Abstract
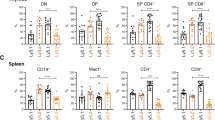
Overexpression of the transcriptional regulator Myc is thought to be the cause or a contributing factor in the development of a large number of human lymphomas and certain other cancers. Apoptotic cell death constitutes a tumor suppressive mechanism, particularly in the context of Myc overexpression. Accordingly, lymphoma development in Eμ-Myc transgenic mice, which mimic the Myc/IgH chromosomal translocation that causes Burkitt lymphoma, is accelerated by concomitant overexpression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members or loss of pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins, such as Bim. Bim binds with high affinity to all pro-survival Bcl-2-like proteins and can also interact with Bax/Bak, but it remains unclear which of these interactions are critical for its tumor suppressive function. We have previously generated knock-in mutant mice in which the BH3 region of Bim has been exchanged with that for Bad, Noxa or Puma so that it can only bind to select pro-survival Bcl-2-like proteins: BimBad binding to Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Bcl-w, but not Mcl-1 or A1; BimNoxa binding only to Mcl-1 and A1 and as a control, BimPuma, which can still bind all pro-survival Bcl-2-like proteins. We have now inter-crossed these Bim mutant mice with Eμ-Myc transgenic mice, and found that both the BimBad and the BimNoxa mutations but not the BimPuma mutation greatly accelerate Myc-induced lymphoma development and increase leukemic burden. These results demonstrate that for optimal tumor suppressive activity, Bim must be able to interact with all and not just select pro-survival Bcl-2 family members.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S et al. (1985). The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature 318: 533–538.
Anderton E, Yee J, Smith P, Crook T, White RE, Allday MJ . (2008). Two Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oncoproteins cooperate to repress expression of the proapoptotic tumour-suppressor Bim: clues to the pathogenesis of Burkitt's lymphoma. Oncogene 27: 421–433.
Bouillet P, Metcalf D, Huang DCS, Tarlinton DM, Kay TWH, Köntgen F et al. (1999). Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science 286: 1735–1738.
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG et al. (2005). Differential targeting of pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell 17: 393–403.
Chipuk JE, Green DR . (2008). How do BCL-2 proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization? Trends Cell Biol 18: 157–164.
Egle A, Harris AW, Bouillet P, Cory S . (2004). Bim is a suppressor of Myc-induced mouse B cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 6164–6169.
Frenzel A, Labi V, Chmelewskij W, Ploner C, Geley S, Fiegl H et al. (2010). Suppression of B-cell lymphomagenesis by the BH3-only proteins Bmf and Bad. Blood 115: 995–1005.
Garrison SP, Jeffers JR, Yang C, Nilsson JA, Hall MA, Rehg JE et al. (2008). Selection against PUMA gene expression in Myc-driven B-cell lymphomagenesis. Mol Cell Biol 28: 5391–5402.
Hemann MT, Zilfou JT, Zhao Z, Burgess DJ, Hannon GJ, Lowe SW . (2004). Suppression of tumorigenesis by the p53 target PUMA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 9333–9338.
Kelly PN, Puthalakath H, Adams JM, Strasser A . (2007). Endogenous bcl-2 is not required for the development of Eμ-myc-induced B-cell lymphoma. Blood 109: 4907–4913.
Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Chipuk JE, Bonzon C, Sullivan BA, Green DR et al. (2005). BH3 domains of BH3-only proteins differentially regulate bax-mediated mitochondrial membrane permeabilization both directly and indirectly. Mol Cell 17: 525–535.
Langdon WY, Harris AW, Cory S, Adams JM . (1986). The c-myc oncogene perturbs B lymphocyte development in Eμ-myc transgenic mice. Cell 47: 11–18.
Letai A, Sorcinelli MD, Beard C, Korsmeyer SJ . (2004). Antiapoptotic BCL-2 is required for maintenance of a model leukemia. Cancer Cell 6: 241–249.
Merino D, Giam M, Hughes PD, Siggs OM, Heger K, O'Reilly LA et al. (2009). The role of BH3-only protein Bim extends beyond inhibiting Bcl-2-like prosurvival proteins. J Cell Biol 186: 355–362.
Michalak EM, Jansen ES, Happo L, Cragg MS, Tai L, Smyth GK et al. (2009). Puma and to a lesser extent Noxa are suppressors of Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. Cell Death Differ 16: 684–696.
Pelengaris S, Khan M, Evan G . (2002). c-MYC: more than just a matter of life and death. Nature Reviews Cancer 2: 764–776.
Strasser A, Cory S, Adams JM . (2011). Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J 30: 3667–3683.
Strasser A, Elefanty AG, Harris AW, Cory S . (1996). Progenitor tumours from Em-bcl-2-myc transgenic mice have lymphomyeloid differentiation potential and reveal developmental differences in cell survival. EMBO J 15: 3823–3834.
Strasser A, Harris AW, Bath ML, Cory S . (1990). Novel primitive lymphoid tumours induced in transgenic mice by cooperation between myc and bcl-2. Nature 348: 331–333.
Tagawa H, Karnan S, Suzuki R, Matsuo K, Zhang X, Ota A et al. (2005). Genome-wide array-based CGH for mantle cell lymphoma: identification of homozygous deletions of the proapoptotic gene BIM. Oncogene 24: 1348–1358.
Xiang Z, Luo H, Payton JE, Cain J, Ley TJ, Opferman JT et al. (2010). Mcl1 haploinsufficiency protects mice from Myc-induced acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest 120: 2109–2118.
Youle RJ, Strasser A . (2008). The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9: 47–59.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mikara Robati and Owen Siggs for help with experiments; Jerry Adams, Suzanne Cory, Clare Scott and Cyril Clybouw for insightful discussions; and Eμ-Myc mice, Bruno Helbert and Carley Young for mouse genotyping; Emily Sutherland and Giovanni Siciliano for mouse husbandry; and Jason Corbin for blood sample analysis. This work was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (program grant 461221, Australia Fellowship (AS) and Career Development Award (PB)), the National Cancer Institute (CA43540), the Australian Research Council (DM), the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (LLS Specialized Center of Research grant 7015) and operational infrastructure grants through the Australian Government (IRISS) and the Victorian State Government (OIS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mérino, D., Strasser, A. & Bouillet, P. Bim must be able to engage all pro-survival Bcl-2 family members for efficient tumor suppression. Oncogene 31, 3392–3396 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.508
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.508