone
-
Letter |
 Mechanical induction of the tumorigenic β-catenin pathway by tumour growth pressure
Mechanical induction of the tumorigenic β-catenin pathway by tumour growth pressure
Magnetically induced mechanical strain mimicking the pressure exerted by a growing tumour in the mouse colon is shown to activate the tumorigenic β-catenin pathway in healthy epithelia, suggesting an alternative pathway, mechanotransductive in nature, in the propagation of tumorigenesis and growth from tumour to healthy tissue.
- María Elena Fernández-Sánchez
- , Sandrine Barbier
- & Emmanuel Farge
-
Letter |
 Melanoma-intrinsic β-catenin signalling prevents anti-tumour immunity
Melanoma-intrinsic β-catenin signalling prevents anti-tumour immunity
Only a subset of patients with melanoma responds to new immunotherapeutic therapies; here, β-catenin signalling is identified as an important pathway that confers resistance to this type of approach, with implications for future treatment strategies.
- Stefani Spranger
- , Riyue Bao
- & Thomas F. Gajewski
-
Letter |
 SHMT2 drives glioma cell survival in ischaemia but imposes a dependence on glycine clearance
SHMT2 drives glioma cell survival in ischaemia but imposes a dependence on glycine clearance
Tumours are a low-oxygen environment, in this study glioblastoma cells are found to overexpress the serine hydroxymethyltransferase SHMT2; SHMT acts to reduce oxygen consumption, which confers the tumour cells with a survival advantage.
- Dohoon Kim
- , Brian P. Fiske
- & David M. Sabatini
-
Letter |
 IL-17-producing γδ T cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis
IL-17-producing γδ T cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis
Tumours maximize their chance of metastasizing by evoking a systemic inflammatory cascade in mouse models of spontaneous breast cancer metastasis.
- Seth B. Coffelt
- , Kelly Kersten
- & Karin E. de Visser
-
Letter |
 Therapy-induced tumour secretomes promote resistance and tumour progression
Therapy-induced tumour secretomes promote resistance and tumour progression
Tumour cells respond to an effective, targeted drug treatment with BRAF, ALK or EGFR kinase inhibitors by inducing a complex network of secreted signals that promote tumour growth, dissemination and metastasis of drug-resistant cancer cell clones, and increase the survival of drug-sensitive tumour cells, potentially contributing to incomplete tumour regression.
- Anna C. Obenauf
- , Yilong Zou
- & Joan Massagué
-
Letter |
 Endothelial-cell FAK targeting sensitizes tumours to DNA-damaging therapy
Endothelial-cell FAK targeting sensitizes tumours to DNA-damaging therapy
The tumour microenvironment can influence its response to anticancer therapies; here, the enzyme FAK in endothelial cells is shown to have a role in the induction of a number of cytokines during chemotherapy or irradiation, which in turn protect tumours from DNA-damaging agents.
- Bernardo Tavora
- , Louise E. Reynolds
- & Kairbaan M. Hodivala-Dilke
-
Letter |
 RETRACTED ARTICLE: miR-34a blocks osteoporosis and bone metastasis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and Tgif2
RETRACTED ARTICLE: miR-34a blocks osteoporosis and bone metastasis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and Tgif2
A microRNA, miR-34a, is a novel and critical suppressor of osteoclastogenesis, bone resorption and the bone metastatic niche.
- Jing Y. Krzeszinski
- , Wei Wei
- & Yihong Wan
-
Letter |
 Neuropathy of haematopoietic stem cell niche is essential for myeloproliferative neoplasms
Neuropathy of haematopoietic stem cell niche is essential for myeloproliferative neoplasms
Myeloproliferative neoplasms are caused by mutations in the haematopoietic stem cell (HSC) compartment, and here the authors show that the HSC niche contributes to the pathogenesis; sympathetic innervation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is reduced in the bone marrow of patients, which leads to reduced MSC numbers and increased mutant HSC expansion, and restoring sympathetic regulation of MSCs with neuroprotective/sympathomimetic drugs prevents mutant HSC expansion.
- Lorena Arranz
- , Abel Sánchez-Aguilera
- & Simón Méndez-Ferrer
-
Letter |
 PTEN action in leukaemia dictated by the tissue microenvironment
PTEN action in leukaemia dictated by the tissue microenvironment
A mouse model of T-cell leukaemia is used to test whether PTEN loss is required for tumour maintenance as well as initiation; although it had little effect on tumour load in haematopoietic organs, PTEN reactivation reduced the CCR9-dependent tumour dissemination to the intestine that was amplified on PTEN loss, exposing the importance of tumour microenvironment in PTEN-deficient settings.
- Cornelius Miething
- , Claudio Scuoppo
- & Scott W. Lowe
-
Letter |
 Leukaemogenesis induced by an activating β-catenin mutation in osteoblasts
Leukaemogenesis induced by an activating β-catenin mutation in osteoblasts
A mouse model shows that osteoblast activating β-catenin mutations alone are sufficient to initiate the development of acute myeloid leukaemia acting through increased Notch signalling.
- Aruna Kode
- , John S. Manavalan
- & Stavroula Kousteni
-
Outlook |
 Medical imaging: Removing the blindfold
Medical imaging: Removing the blindfold
Using a variety of creative imaging techniques, researchers are tracking the dynamic interactions of immune and cancer cells. Their results will guide drug development.
- Katherine Bourzac
-
Letter |
 High-molecular-mass hyaluronan mediates the cancer resistance of the naked mole rat
High-molecular-mass hyaluronan mediates the cancer resistance of the naked mole rat
Naked mole rats seem almost entirely protected from developing cancer, and this can now, at least in part, be explained by the production of a unique high-molecular-mass form of hyaluronan, a component of the extracellular matrix; together with an increased sensitivity of naked mole-rat cells to hyaluronan signalling, this form protects its cells from oncogenic transformation.
- Xiao Tian
- , Jorge Azpurua
- & Andrei Seluanov
-
News |
 Neighbouring cells help cancers dodge drugs
Neighbouring cells help cancers dodge drugs
Proteins in a tumour's microenvironment play a part in drug resistance.
- Jennifer Carpenter
-
Letter |
 Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion
Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion
The secretion of hepatocyte growth factor by stromal cells in the tumour micro-environment can make melanoma resistant to RAF inhibitors, through the activation of the MET signalling pathway, but a combination of RAF and MET inhibitors can overcome this resistance.
- Ravid Straussman
- , Teppei Morikawa
- & Todd R. Golub
-
Research Highlights |
Environment of chemo success
-
Letter |
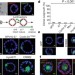 Outgrowth of single oncogene-expressing cells from suppressive epithelial environments
Outgrowth of single oncogene-expressing cells from suppressive epithelial environments
The earliest stages of tumorigenesis are mimicked in a three-dimensional model of mammary epithelial cells, showing that oncogenes that can promote cell translocation can also drive clonal outgrowth.
- Cheuk T. Leung
- & Joan S. Brugge
-
Outlook |
 Microenvironment: Neighbourhood watch
Microenvironment: Neighbourhood watch
In the fight against myeloma, researchers are investigating its interactions with molecular neighbours in the bone marrow.
- Virginia Hughes
-
Letter |
 Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization
Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization
For the initiation of metastasis, there must be a small population of cancer stem cells at the secondary site and, to maintain this population and allow proliferation, infiltrating cancer cells must induce the expression of stromal periostin.
- Ilaria Malanchi
- , Albert Santamaria-Martínez
- & Joerg Huelsken
-
Article |
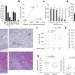 An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor
An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- Christiane A. Opitz
- , Ulrike M. Litzenburger
- & Michael Platten
-
Review Article |
 Microenvironmental regulation of stem cells in intestinal homeostasis and cancer
Microenvironmental regulation of stem cells in intestinal homeostasis and cancer
- Jan Paul Medema
- & Louis Vermeulen
-
Research Highlights |
Cell biology: Communication key to cancer virus

 Fatty acid transport protein 2 reprograms neutrophils in cancer
Fatty acid transport protein 2 reprograms neutrophils in cancer