Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access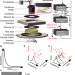 High-resolution mass measurements of single budding yeast reveal linear growth segments
High-resolution mass measurements of single budding yeast reveal linear growth segments
Measuring the mass of individual microbial cells remains challenging. Here, the authors present a cell balance to monitor the proliferation of single budding yeast cells under culture conditions in real time, showing that single cells increase total mass in multiple linear segments of constant growth rates.
- Andreas P. Cuny
- , K. Tanuj Sapra
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access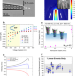 On the origins of conductive pulse sensing inside a nanopore
On the origins of conductive pulse sensing inside a nanopore
Conductive events during nanopore sensing, are seen typically under low salt conditions and widely thought to arise from counterions brought into the pore via analyte. Here, authors show that an imbalance of ionic fluxes lead to conductive events.
- Lauren S. Lastra
- , Y. M. Nuwan D. Y. Bandara
- & Kevin J. Freedman
-
Article
| Open Access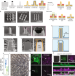 Nanocrown electrodes for parallel and robust intracellular recording of cardiomyocytes
Nanocrown electrodes for parallel and robust intracellular recording of cardiomyocytes
Nanoelectrodes for measuring intracellular action potentials suffer from issues with success rate, signal strength and fabrication. Here, the authors report on a scalable technique which creates robust nanocrown electrodes with high success rates by electroporation and demonstrate the advance towards preclinical drug evaluation.
- Zeinab Jahed
- , Yang Yang
- & Bianxiao Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Open-channel microfluidics via resonant wireless power transfer
Open-channel microfluidics via resonant wireless power transfer
Open microfluidics enables precise positioning of liquid sample with direct channel access. Here, authors demonstrate a geometrical solution for actively manipulating open microchannels using a wireless radio frequency signal.
- Christopher T. Ertsgaard
- , Daehan Yoo
- & Sang-Hyun Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Digital plasmonic nanobubble detection for rapid and ultrasensitive virus diagnostics
Digital plasmonic nanobubble detection for rapid and ultrasensitive virus diagnostics
Digital immunoassays are powerful platforms but are complex and require multiple steps to perform. Here the authors show that digital plasmonic nanobubble detection allows rapid and ultrasensitive diagnostics via a one-step homogeneous immunoassay.
- Yaning Liu
- , Haihang Ye
- & Zhenpeng Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Single amino acid bionanozyme for environmental remediation
Single amino acid bionanozyme for environmental remediation
In the context of enviromental applications, refining enzymes into more minimalist structures could ease production costs, improve stability, and improve reusability. Here, the authors report a single amino acid bionanozyme that can catalyze the rapid oxidation of environmentally toxic phenolic contaminates and serves as a tool to detect biologically important neurotransmitters similar to the laccase enzyme.
- Pandeeswar Makam
- , Sharma S. R. K. C. Yamijala
- & Ehud Gazit
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable and scalable fabrication of block copolymer-based 3D polymorphic artificial cell membrane array
Tunable and scalable fabrication of block copolymer-based 3D polymorphic artificial cell membrane array
In this manuscript, an electric-field-assisted self-assembly technique that can allow controllable and scalable fabrication of 3-dimensional block copolymer (BCP)-based artificial cell membranes (3DBCPMs) immobilized on predefined locations is presented.
Topographically and chemically structured microwell array templates facilitate uniform patterning of BCPs and serve as reactors for the effective growth of 3DBCPMs, which diverse shapes, sizes and stability can be tuned by modulating the BCP concentration and the amplitude/frequency of the electric field.
The potential of 3DBCPMs for a variety of biological applications is highlighted by performance of in vitro protein-membrane assays and mimicking of human intestinal organs.
- Dong-Hyun Kang
- , Won Bae Han
- & Tae Song Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Fast microwave heating-based one-step synthesis of DNA and RNA modified gold nanoparticles
Fast microwave heating-based one-step synthesis of DNA and RNA modified gold nanoparticles
Simple methods for attaching polynucleotides to gold nanoparticles are of interest for simplifying conjugation in a range of applications. Here, the authors report a microwave heating-based method for the fast, one-step attachment of a range of thiolated or non-thiolated DNA and RNA to gold nanoparticles.
- Mengqi Huang
- , Erhu Xiong
- & Xiaoming Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Breaking the barrier to biomolecule limit-of-detection via 3D printed multi-length-scale graphene-coated electrodes
Breaking the barrier to biomolecule limit-of-detection via 3D printed multi-length-scale graphene-coated electrodes
Here, the authors introduce a biosensing platform with multi-length-scale electrode architecture consisting of 3D printed silver micropillars decorated with graphene flakes. They demonstrate that this breaks a barrier to the biomolecule limit-of-detection, enabling detection down to femtomolar level.
- Md. Azahar Ali
- , Chunshan Hu
- & Rahul Panat
-
Article
| Open Access A genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor for extracellular l-lactate
A genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor for extracellular l-lactate
l-lactate is an important intercellular energy currency. Here the authors report a genetically encoded biosensor eLACCO1.1 to monitor extracellular l-lactate; they use eLACCO1.1 to image extracellular l-lactate in cultured mammalian cells and brain tissue.
- Yusuke Nasu
- , Ciaran Murphy-Royal
- & Robert E. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access A Fabry-Pérot cavity coupled surface plasmon photodiode for electrical biomolecular sensing
A Fabry-Pérot cavity coupled surface plasmon photodiode for electrical biomolecular sensing
Surface plasmon resonance is well established for biosensing applications, but commonly limited by complex optical detection. Here, the authors present a plasmonic sensor integrated in a photovoltaic cell, which generates an electronic signal sensitive to the solution refractive index via plasmon interaction
- Giles Allison
- , Amrita Kumar Sana
- & Hironori Suzuki
-
Article
| Open Access Genetically encoded cell-death indicators (GEDI) to detect an early irreversible commitment to neurodegeneration
Genetically encoded cell-death indicators (GEDI) to detect an early irreversible commitment to neurodegeneration
Cell death is a critical process in health and disease, yet available markers record later stages of cell death once a cell has already begun to decompose. Here the authors show the use of a genetically encoded calcium indicator that demarcates an irreversible stage of cell death earlier than previously possible.
- Jeremy W. Linsley
- , Kevan Shah
- & Steven Finkbeiner
-
Article
| Open Access A non-printed integrated-circuit textile for wireless theranostics
A non-printed integrated-circuit textile for wireless theranostics
The typical approach to electronics is to integrate sensors, power units, and controlling components on a printed circuit board (PCB). Here, the authors demonstrate a self-powered and fully integrated combination of sensors and controlling components that is woven, rather than integrated onto a PCB, allowing for wearable health monitoring.”
- Yuxin Yang
- , Xiaofei Wei
- & Xing Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Turn-key mapping of cell receptor force orientation and magnitude using a commercial structured illumination microscope
Turn-key mapping of cell receptor force orientation and magnitude using a commercial structured illumination microscope
The authors have recently developed molecular force microscopy (MFM) which uses fluorescence polarisation to measure cell-surface receptor force orientation. Here they show that structured illumination microscopes, which inherently use fluorescence polarisation, can be used for MFM in a turn-key manner.
- Aaron Blanchard
- , J. Dale Combs
- & Khalid Salaita
-
Article
| Open Access Surfactant-guided spatial assembly of nano-architectures for molecular profiling of extracellular vesicles
Surfactant-guided spatial assembly of nano-architectures for molecular profiling of extracellular vesicles
Current methods for controlled assembly of nanomaterials into desired architectures often lack the precision and versatility to develop complex architectures. Here the authors report STAR, surfactant tunable spatial architecture, to guide nanomaterial integration in metal-organic frameworks.
- Zhigang Wang
- , Haitao Zhao
- & Huilin Shao
-
Review Article
| Open Access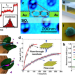 Nanophotonic biosensors harnessing van der Waals materials
Nanophotonic biosensors harnessing van der Waals materials
This review presents an overview of scenarios where van der Waals (vdW) materials provide unique advantages for nanophotonic biosensing applications. The authors discuss basic sensing principles based on vdW materials, advantages of the reduced dimensionality as well as technological challenges.
- Sang-Hyun Oh
- , Hatice Altug
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article
| Open Access Ionic contrast across a lipid membrane for Debye length extension: towards an ultimate bioelectronic transducer
Ionic contrast across a lipid membrane for Debye length extension: towards an ultimate bioelectronic transducer
The design of bioelectronic devices that enables accurate detection of biomolecules in ionic solutions at physiologically-relevant concentrations remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a ion-impermeable supported lipid bilayer-assisted field-effect transistor platform for biomolecule detection.
- Donggeun Lee
- , Woo Hyuk Jung
- & Chulki Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Geometrically encoded SERS nanobarcodes for the logical detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-related progression biomarkers
Geometrically encoded SERS nanobarcodes for the logical detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-related progression biomarkers
SERS assays have potential for multiplexed detection of biomarkers but differentiation of SERS tags remains a challenge. Here, the authors report the creation of 14 distinct geometrically controlled metal carbonyl tags and demonstrate multiplexed detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma biomarkers from patient blood.
- Duo Lin
- , Chang-Lin Hsieh
- & Kien Voon Kong
-
Article
| Open Access Dielectric nanohole array metasurface for high-resolution near-field sensing and imaging
Dielectric nanohole array metasurface for high-resolution near-field sensing and imaging
Dielectric metasurfaces have different Q-factor and light localisation requirements for sensing and imaging. Here, the authors present a dielectric metasurface, supporting two optical modes with sharp Fano resonances for high Q-factors and strong spatial confinement, allowing both sensing and imaging.
- Donato Conteduca
- , Isabel Barth
- & Thomas F. Krauss
-
Article
| Open Access An electronic neuromorphic system for real-time detection of high frequency oscillations (HFO) in intracranial EEG
An electronic neuromorphic system for real-time detection of high frequency oscillations (HFO) in intracranial EEG
A major challenge across a variety of fields is how to process the vast quantities of data produced by sensors without large computation resources. Here, the authors present a neuromorphic chip which can detect a relevant signature of epileptogenic tissue from intracranial recordings in patients.
- Mohammadali Sharifshazileh
- , Karla Burelo
- & Giacomo Indiveri
-
Article
| Open Access Cellular lensing and near infrared fluorescent nanosensor arrays to enable chemical efflux cytometry
Cellular lensing and near infrared fluorescent nanosensor arrays to enable chemical efflux cytometry
The authors present nanosensor chemical cytometry, based on an array of nIR fluorescent single walled carbon nanotube integrated along a microfluidic channel. The lensing effect of the flowing cells allows for extracting information, and correlating biomolecular information with physical properties.
- Soo-Yeon Cho
- , Xun Gong
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article
| Open Access Wireless battery free fully implantable multimodal recording and neuromodulation tools for songbirds
Wireless battery free fully implantable multimodal recording and neuromodulation tools for songbirds
Studies requiring neural modulation in species that fly are difficult because of the need for wired connections to record experimental data. Here, Ausra et al. present a wireless and battery free device that achieves this in songbirds, model organisms used to study vocal learning and maintenance.
- Jokubas Ausra
- , Stephanie J. Munger
- & Philipp Gutruf
-
Article
| Open Access Enzymatic enhancing of triplet–triplet annihilation upconversion by breaking oxygen quenching for background-free biological sensing
Enzymatic enhancing of triplet–triplet annihilation upconversion by breaking oxygen quenching for background-free biological sensing
Triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion (TTA-UC) nanoparticles (NPs) are a promising material for diverse applications, but TTA-UC is sensitive to oxygen, which hinders its biological utility. Here, the authors report an enzymatic method to deplete oxygen and amplify the upconversion of TTA-UCNP in aqueous solution, and develop background-free glucose and glucose metabolism enzyme sensors.
- Ling Huang
- , Timmy Le
- & Gang Han
-
Article
| Open Access Addressable nanoantennas with cleared hotspots for single-molecule detection on a portable smartphone microscope
Addressable nanoantennas with cleared hotspots for single-molecule detection on a portable smartphone microscope
Single-molecule fluorescence currently requires specialized imaging equipment due to the low signal of a single emitter. Here the authors introduce NanoAntennas with Cleared HOtSpots (NACHOS) to boost the signal sufficient for detection of a single emitter by a smartphone, opening the door to point-of-care applications.
- Kateryna Trofymchuk
- , Viktorija Glembockyte
- & Philip Tinnefeld
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous Zn2+ tracking in multiple organelles using super-resolution morphology-correlated organelle identification in living cells
Simultaneous Zn2+ tracking in multiple organelles using super-resolution morphology-correlated organelle identification in living cells
Subcellular Zn2+ compartmentalisation is essential for cell biology. Here the authors make a turn-on fluorescent Zn2+ probe that localises to multiple organelles, and correlate its location using organelle morphology derived from structured illumination microscopy.
- Hongbao Fang
- , Shanshan Geng
- & Jiajie Diao
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive antibody-aptamer plasmonic biosensor for malaria biomarker detection in whole blood
Ultrasensitive antibody-aptamer plasmonic biosensor for malaria biomarker detection in whole blood
Reliable plasmonic biosensors with high throughput and ease of use are highly sought after. Here, the authors report a plasmon-enhanced fluorescence antibody-aptamer biosensor based on a gold nanoparticle array, and demonstrate its use for effective specific detection of a malaria marker, at femtomolar level, in whole blood.
- Antonio Minopoli
- , Bartolomeo Della Ventura
- & Raffaele Velotta
-
Article
| Open Access Fibronectin-based nanomechanical biosensors to map 3D surface strains in live cells and tissue
Fibronectin-based nanomechanical biosensors to map 3D surface strains in live cells and tissue
The ability to measure strain in cells and tissues in vitro with minimal perturbation and at high spatial resolution has proven challenging. Here the authors develop a fluorescently-labelled fibronectin square lattice mesh that can be applied to the surface of cells and tissues to enable direct quantification and mapping of strain over time.
- Daniel J. Shiwarski
- , Joshua W. Tashman
- & Adam W. Feinberg
-
Article
| Open Access High precision epidermal radio frequency antenna via nanofiber network for wireless stretchable multifunction electronics
High precision epidermal radio frequency antenna via nanofiber network for wireless stretchable multifunction electronics
Designing efficient radio frequency antenna for wireless stretchable multifunction electronics remains a challenge. Here, the authors present epidermal radio frequency antenna based on silver nanofibers network for wireless power transfer and information identification.
- Yufei Zhang
- , Zhihao Huo
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Optical imaging of single-protein size, charge, mobility, and binding
Optical imaging of single-protein size, charge, mobility, and binding
Protein identification at the single-molecule level is the ultimate goal for biological research and disease diagnosis. Here, the authors identify the size, charge, mobility, and binding of individual protein molecules by measuring the optical and electrical responses of each protein molecule tethered to a surface.
- Guangzhong Ma
- , Zijian Wan
- & Nongjian Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of DNA nanostructures for single molecule biosensing
Rational design of DNA nanostructures for single molecule biosensing
A key attribute for modern healthcare is the ability to detect low concentrations of biomarkers. Here, the authors use nanopores and DNA origami with target-specific aptamers for detection of CRP.
- Mukhil Raveendran
- , Andrew J. Lee
- & Paolo Actis
-
Article
| Open Access NIR-II bioluminescence for in vivo high contrast imaging and in situ ATP-mediated metastases tracing
NIR-II bioluminescence for in vivo high contrast imaging and in situ ATP-mediated metastases tracing
Conventional bioluminescence imaging usually operates in the visible region and its performance is limited by strong tissue absorption and scattering. Here, the authors present bioluminescence probes (BPs) with emission in the second near infrared (NIR-II) region, and show the NIR-II-BPs could sensitively recognize tumor metastasis with a high tumor-to-normal tissue ratio.
- Lingfei Lu
- , Benhao Li
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Development of A4 antibody for detection of neuraminidase I223R/H275Y-associated antiviral multidrug-resistant influenza virus
Development of A4 antibody for detection of neuraminidase I223R/H275Y-associated antiviral multidrug-resistant influenza virus
Rapid detection of antiviral resistant strains is important for effective clinical treatment. Here the authors develop an antibody which specifically binds to multidrug-resistant influenza virus and demonstrated detection in a number of different systems using the antibody.
- Kyeonghye Guk
- , Hyeran Kim
- & Juyeon Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of aptamer switches with programmable pH response
Rational design of aptamer switches with programmable pH response
Previous design strategies for pH sensitive aptamers were not readily tunable across pH ranges. Here the authors present a general method to convert aptamers into pH-responsive switches using two orthogonal motifs.
- Ian A. P. Thompson
- , Liwei Zheng
- & H. Tom Soh
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming evanescent field decay using 3D-tapered nanocavities for on-chip targeted molecular analysis
Overcoming evanescent field decay using 3D-tapered nanocavities for on-chip targeted molecular analysis
Plasmon-enhanced fluorescence is strictly dependent on molecule size and surface position, restricting application of diversely sized molecules. Here, the authors overcome this by introducing a 3D tapered gap plasmon nanocavity with fluidic access and near homogeneous confinement of the electromagnetic fields.
- Shailabh Kumar
- , Haeri Park
- & Hyuck Choo
-
Article
| Open Access Precise capture and dynamic relocation of nanoparticulate biomolecules through dielectrophoretic enhancement by vertical nanogap architectures
Precise capture and dynamic relocation of nanoparticulate biomolecules through dielectrophoretic enhancement by vertical nanogap architectures
Label-free trapping of nanoparticles via dielectophoretic forces is traditionally done with electrodes in a horizontal gap layout. Here, the authors present a vertical nanogap architecture, which allows for precise capture and spatiotemporal manipulation of nanoparticles and molecular assemblies.
- Eui-Sang Yu
- , Hyojin Lee
- & Yong-Sang Ryu
-
Article
| Open Access Artifact-free and high-temporal-resolution in vivo opto-electrophysiology with microLED optoelectrodes
Artifact-free and high-temporal-resolution in vivo opto-electrophysiology with microLED optoelectrodes
Artifact-free opto-electrophysiology is key for precise modulation and monitoring of individual neurons at high spatio-temporal resolution. The authors present a method for eliminating stimulation artifacts in high-density micro-LED optoelectrodes for accurate functional mapping of local circuits.
- Kanghwan Kim
- , Mihály Vöröslakos
- & Euisik Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive detection of nucleic acids using deformed graphene channel field effect biosensors
Ultrasensitive detection of nucleic acids using deformed graphene channel field effect biosensors
Field effect transistors based on graphene hold promise for sensing applications. Here, the authors report a millimeter-sized transistor based on deformed graphene as a biosensor that can detect nucleic acid molecules having detection limit of ~18 molecules of DNA in physiological buffer solution and ~600 molecules in human serum.
- Michael Taeyoung Hwang
- , Mohammad Heiranian
- & Rashid Bashir
-
Article
| Open Access A progesterone biosensor derived from microbial screening
A progesterone biosensor derived from microbial screening
Bacteria represent an unexploited reservoir of biosensing proteins. Here the authors use genomic screens and functional assays to isolate a progesterone sensing allosteric transcription factor and use a FRET-based method to develop an optical progesterone sensor.
- Chloé Grazon
- , R C. Baer
- & James E. Galagan
-
Article
| Open Access Photosynthesis-inspired H2 generation using a chlorophyll-loaded liposomal nanoplatform to detect and scavenge excess ROS
Photosynthesis-inspired H2 generation using a chlorophyll-loaded liposomal nanoplatform to detect and scavenge excess ROS
Hydrogen can be used to reduce the concentration of reactive oxygen species (ROS), but its delivery to diseased tissues is challenging due to its low solubility. Here the authors develop a photosynthesis-inspired FRET nanocomplex to detect and scavenge local excess of ROS in the tissue using photocatalytic hydrogen production.
- Wei-Lin Wan
- , Bo Tian
- & Hsing-Wen Sung
-
Article
| Open Access An electrochemical biosensor for the detection of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
An electrochemical biosensor for the detection of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) plays a key role in embryonic development, wound healing and cancer. Here the authors develop an electrochemical sensor to detect EMT using E-cadherin antibody-quantum dot conjugates and a carbon nanotube-gold nanoparticle-modified electrode as a detection platform.
- Xin Du
- , Zhenhua Zhang
- & Jun Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Surface enhanced Raman scattering artificial nose for high dimensionality fingerprinting
Surface enhanced Raman scattering artificial nose for high dimensionality fingerprinting
Label-free surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy is an emergent method for the detection and discrimination of biological analytes. Here, the authors describe SERS sensors with arrayed mildly-selective surface chemistries to give a fingerprint based on different interactions for analysing biological samples.
- Nayoung Kim
- , Michael R. Thomas
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Clinically accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease via multiplexed sensing of core biomarkers in human plasma
Clinically accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease via multiplexed sensing of core biomarkers in human plasma
Detection of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) biomarkers from patients’ blood is challenging because these are present in very low concentrations in the plasma. Here the authors develop a sensor array of densely aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes for clinically accurate detection of femtomolar AD biomarkers in human plasma samples.
- Kayoung Kim
- , Min-Ji Kim
- & Chan Beum Park
-
Article
| Open Access Ratiometric upconversion nanothermometry with dual emission at the same wavelength decoded via a time-resolved technique
Ratiometric upconversion nanothermometry with dual emission at the same wavelength decoded via a time-resolved technique
Traditional ratiometric temperature monitoring is challenging due to the variation in tissue absorption and scattering of different wavelengths. Here, the authors show improved accuracy by using emission at the same wavelength, but different luminescent lifetimes decoded by a time-resolved technique.
- Xiaochen Qiu
- , Qianwen Zhou
- & Fuyou Li
-
Article
| Open Access Giant single molecule chemistry events observed from a tetrachloroaurate(III) embedded Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A nanopore
Giant single molecule chemistry events observed from a tetrachloroaurate(III) embedded Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A nanopore
Engineered biological nanopores enable observation of single molecule chemistry events; however a cylindrical pore geometry can have undesired effects. The authors report a conical biological pore which was embedded with tetrachloroaurate(III) to allow for discrimination between different biothiols.
- Jiao Cao
- , Wendong Jia
- & Shuo Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Active DNA unwinding and transport by a membrane-adapted helicase nanopore
Active DNA unwinding and transport by a membrane-adapted helicase nanopore
Active translocation of DNA through nanopores usually needs enzyme assistance. Here authors present a nanopore derived from helicase E1 of bovine papillomavirus (BPV) which acts as a conductive pore embedded in lipid membrane to allow the translocation of ssDNA and unwinding of dsDNA.
- Ke Sun
- , Changjian Zhao
- & Jia Geng
-
Article
| Open Access Independent control of the thermodynamic and kinetic properties of aptamer switches
Independent control of the thermodynamic and kinetic properties of aptamer switches
Aptamer switches are promising biotechnological tools but coupling of their affinity and temporal response limits their versatility. Here, the authors developed an intramolecular strand-displacement strategy that allows for independent fine-tuning of thermodynamics and kinetics of aptamer switches.
- Brandon D. Wilson
- , Amani A. Hariri
- & H. Tom Soh
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule sensing of peptides and nucleic acids by engineered aerolysin nanopores
Single-molecule sensing of peptides and nucleic acids by engineered aerolysin nanopores
Aerolysin pores have potential to improve the accuracy of DNA sequencing and single-molecule proteomics. Here, the authors rationally design a set of mutated pores to achieve a more accurate detection of peptides and nucleic acids.
- Chan Cao
- , Nuria Cirauqui
- & Matteo Dal Peraro
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic molecular recognition nanosensor paint for microalbuminuria
Synthetic molecular recognition nanosensor paint for microalbuminuria
Microalbuminuria, a clinical marker associated with cancer and hypertension, defined by low albumin levels in the urine, is normally detected by immunoassay. Herein, a nanosensor paint was developed using a polymer to mimic fatty acid binding to albumin, transduced by carbon nanotube fluorescence.
- Januka Budhathoki-Uprety
- , Janki Shah
- & Daniel A. Heller
-
Article
| Open Access Virus lasers for biological detection
Virus lasers for biological detection
Many ligand-binding assays still rely on signals that scale linearly with probe concentration. The authors present lasing detection probes with a dye-labelled virus as the gain medium to optically amplify the signal, which could enable much higher signals than for fluorescent quantification.
- John E. Hales
- , Guy Matmon
- & Gabriel Aeppli

 Spatial regulation of AMPK signaling revealed by a sensitive kinase activity reporter
Spatial regulation of AMPK signaling revealed by a sensitive kinase activity reporter