Abstract
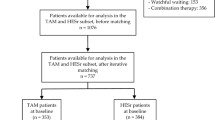
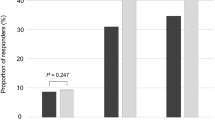
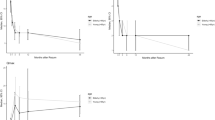
Although ethnicity-based differences in prostate size and physiology have been reported, results of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) treatment trials in predominantly Caucasian patients are assumed to be applicable to non-Caucasian populations. This post hoc analysis investigated whether an Asian subpopulation of men with moderate-to-severe BPH in the CombAT study achieves treatment responses in line with those of the overall study population. In this double-blind, randomized, parallel-group trial, 325 Asian men were assigned to treatment with 0.5 mg dutasteride once daily, 0.4 mg tamsulosin once daily or the combination. Decrease in international prostate symptom score (IPSS) at month 24 from baseline (the primary endpoint) was significantly greater with combination treatment compared with tamsulosin (P<0.05), and numerically, but not statistically significantly, greater compared with dutasteride. Mean IPSS was reduced from baseline by 7.5 (±0.84) in the combination group, by 6.3 (±0.86) in the dutasteride group and by 4.5 (±0.78) in the tamsulosin group, resulting in respective mean IPSS at months 24 of 11.4 (±0.60), 12.7 (±0.70) and 14.3 (±0.74). The adverse event profile was similar to that observed in the overall CombAT population, and drug-related adverse events were more common with combination therapy (26%) than with tamsulosin (15%) or dutasteride (9%). No unexpected adverse events emerged. In conclusion, in Asian men with moderate-to-severe lower urinary tract symptoms and an enlarged prostate, combination therapy achieved significantly greater improvements from baseline BPH symptoms, flow rate, quality of life, reduced prostate volume and improved treatment satisfaction compared with tamsulosin monotherapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearing House (NKUDIC). Prostate enlargement: benign prostatic hyperplasia. [Cited 10 January 2008]; Available from: http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/kudiseases/pubs/prostateenlargement/.
Mariappan P, Turner KJ, Sothilingam S, Rajan P, Sundram M, Stewart LH . Nocturia, nocturia indices and variables from frequency–volume charts are significantly different in Asian and Caucasian men with lower urinary tract symptoms: a prospective comparison study. BJU Int 2007; 100: 332–336.
Homma Y, Kawabe K, Tsukamoto T, Yamanaka H, Okada K, Okajima E et al. Epidemiologic survey of lower urinary tract symptoms in Asia and Australia using the international prostate symptom score. Int J Urol 1997; 4: 40–46.
Kang D, Andriole GL, Van De Vooren RC, Crawford D, Chia D, Urban DA et al. Risk behaviours and benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int 2004; 93: 1241–1245.
Roehrborn C, McConnell JD . Etiology, pathophysiology, epidemiology and natural history of BPH. In: Walsh P (ed). Campbell's Urology. WB Saunders: Philadelphia, 2002, pp 1297–1336.
Oesterling JE, Kumamoto Y, Tsukamoto T, Girman CJ, Guess HA, Masumori N et al. Serum prostate-specific antigen in a community-based population of healthy Japanese men: lower values than for similarly aged white men. Br J Urol 1995; 75: 347–353.
Lee SE, Kwak C, Park MS, Lee CH, Kang W, Oh SJ . Ethnic differences in the age-related distribution of serum prostate-specific antigen values: a study in a healthy Korean male population. Urology 2000; 56: 1007–1010.
Masumori N, Tsukamoto T, Kumamoto Y, Miyake H, Rhodes T, Girman CJ et al. Japanese men have smaller prostate volumes but comparable urinary flow rates relative to American men: results of community based studies in 2 countries. J Urol 1996; 155: 1324–1327.
Jin B, Turner L, Zhou Z, Zhou EL, Handelsman DJ . Ethnicity and migration as determinants of human prostate size. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 3613–3619.
Wang MZ, Gao ZW, He DL, Chen XF, He H, Wang WS et al. Age-specific reference ranges for serum prostate-specific antigen in Chinese men. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2003; 83: 1665–1667.
Madanay LD, Johnson DB, Miyamoto LA, Gilbert Jr FI . Prostate-specific antigen concentration: influence of age and ethnicity. Hawaii Med J 1995; 54: 606–608.
Cheng I, Yu MC, Koh WP, Pike MC, Kolonel LN, Henderson BE et al. Comparison of prostate-specific antigen and hormone levels among men in Singapore and the United States. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2005; 14: 1692–1696.
Clark RV, Hermann DJ, Cunningham GR, Wilson TH, Morrill BB, Hobbs S . Marked suppression of dihydrotestosterone in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia by dutasteride, a dual 5alpha-reductase inhibitor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 2179–2184.
Vela-Navarrete R, Gonzalez-Enguita C, Garcia-Cardoso JV, Manzarbeitia F, Sarasa-Corral JL, Granizo JJ . The impact of medical therapy on surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a study comparing changes in a decade (1992–2002). BJU Int 2005; 96: 1045–1048.
Boyle P, Roehrborn C, Harkaway R, Logie J, de la Rosette J, Emberton M . 5-Alpha reductase inhibition provides superior benefits to alpha blockade by preventing AUR and BPH-related surgery. Eur Urol 2004; 45: 620–626; [discussion 626–627].
Barkin J, Guimaraes M, Jacobi G, Pushkar D, Taylor S, van Vierssen Trip OB . Alpha-blocker therapy can be withdrawn in the majority of men following initial combination therapy with the dual 5alpha-reductase inhibitor dutasteride. Eur Urol 2003; 44: 461–466.
Marberger M, Harkaway R, de la Rosette J . Optimising the medical management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol 2004; 45: 411–419.
Andriole G, Bruchovsky N, Chung LW, Matsumoto AM, Rittmaster R, Roehrborn C et al. Dihydrotestosterone and the prostate: the scientific rationale for 5alpha-reductase inhibitors in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2004; 172: 1399–1403.
Carson III C, Rittmaster R . The role of dihydrotestosterone in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 2003; 61: 2–7.
Gittelman M, Ramsdell J, Young J, McNicholas T . Dutasteride improves objective and subjective disease measures in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia and modest or severe prostate enlargement. J Urol 2006; 176: 1045–1050; [discussion 1050].
Roehrborn CG . Combination medical therapy for lower urinary tract symptoms and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Rev Urol 2005; 7 (Suppl 8): S43–S51.
Roehrborn CG, Boyle P, Nickel JC, Hoefner K, Andriole G . Efficacy and safety of a dual inhibitor of 5-alpha-reductase types 1 and 2 (dutasteride) in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 2002; 60: 434–441.
McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Bautista OM, Andriole Jr GL, Dixon CM, Kusek JW, et al., Medical Therapy of Prostatic Symptoms (MTOPS) Research Group. The long-term effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2387–2398.
Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damião R, Major-Walker K, Morrill B, et al., CombAT Study Group. The effects of dutasteride, tamsulosin and combination therapy on lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic enlargement: 2-year results from the CombAT study. J Urol 2007; 179: 616–621.
Siami P, Roehrborn CG, Barkin J, Damiao R, Wyczolkowski M, Duggan A, et al., CombAT study group. Combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin in men with moderate-to-severe benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate enlargement: the CombAT (Combination of Avodart and Tamsulosin) trial rationale and study design. Contemp Clin Trials 2007; 28: 770–779.
Black L . The psychometric validation of a US English satisfaction measure in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Abstract Presented at the 2008 International Society of Pharmacoeconomic and Outcomes Research (ISPOR), Toronto, Canada, May 2008.
Lepor H . Long-term evaluation of tamsulosin in benign prostatic hyperplasia: placebo-controlled, double-blind extension of phase III trial. Tamsulosin Investigator Group. Urology 1998; 51: 901–906.
Lepor H . Phase III multicenter placebo-controlled study of tamsulosin in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Tamsulosin Investigator Group. Urology 1998; 51: 892–900.
Narayan P, Lepor H . Long-term, open-label, phase III multicenter study of tamsulosin in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 2001; 57: 466–470.
Chung BH, Hong SJ, Lee MS . Doxazosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia: an open-label, baseline-controlled study in Korean general practice. Int J Urol 2005; 12: 159–165.
Horiuchi K, Tsuboi N, Hattori T, Yoshida K, Akimoto M . The short-term effects of tamsulosin in Japanese men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Nippon Ika Daigaku Zasshi 1999; 66: 382–387.
Lee E . Comparison of tamsulosin and finasteride for lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia in Korean patients. J Int Med Res 2002; 30: 584–590.
Li NC, Chen S, Yang XH, Du LD, Wang JY, Na YQ . Efficacy of low-dose tamsulosin in chinese patients with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Clin Drug Investig 2003; 23: 781–787.
Park CH, Chang HS, Oh BR, Kim HJ, Sul CK, Chung SK et al. Efficacy of low-dose tamsulosin on lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a nonblind multicentre korean study. Clin Drug Investig 2004; 24: 41–47.
Suzuki H, Yano M, Awa Y, Nakatsu H, Egoshi K, Mikami K et al. Clinical impact of tamsulosin on generic and symptom-specific quality of life for benign prostatic hyperplasia patients: using international prostate symptom score and Rand Medical Outcomes Study 36-item Health Survey. Int J Urol 2006; 13: 1202–1206.
Chueh SC, Yu HJ, Chiu TY, Huang CY, Lai MK . Treating benign prostatic hyperplasia with finasteride in Chinese men: one-year experience. J Formos Med Assoc 1996; 95: 650–652.
Mochtar CA, Rahardjo D, Umbas R . A higher PSA-density cut-off level in patients with intermediate PSA values for the early detection of prostate cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 2000; 27 (Suppl 2): 514–522.
Gupta A, Aragaki C, Gotoh M, Masumori N, Ohshima S, Tsukamoto T et al. Relationship between prostate specific antigen and indexes of prostate volume in Japanese men. J Urol 2005; 173: 503–506.
Chang YL, Lin AT, Chen KK, Chang YH, Wu HH, Kuo JY et al. Correlation between serum prostate specific antigen and prostate volume in Taiwanese men with biopsy proven benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2006; 176: 196–199.
Iehle C, Radvanyi F, Gil Diez de Medina S, Ouafik LH, Gérard H, Chopin D et al. Differences in steroid 5alpha-reductase iso-enzymes expression between normal and pathological human prostate tissue. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1999; 68: 189–195.
Boyle P, Gould AL, Roehrborn CG . Prostate volume predicts outcome of treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with finasteride: meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Urology 1996; 48: 398–405.
Lloyd SN, Kavanagh J, Chan PS, Ferreira AM, Gu FL, Pavone-Macaluso M et al. A multicentre prospective study of prostatic volume in asymptomatic men in various continents. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 1997; 1: 97–100.
McNeal JE . Origin and evolution of benign prostatic enlargement. Invest Urol 1978; 15: 340–345.
Aoki Y, Arai Y, Maeda H, Okubo K, Shinohara K . Racial differences in cellular composition of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate 2001; 49: 243–250.
Schuster GA, Schuster TG . The relative amount of epithelium, muscle, connective tissue and lumen in prostatic hyperplasia as a function of the mass of tissue resected. J Urol 1999; 161: 1168–1173.
Pettaway CA . Racial differences in the androgen/androgen receptor pathway in prostate cancer. J Natl Med Assoc 1999; 91: 653–660.
Zeigler-Johnson CM, Walker AH, Mancke B, Spangler E, Jalloh M, McBride S et al. Ethnic differences in the frequency of prostate cancer susceptibility alleles at SRD5A2 and CYP3A4. Hum Hered 2002; 54: 13–21.
Chung BH, Hong SJ, Cho JS, Seong DH . Relationship between serum prostate-specific antigen and prostate volume in Korean men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a multicentre study. BJU Int 2006; 97: 742–746.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, BH., Roehrborn, C., Siami, P. et al. Efficacy and safety of dutasteride, tamsulosin and their combination in a subpopulation of the CombAT study: 2-year results in Asian men with moderate-to-severe BPH. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 12, 152–159 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2008.49
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2008.49
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Urinary Biomarkers and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Current Bladder Dysfunction Reports (2019)
-
Effect of tamsulosin on ejaculatory function in BPH/LUTS
Asian Journal of Andrology (2011)