Abstract
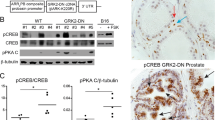
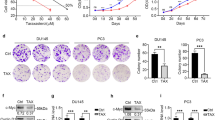
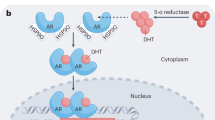
Transgenic (TG) rats bearing a probasin promoter/simian virus 40 T antigen (SV40 Tag) construct were treated with antiandrogens to examine their ability to suppress prostate carcinogenesis. Finasteride and flutamide were administered to 10-week-old TG rats five times a week for 2, 5 and 7 weeks. Antiandrogen-treated prostates exhibited atrophic glandular structures with almost no expression of SV40 Tag and only weak signals for androgen receptors. Furthermore, quantitative data for ventral prostate adenocarcinomas showed significant decrease with antiandrogen treatment. Both finasteride and flutamide had the ability to suppress SV40 Tag-driven carcinogenesis through their different antiandrogenic mechanisms, suggesting that this TG model is suitable for exploring the potential of agents to inhibit prostate cancer development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 2006; 56: 106–130.
Sheldon CA, Williams RD, Fraley EE . Incidental carcinoma of the prostate: a review of the literature and critical reappraisal of classification. J Urol 1980; 124: 626–631.
Cunha GR, Donjacour AA, Cooke PS, Mee S, Bigsby RM, Higgins SJ et al. The endocrinology and developmental biology of the prostate. Endocr Rev 1987; 8: 338–362.
Crawford ED, Eisenberger MA, McLeod DG, Spaulding JT, Benson R, Dorr FA et al. A controlled trial of leuprolide with and without flutamide in prostatic carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1989; 321: 419–424.
Denis LJ, Griffiths K . Endocrine treatment in prostate cancer. Semin Surg Oncol 2000; 18: 52–74.
Raghow S, Kuliyev E, Steakley M, Greenberg N, Steiner MS . Efficacious chemoprevention of primary prostate cancer by flutamide in an autochthonous transgenic model. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 4093–4097.
Steiner JF . Finasteride: a 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor. Clin Pharm 1993; 12: 15–23.
Asamoto M, Hokaiwado N, Cho YM, Takahashi S, Ikeda Y, Imaida K et al. Prostate carcinomas developing in transgenic rats with SV40 T antigen expression under probasin promoter control are strictly androgen dependent. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 4693–4700.
Cho YM, Takahashi S, Asamoto M, Suzuki S, Inaguma S, Hokaiwado N et al. Age-dependent histopathological findings in the prostate of probasin/SV40 T antigen transgenic rats: lack of influence of carcinogen or testosterone treatment. Cancer Sci 2003; 94: 153–157.
Asamoto M, Hokaiwado N, Cho YM, Shirai T . Effects of genetic background on prostate and taste bud carcinogenesis due to SV40 T antigen expression under probasin gene promoter control. Carcinogenesis 2002; 23: 463–467.
Shirai T, Iwasaki S, Masui T, Mori T, Kato T, Ito N . Enhancing effect of cadmium on rat ventral prostate carcinogenesis induced by 3,2′-dimethyl-4-aminobiphenyl. Jpn J Cancer Res 1993; 84: 1023–1030.
Shirai T, Imaida K, Masui T, Iwasaki S, Mori T, Kato T et al. Effects of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone and estrogen on 3,2′-dimethyl-4-aminobiphenyl-induced rat prostate carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer 1994; 57: 224–228.
Shirai T, Tamano S, Sano M, Imaida K, Hagiwara A, Futakuchi M et al. Site-specific effects of testosterone propionate on the prostate of rat pretreated with 3,2′-dimethyl-4-aminobiphenyl: dose-dependent induction of invasive carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res 1995; 86: 645–648.
Shirai T, Fukushima S, Ikawa E, Tagawa Y, Ito N . Induction of prostate carcinoma in situ at high incidence in F344 rats by a combination of 3,2′-dimethyl-4-aminobiphenyl and ethinyl estradiol. Cancer Res 1986; 46: 6423–6426.
Kawabe M, Shibata MA, Sano M, Takesada Y, Tamano S, Ito N et al. Decrease of prostaglandin E2 and 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine labeling but not prostate tumor development by indomethacin treatment of rats given 3,2′-dimethyl-4-aminobiphenyl and testosterone propionate. Jpn J Cancer Res 1997; 88: 350–355.
Miyata E, Kawabe M, Sano M, Takesada Y, Takahashi S, Shirai T . Effects of tamoxifen, an antiestrogen, on rat prostate carcinogenesis by 3,2′-dimethyl-4-aminobiphenyl and testosterone do not support an estrogen role in testosterone promotion. Prostate 1997; 31: 9–13.
Cui L, Mori T, Takahashi S, Imaida K, Akagi K, Yada H et al. Slight promotion effects of intermittent administration of testosterone propionate and/or diethylstilbestrol on 3,2′-dimethyl-4-aminobiphenyl- initiated rat prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 1998; 122: 195–199.
Tsukamoto S, Akaza H, Onozawa M, Shirai T, Ideyama Y . A five-alpha reductase inhibitor or an antiandrogen prevents the progression of microscopic prostate carcinoma to macroscopic carcinoma in rats. Cancer 1998; 82: 531–537.
Bosland MC . Use of animal models in defining efficacy of chemoprevention agents against prostate cancer. Eur Urol 1999; 35: 459–463.
Kasper S, Smith Jr JA . Genetically modified mice and their use in developing therapeutic strategies for prostate cancer. J Urol 2004; 172: 12–19.
Shappell SB, Thomas GV, Roberts RL, Herbert R, Ittmann MM, Rubin MA et al. Prostate pathology of genetically engineered mice: definitions and classification. The concensus report from the Bar Harbor Meeting of the Mouse Models of Human Cancer Consortium Prostate Pathology Committee. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 2270–2305.
Gingrich JR, Barrios RJ, Morton RA, Boyce BF, DeMayo FJ, Finegold MJ et al. Metastatic prostate cancer in a transgenic mouse. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 4096–4102.
Gingrich JR, Barrios RJ, Kattan MW, Nahm HS, Finegold MJ, Greenberg NM . Androgen-independent prostate cancer progression in the TRAMP model. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 4687–4691.
Esmat AY, Refaie FM, Shaheen MH, Said MM . Chemoprevention of prostate carcinogenesis by DFMO and/or finasteride treatment in male Wistar rats. Tumori 2002; 88: 513–521.
Thompson IM, Goodman PJ, Tangen CM, Lucia MS, Miller GJ, Ford LG et al. The influence of finasteride on the development of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 215–224.
Bostwick DG, Qian J, Civantos F, Roehrborn CG, Montironi R . Does finasteride alter the pathology of the prostate and cancer grading? Clin Prostate Cancer 2004; 2: 228–235.
Marchetti B, Labrie F . Characteristics of flutamide action on prostatic and testicular functions in the rat. J Steroid Biochem 1988; 29: 691–698.
DeCaprio JA, Ludlow JW, Figge J, Shew JY, Huang CM, Lee WH et al. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell 1988; 54: 275–283.
Lane DP, Crawford LV . T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature 1979; 278: 261–263.
Linzer DI, Levine AJ . Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell 1979; 17: 43–52.
Levine AJ, Momand J, Finlay CA . The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature 1991; 351: 453–456.
Bookstein R, Rio P, Madreperla SA, Hong F, Allred C, Grizzle WE et al. Promoter deletion and loss of retinoblastoma gene expression in human prostate carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 7762–7766.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in Aid for cancer research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan, and a grant from the Society for Promotion of Toxicological Pathology in Nagoya, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, YM., Takahashi, S., Asamoto, M. et al. Suppressive effects of antiandrogens, finasteride and flutamide on development of prostatic lesions in a transgenic rat model. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 10, 378–383 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500971
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500971