Abstract
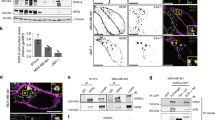
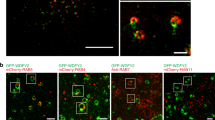
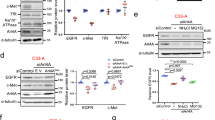
The aspartic protease cathepsin-D (cath-D) is a marker of poor prognosis in breast cancer that is overexpressed and hypersecreted by human breast cancer cells. Secreted pro-cath-D binds to the extracellular domain of the β-chain of the LDL receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1) in fibroblasts. The LRP1 receptor has an 85-kDa transmembrane β-chain and a noncovalently attached 515-kDa extracellular α-chain. LRP1 acts by (1) internalizing many ligands via its α-chain, (2) activating signaling pathways by phosphorylating the LRP1β-chain tyrosine and (3) modulating gene transcription by regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP) of its β-chain. LRP1 RIP involves two cleavages: the first liberates the LRP1 ectodomain to give a membrane-associated form, LRP1β-CTF, and the second generates the LRP1β-intracellular domain, LRP1β-ICD, that modulates gene transcription. Here, we investigated the endocytosis of pro-cath-D by LRP1 and the effect of pro-cath-D/LRP1β interaction on LRP1β tyrosine phosphorylation and/or LRP1β RIP. Our results indicate that pro-cath-D was partially endocytosed by LRP1 in fibroblasts. However, pro-cath-D and ectopic cath-D did not stimulate phosphorylation of the LRP1β-chain tyrosine. Interestingly, ectopic cath-D and its catalytically inactive D231Ncath-D, and pro-D231Ncath-D all significantly inhibited LRP1 RIP by preventing LRP1β-CTF production. Thus, cath-D inhibits LRP1 RIP independently of its catalytic activity by blocking the first cleavage. As cath-D triggers fibroblast outgrowth by LRP1, we propose that cath-D modulates the growth of fibroblasts by inhibiting LRP1 RIP in the breast tumor microenvironment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes H, Ackermann EJ, van der Geer P . (2003). v-Src induces Shc binding to tyrosine 63 in the cytoplasmic domain of the LDL receptor-related protein 1. Oncogene 22: 3589–3597.
Barnes H, Larsen B, Tyers M, van Der Geer P . (2001). Tyrosine-phosphorylated low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (Lrp1) associates with the adaptor protein SHC in SRC-transformed cells. J Biol Chem 276: 19119–19125.
Beaujouin M, Prebois C, Derocq D, Laurent-Matha V, Masson O, Pattingre S et al. (2010). Pro-cathepsin D interacts with the extracellular domain of the beta chain of LRP1 and promotes LRP1-dependent fibroblast outgrowth. J Cell Sci 123: 3336–3346.
Berchem G, Glondu M, Gleizes M, Brouillet JP, Vignon F, Garcia M et al. (2002). Cathepsin-D affects multiple tumor progression steps in vivo: proliferation, angiogenesis and apoptosis. Oncogene 21: 5951–5955.
Bidere N, Lorenzo HK, Carmona S, Laforge M, Harper F, Dumont C et al. (2003). Cathepsin D triggers Bax activation, resulting in selective apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) relocation in T lymphocytes entering the early commitment phase to apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278: 31401–31411.
Boucher P, Gotthardt M . (2004). LRP and PDGF signaling: a pathway to atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc Med 14: 55–60.
Boucher P, Liu P, Gotthardt M, Hiesberger T, Anderson RG, Herz J . (2002). Platelet-derived growth factor mediates tyrosine phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in caveolae. J Biol Chem 277: 15507–15513.
Capony F, Braulke T, Rougeot C, Roux S, Montcourrier P, Rochefort H . (1994). Specific mannose-6-phosphate receptor-independent sorting of pro-cathepsin D in breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res 215: 154–163.
Capony F, Morisset M, Barrett AJ, Capony JP, Broquet P, Vignon F et al. (1987). Phosphorylation, glycosylation, and proteolytic activity of the 52-kD estrogen-induced protein secreted by MCF7 cells. J Cell Biol 104: 253–262.
Capony F, Rougeot C, Montcourrier P, Cavailles V, Salazar G, Rochefort H . (1989). Increased secretion, altered processing, and glycosylation of pro-cathepsin D in human mammary cancer cells. Cancer Res 49: 3904–3909.
De Strooper B, Annaert W, Cupers P, Saftig P, Craessaerts K, Mumm JS et al. (1999). A presenilin-1-dependent gamma-secretase-like protease mediates release of Notch intracellular domain. Nature 398: 518–522.
De Strooper B, Saftig P, Craessaerts K, Vanderstichele H, Guhde G, Annaert W et al. (1998). Deficiency of presenilin-1 inhibits the normal cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. Nature 391: 387–390.
Emonard H, Bellon G, de Diesbach P, Mettlen M, Hornebeck W, Courtoy PJ . (2005). Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity by the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). A new function for an ″old friend″. Biochimie 87: 369–376.
Fears CY, Grammer JR, Stewart Jr JE, Annis DS, Mosher DF, Bornstein P et al. (2005). Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein contributes to the antiangiogenic activity of thrombospondin-2 in a murine glioma model. Cancer Res 65: 9338–9346.
Ferrandina G, Scambia G, Bardelli F, Benedetti Panici P, Mancuso S, Messori A . (1997). Relationship between cathepsin-D content and disease-free survival in node-negative breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer 76: 661–666.
Foekens JA, Dall P, Klijn JG, Skroch-Angel P, Claassen CJ, Look MP et al. (1999). Prognostic value of CD44 variant expression in primary breast cancer. Int J Cancer 84: 209–215.
Fusek M, Vetvicka V . (1994). Mitogenic function of human procathepsin D: the role of the propeptide. Biochem J 303 (Part 3): 775–780.
Gieselmann V, Hasilik A, von Figura K . (1985). Processing of human cathepsin D in lysosomes in vitro. J Biol Chem 260: 3215–3220.
Glondu M, Coopman P, Laurent-Matha V, Garcia M, Rochefort H, Liaudet-Coopman E . (2001). A mutated cathepsin-D devoid of its catalytic activity stimulates the growth of cancer cells. Oncogene 20: 6920–6929.
Glondu M, Liaudet-Coopman E, Derocq D, Platet N, Rochefort H, Garcia M . (2002). Down-regulation of cathepsin-D expression by antisense gene transfer inhibits tumor growth and experimental lung metastasis of human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 21: 5127–5134.
Gonias SL, Wu L, Salicioni AM . (2004). Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein: regulation of the plasma membrane proteome. Thromb Haemost 91: 1056–1064.
Hass MR, Sato C, Kopan R, Zhao G . (2009). Presenilin: RIP and beyond. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20: 201–210.
Herz J, Strickland DK . (2001). LRP: a multifunctional scavenger and signaling receptor. J Clin Invest 108: 779–784.
Hu K, Yang J, Tanaka S, Gonias SL, Mars WM, Liu Y . (2006). Tissue-type plasminogen activator acts as a cytokine that triggers intracellular signal transduction and induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression. J Biol Chem 281: 2120–2127.
Hu L, Roth JM, Brooks P, Luty J, Karpatkin S . (2008). Thrombin up-regulates cathepsin D which enhances angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis. Cancer Res 68: 4666–4673.
Kinoshita A, Shah T, Tangredi MM, Strickland DK, Hyman BT . (2003). The intracellular domain of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein modulates transactivation mediated by amyloid precursor protein and Fe65. J Biol Chem 278: 41182–41188.
Laurent-Matha V, Lucas A, Huttler S, Sandhoff K, Garcia M, Rochefort H . (2002). Procathepsin D interacts with prosaposin in cancer cells but its internalization is not mediated by LDL receptor-related protein. Exp Cell Res 277: 210–219.
Laurent-Matha V, Maruani-Herrmann S, Prebois C, Beaujouin M, Glondu M, Noel A et al. (2005). Catalytically inactive human cathepsin D triggers fibroblast invasive growth. J Cell Biol 168: 489–499.
Li Y, Lu W, Bu G . (2003). Essential role of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in vascular smooth muscle cell migration. FEBS Lett 555: 346–350.
Liaudet-Coopman E, Beaujouin M, Derocq D, Garcia M, Glondu-Lassis M, Laurent-Matha V et al. (2006). Cathepsin D: newly discovered functions of a long-standing aspartic protease in cancer and apoptosis. Cancer Lett 237: 167–179.
Lillis AP, Mikhailenko I, Strickland DK . (2005). Beyond endocytosis: LRP function in cell migration, proliferation and vascular permeability. J Thromb Haemost 3: 1884–1893.
Liu CX, Ranganathan S, Robinson S, Strickland DK . (2007). gamma-Secretase-mediated release of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1B intracellular domain suppresses anchorage-independent growth of neuroglioma cells. J Biol Chem 282: 7504–7511.
Liu Q, Zhang J, Tran H, Verbeek MM, Reiss K, Estus S et al. (2009). LRP1 shedding in human brain: roles of ADAM10 and ADAM17. Mol Neurodegener 4: 17.
Loukinova E, Ranganathan S, Kuznetsov S, Gorlatova N, Migliorini MM, Loukinov D et al. (2002). Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). Evidence for integrated co-receptor function between LRP and the PDGF. J Biol Chem 277: 15499–15506.
May P, Reddy YK, Herz J . (2002). Proteolytic processing of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates regulated release of its intracellular domain. J Biol Chem 277: 18736–18743.
May P, Woldt E, Matz RL, Boucher P . (2007). The LDL receptor-related protein (LRP) family: an old family of proteins with new physiological functions. Ann Med 39: 219–228.
Mi K, Johnson GV . (2007). Regulated proteolytic processing of LRP6 results in release of its intracellular domain. J Neurochem 101: 517–529.
Montel V, Gaultier A, Lester RD, Campana WM, Gonias SL . (2007). The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein regulates cancer cell survival and metastasis development. Cancer Res 67: 9817–9824.
Newton CS, Loukinova E, Mikhailenko I, Ranganathan S, Gao Y, Haudenschild C et al. (2005). Platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta (PDGFR-beta) activation promotes its association with the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). Evidence for co-receptor function. J Biol Chem 280: 27872–27878.
Ohri SS, Vashishta A, Proctor M, Fusek M, Vetvicka V . (2007). Depletion of procathepsin D gene expression by RNA interference: a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 6: 1081–1087.
Ohri SS, Vashishta A, Proctor M, Fusek M, Vetvicka V . (2008). The propeptide of cathepsin D increases proliferation, invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol 32: 491–498.
Polavarapu R, An J, Zhang C, Yepes M . (2008). Regulated intramembrane proteolysis of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates ischemic cell death. Am J Pathol 172: 1355–1362.
Quinn KA, Grimsley PG, Dai YP, Tapner M, Chesterman CN, Owensby DA . (1997). Soluble low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) circulates in human plasma. J Biol Chem 272: 23946–23951.
Quinn KA, Pye VJ, Dai YP, Chesterman CN, Owensby DA . (1999). Characterization of the soluble form of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). Exp Cell Res 251: 433–441.
Rijnboutt S, Kal AJ, Geuze HJ, Aerts H, Strous GJ . (1991). Mannose 6-phosphate-independent targeting of cathepsin D to lysosomes in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem 266: 23586–23592.
Rochefort H, Liaudet-Coopman E . (1999). Cathepsin D in cancer metastasis: a protease and a ligand. Apmis 107: 86–95.
Rodriguez J, Vazquez J, Corte MD, Lamelas M, Bongera M, Corte MG et al. (2005). Clinical significance of cathepsin D concentration in tumor cytosol of primary breast cancer. Int J Biol Markers 20: 103–111.
Rozanov DV, Hahn-Dantona E, Strickland DK, Strongin AY . (2004). The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein LRP is regulated by membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) proteolysis in malignant cells. J Biol Chem 279: 4260–4268.
Selvais C, D'Auria L, Tyteca D, Perrot G, Lemoine P, Troeberg L et al. (2011). Cell cholesterol modulates metalloproteinase-dependent shedding of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1) and clearance function. FASEB J 25: 2770–2781.
Selvais C, Gaide Chevronnay HP, Lemoine P, Dedieu S, Henriet P, Courtoy PJ et al. (2009). Metalloproteinase-dependent shedding of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 ectodomain decreases endocytic clearance of endometrial matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 at menstruation. Endocrinology 150: 3792–3799.
Strickland DK, Ranganathan S . (2003). Diverse role of LDL receptor-related protein in the clearance of proteases and in signaling. J Thromb Haemost 1: 1663–1670.
Vashishta A, Ohri SS, Proctor M, Fusek M, Vetvicka V . (2007). Ribozyme-targeting procathepsin D and its effect on invasion and growth of breast cancer cells: an implication in breast cancer therapy. Int J Oncol 30: 1223–1230.
Vetvicka V, Vektvickova J, Fusek M . (1994). Effect of human procathepsin D on proliferation of human cell lines. Cancer Lett 79: 131–135.
Vignon F, Capony F, Chambon M, Freiss G, Garcia M, Rochefort H . (1986). Autocrine growth stimulation of the MCF 7 breast cancer cells by the estrogen-regulated 52K protein. Endocrinology 118: 1537–1545.
von Arnim CA, Kinoshita A, Peltan ID, Tangredi MM, Herl L, Lee BM et al. (2005). The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) is a novel beta-secretase (BACE1) substrate. J Biol Chem 280: 17777–17785.
Wu L, Gonias SL . (2005). The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 associates transiently with lipid rafts. J Cell Biochem 96: 1021–1033.
Yang M, Huang H, Li J, Li D, Wang H . (2004). Tyrosine phosphorylation of the LDL receptor-related protein (LRP) and activation of the ERK pathway are required for connective tissue growth factor to potentiate myofibroblast differentiation. Faseb J 18: 1920–1921.
Zhang H, Links PH, Ngsee JK, Tran K, Cui Z, Ko KW et al. (2004). Localization of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 to caveolae in 3T3-L1 adipocytes in response to insulin treatment. J Biol Chem 279: 2221–2230.
Zurhove K, Nakajima C, Herz J, Bock HH, May P . (2008). Gamma-secretase limits the inflammatory response through the processing of LRP1. Sci Signal 1: ra15.
Acknowledgements
We thank Françoise Berthet and Nadia Kerdjadj for secretarial assistance, and Jean-Yves Cance for the photographs. We also thank Vincent Cavaillès for pertinent suggestions for the gene reporter experiments, Hervé Emonard for helpful discussions and Owen Parkes for English corrections. This work was supported by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, University of Montpellier I, ANR Jeunes Chercheuses, Jeunes Chercheurs and the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer; the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer provided a fellowship for Mélanie Beaujouin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derocq, D., Prébois, C., Beaujouin, M. et al. Cathepsin D is partly endocytosed by the LRP1 receptor and inhibits LRP1-regulated intramembrane proteolysis. Oncogene 31, 3202–3212 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.501
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.501
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Immunotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer with cathepsin D-targeting antibodies
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (2019)
-
Endothelial LRP1 – A Potential Target for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
Pharmaceutical Research (2017)