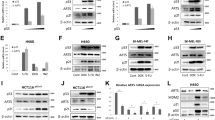
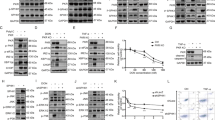
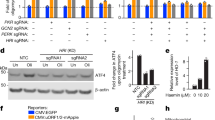
Abstract
The serine/threonine kinase, PIM1, is involved in promoting cell survival in part by phosphorylation and inhibition of proapoptotic proteins. Apoptosis signaling kinase 1 (ASK1), a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase, is involved in the so-called stress-activated pathways that contribute to apoptotic cell death. Here we show that PIM1 phosphorylates ASK1 specifically on serine residue 83 (Ser83) both in vitro and in vivo and that PIM1 binds to ASK1 in cells by co-immunoprecipitation. Using H1299 cells, our results further demonstrate that PIM1 phosphorylation of ASK1 decreases its kinase activity induced by oxidative stress. PIM1 phosphorylation of ASK1 on Ser83 inhibited ASK1-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation as well as p38 kinase phosphorylation. Under H2O2-induced stress conditions that normally lead to apoptosis, these phosphorylation events were associated with inhibition of caspase-3 activation and resulted in reduced cell death. Moreover, knockdown of PIM1 in H1299 cells decreased phosphorylation of endogenous Ser83 of ASK1 and was associated with a decrease in cell viability after H2O2 treatment. Taken together, these data reveal a novel mechanism by which PIM1 promotes cell survival that involves negative regulation of the stress-activated kinase, ASK1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho TL, Sandholm J, Peltola KJ, Mankonen HP, Lilly M, Koskinen PJ . (2004). Pim-1 kinase promotes inactivation of the pro-apoptotic Bad protein by phosphorylating it on the Ser112 gatekeeper site. FEBS Lett 571: 43–49.
Bachmann M, Hennemann H, Xing PX, Hoffmann I, Moroy T . (2004). The oncogenic serine/threonine kinase Pim-1 phosphorylates and inhibits the activity of Cdc25C-associated kinase 1 (C-TAK1): a novel role for Pim-1 at the G2/M cell cycle checkpoint. J Biol Chem 279: 48319–48328.
Chang HY, Nishitoh H, Yang X, Ichijo H, Baltimore D . (1998). Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by the adapter protein Daxx. Science 281: 1860–1863.
Chen Z, Seimiya H, Naito M, Mashima T, Kizaki A, Dan S et al. (1999). ASK1 mediates apoptotic cell death induced by genotoxic stress. Oncogene 18: 173–180.
Cross JV, Templeton DJ . (2006). Regulation of signal transduction through protein cysteine oxidation. Antioxid Redox Signal 8: 1819–1827.
Cuypers HT, Selten G, Quint W, Zijlstra M, Maandag ER, Boelens W et al. (1984). Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell 37: 141–150.
Engelman JA, Mukohara T, Zejnullahu K, Lifshits E, Borras AM, Gale CM et al. (2006). Allelic dilution obscures detection of a biologically significant resistance mutation in EGFR-amplified lung cancer. J Clin Invest 116: 2695–2706.
Friedmann M, Nissen MS, Hoover DS, Reeves R, Magnuson NS . (1992). Characterization of the proto-oncogene pim-1: kinase activity and substrate recognition sequence. Arch Biochem Biophys 298: 594–601.
Fujii K, Goldman EH, Park HR, Zhang L, Chen J, Fu H . (2004). Negative control of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 through phosphorylation of Ser-1034. Oncogene 23: 5099–5104.
Galvan V, Logvinova A, Sperandio S, Ichijo H, Bredesen DE . (2003). Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) signaling inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1). J Biol Chem 278: 13325–13332.
Goldman EH, Chen L, Fu H . (2004). Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 by reactive oxygen species through dephosphorylation at serine 967 and 14-3-3 dissociation. J Biol Chem 279: 10442–10449.
Hatai T, Matsuzawa A, Inoshita S, Mochida Y, Kuroda T, Sakamaki K et al (2000). Execution of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)-induced apoptosis by the mitochondria-dependent caspase activation. J Biol Chem 275: 26576–26581.
Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, ten Dijke P, Saitoh M, Moriguchi T et al. (1997). Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science 275: 90–94.
Karin M, Delhase M . (1998). JNK or IKK, AP-1 or NF-kappaB, which are the targets for MEK kinase 1 action? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 9067–9069.
Katakami N, Kaneto H, Hao H, Umayahara Y, Fujitani Y, Sakamoto K et al. (2004). Role of pim-1 in smooth muscle cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 279: 54742–54749.
Kim AH, Khursigara G, Sun X, Franke TF, Chao MV . (2001). Akt phosphorylates and negatively regulates apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol 21: 893–901.
Kim SD, Moon CK, Eun SY, Ryu PD, Jo SA . (2005). Identification of ASK1, MKK4, JNK, c-Jun, and caspase-3 as a signaling cascade involved in cadmium-induced neuronal cell apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 328: 326–334.
Kumar A, Mandiyan V, Suzuki Y, Zhang C, Rice J, Tsai J et al. (2005). Crystal structures of proto-oncogene kinase Pim1: a target of aberrant somatic hypermutations in diffuse large cell lymphoma. J Mol Biol 348: 183–193.
Liu H, Nishitoh H, Ichijo H, Kyriakis JM . (2000). Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 requires prior dissociation of the ASK1 inhibitor thioredoxin. Mol Cell Biol 20: 2198–2208.
Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H . (2001). Molecular mechanisms of the decision between life and death: regulation of apoptosis by apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. J Biochem 130: 1–8.
Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H . (2008). Redox control of cell fate by MAP kinase: physiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase pathway in stress signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780: 1325–1336.
Morishita D, Katayama R, Sekimizu K, Tsuruo T, Fujita N . (2008). Pim kinases promote cell cycle progression by phosphorylating and down-regulating p27Kip1 at the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Cancer Res 68: 5076–5085.
Morita K, Saitoh M, Tobiume K, Matsuura H, Enomoto S, Nishitoh H et al. (2001). Negative feedback regulation of ASK1 by protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) in response to oxidative stress. EMBO J 20: 6028–6036.
Nishitoh H, Matsuzawa A, Tobiume K, Saegusa K, Takeda K, Inoue K et al. (2002). ASK1 is essential for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal cell death triggered by expanded polyglutamine repeats. Genes Dev 16: 1345–1355.
Nishitoh H, Saitoh M, Mochida Y, Takeda K, Nakano H, Rothe M et al. (1998). ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2. Mol Cell 2: 389–395.
Peng C, Knebel A, Morrice NA, Li X, Barringer K, Li J et al. (2007). Pim kinase substrate identification and specificity. J Biochem 141: 353–362.
Pircher TJ, Zhao S, Geiger JN, Joneja B, Wojchowski DM . (2000). Pim-1 kinase protects hematopoietic FDC cells from genotoxin-induced death. Oncogene 19: 3684–3692.
Rhee SG . (2006). Cell signaling. H2O2, a necessary evil for cell signaling. Science 312: 1882–1883.
Saitoh M, Nishitoh H, Fujii M, Takeda K, Tobiume K, Sawada Y et al. (1998). Mammalian thioredoxin is a direct inhibitor of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase (ASK) 1. EMBO J 17: 2596–2606.
Shah N, Pang B, Yeoh KG, Thorn S, Chen CS, Lilly MB et al. (2008). Potential roles for the PIM1 kinase in human cancer—a molecular and therapeutic appraisal. Eur J Cancer 44: 2144–2151.
Shay KP, Wang Z, Xing PX, McKenzie IF, Magnuson NS . (2005). Pim-1 kinase stability is regulated by heat shock proteins and the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. Mol Cancer Res 3: 170–181.
Teh BG . (2004). [Pim-1 induced by hypoxia is involved in drug resistance and tumorigenesis of solid tumor cells]. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi 79: 19–26.
Tobiume K, Matsuzawa A, Takahashi T, Nishitoh H, Morita K, Takeda K et al. (2001). ASK1 is required for sustained activations of JNK/p38 MAP kinases and apoptosis. EMBO Rep 2: 222–228.
Wang Z, Bhattacharya N, Weaver M, Petersen K, Meyer M, Gapter L et al. (2001). Pim-1: a serine/threonine kinase with a role in cell survival, proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis. J Vet Sci 2: 167–179.
Xie Y, Xu K, Dai B, Guo Z, Jiang T, Chen H et al. (2006). The 44 kDa Pim-1 kinase directly interacts with tyrosine kinase Etk/BMX and protects human prostate cancer cells from apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic drugs. Oncogene 25: 70–78.
Yan W, Arai A, Aoki M, Ichijo H, Miura O . (2007). ASK1 is activated by arsenic trioxide in leukemic cells through accumulation of reactive oxygen species and may play a negative role in induction of apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 355: 1038–1044.
Zemskova M, Sahakian E, Bashkirova S, Lilly M . (2008). The PIM1 kinase is a critical component of a survival pathway activated by docetaxel and promotes survival of docetaxel-treated prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283: 20635–20644.
Zhang L, Chen J, Fu H . (1999). Suppression of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-induced cell death by 14-3-3 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 8511–8515.
Zhang R, Luo D, Miao R, Bai L, Ge Q, Sessa WC et al. (2005). Hsp90-Akt phosphorylates ASK1 and inhibits ASK1-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 24: 3954–3963.
Zhang Y, Wang Z, Li X, Magnuson NS . (2008). Pim kinase-dependent inhibition of c-Myc degradation. Oncogene 27: 4809–4819.
Zhang Y, Wang Z, Magnuson NS . (2007). Pim-1 kinase-dependent phosphorylation of p21Cip1/WAF1 regulates its stability and cellular localization in H1299 cells. Mol Cancer Res 5: 909–922.
Zou X, Tsutsui T, Ray D, Blomquist JF, Ichijo H, Ucker DS et al. (2001). The cell cycle-regulatory CDC25A phosphatase inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol 21: 4818–4828.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH Grants R01-CA104470 and R01-GM071760. We thank Dr Hidenori Ichijo (Tokyo Medical and Dental University) for providing us the ASK1 constructs (wild type, kinase mutant and deltaN-deleted).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, J., Wang, Z., Reeves, R. et al. PIM1 phosphorylates and negatively regulates ASK1-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 28, 4261–4271 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.276
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.276
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ASK1-K716R reduces neuroinflammation and white matter injury via preserving blood–brain barrier integrity after traumatic brain injury
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2023)
-
Targeting Pim kinases in hematological cancers: molecular and clinical review
Molecular Cancer (2023)
-
The mutational profile of immune surveillance genes in diagnostic and refractory/relapsed DLBCLs
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
Safety profiling of genetically engineered Pim-1 kinase overexpression for oncogenicity risk in human c-kit+ cardiac interstitial cells
Gene Therapy (2019)
-
PIM-1 contributes to the malignancy of pancreatic cancer and displays diagnostic and prognostic value
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2016)