Abstract
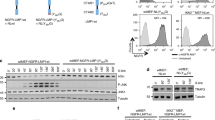
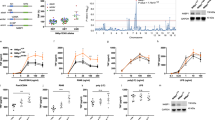
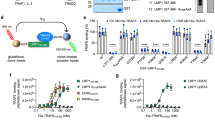
Marginal zone mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) B-cell lymphoma is the most common extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The t(11;18)(q21;q21) translocation occurs frequently in MALT lymphomas and creates a chimeric NF-κB-activating protein containing the baculoviral IAP repeat (BIR) domains of c-IAP2 (inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2) fused with portions of the MALT1 protein. The BIR1 domain of c-IAP2 interacts directly with TRAF2 (TNFα-receptor-associated factor–2), but its role in NF-κB activation is still unclear. Here, we investigated the role of TRAF2 in c-IAP2/MALT1-induced NF-κB activation. We show the BIR1 domain of c-IAP2 is essential for NF-κB activation, whereas BIR2 and BIR3 domains are not. Studies of c-IAP2/MALT1 BIR1 mutant (E47A/R48A) that fails to activate NF-κB showed loss of TRAF2 binding, but retention of TRAF6 binding, suggesting that interaction of c-IAP2/MALT1 with TRAF6 is insufficient for NF-κB induction. In addition, a dominant-negative TRAF2 mutant or downregulation of TRAF2 achieved by small interfering RNA inhibited NF-κB activation by c-IAP2/MALT1 showing that TRAF2 is indispensable. Comparisons of the bioactivity of intact c-IAP2/MALT1 oncoprotein and BIR1 E47A/R48A c-IAP2/MALT1 mutant that cannot bind TRAF2 in a lymphoid cell line provided evidence that TRAF2 interaction is critical for c-IAP2/MALT1-mediated increases in the NF-κB activity, increased expression of endogenous NF-κB target genes (c-FLIP, TRAF1), and resistance to apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi T, Motegi M, Tamura A, Suzuki R, Hosokawa Y, Suzuki H et al. (1999). A novel gene, MALT1 at 18q21, is involved in t(11;18) (q21;q21) found in low-grade B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Oncogene 18: 5785–5794.
Akira S, Takeda K . (2004). Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 499–511.
Chu ZL, McKinsey TA, Liu L, Gentry JJ, Malim MH, Ballard DW . (1997). Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-κB control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 10057–10062.
Dierlamm JM, Baens I, Wlodarska M, Stefanova-Ouzounova M, Hernandez JM, Hossfeld DK et al. (1999). The apoptosis inhibitor gene API2 and a novel 18q gene, MLT, are recurrently rearranged in the t(11;18)(q21;q21) associated with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas. Blood 93: 3601–3609.
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS, Scott FL . (2006). Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: why XIAP is the black sheep of the family. EMBO Rep 7: 988–994.
Habelhah H, Takahashi S, Cho SG, Kadoya T, Watanabe T, Ronai Z . (2004). Ubiquitination and translocation of TRAF2 is required for activation of JNK but not of p38 or NF-κB. EMBO 23: 322–332.
Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Scheurich P, Wajant H . (2001). NF-κB inducers upregulate cFLIP, a cycloheximide-sensitive inhibitor of death receptor signaling. Mol Cell Biol 21: 3964–3973.
Lucas PC, Yonezumi M, Inohara N, McAllister-Lucas LM, Abazeed ME, Chen FF et al. (2001). Bcl10 and MALT1, independent targets of chromosomal translocation in malt lymphoma, cooperate in a novel NF-êB signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 276: 19012–19019.
Lucas PC, Kuffa P, Gu S, Kohrt D, Kim DS, Siu K et al. (2007). A dual role for the API2 moiety in API2-MALT1-dependent NF-κB activation: heterotypic oligomerization and TRAF2 recruitment. Oncogene 26: 5643–5654.
Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos K, Tschopp J . (2001). NF-κB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5299–5305.
Micheau O, Tschopp J . (2003). Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 114: 181–190.
Morgan J, Yin Y, Borowsky A, Kuo F, Nourmand N, Koontz JI et al. (1999). Breakpoints of the t(11;18)(q21;q21) in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma lie within or near the previously undescribed gene MALT1 in chromosome 18. Cancer Res 59: 6205–6213.
Noels H, van Loo G, Hagens S, Broeckx V, Beyaert R, Marynen P et al. (2007). A Novel TRAF6 binding site in MALT1 defines distinct mechanisms of NF-κB activation by API2MALT1 fusions. J Biol Chem 282: 10180–10189.
Rothe M, Wong SC, Henzel WJ, Goeddel DV . (1994). A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 78: 681−–6692.
Rothe M, Pan MG, Henzel WJ, Ayres TM, Goeddel DV . (1995). The TNFR2–TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Cell 83: 1243–1252.
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS . (2002). IAP proteins: blocking the road to death's door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 401–410.
Schimmer AD, Dalili S, Batey RA, Riedl SJ . (2006). Targeting XIAP for the treatment of malignancy. Cell Death Differ 13: 179–188.
Silverman N, Maniatis T . (2001). NF-êB signaling pathways in mammalian and insect innate immunity. Genes Dev 15: 2321–2342.
Streubel B, Lamprecht A, Dierlamm J, Cerroni L, Stolte M, Ott G et al. (2003). T(14;18)(q32;q21) involving IGH and MALT1 is a frequent chromosomal aberration in MALT lymphoma. Blood 101: 2335–2339.
Temesgen S, Welsh K, Lober T, Togo SH, Zapata JM, Reed JC . (2006). Distinct BIR domains of cIAP1 mediate binding to and ubiquitination of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 and second mitochondrial activator of caspases. J Biol Chem 281: 1080–1090.
Thome M . (2004). CARMA1, BCL-10 and MALT1 in lymphocyte development and activation. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 348–359.
Varfolomeev E, Wayson SM, Dixit VM, Fairbrother WJ, Vucic D . (2006). The inhibitor of apoptosis protein fusion c-IAP2MALT1 stimulates NF-êB activation independently of TRAF1 AND TRAF2. J Biol Chem 281: 29022–29029.
Vega F, Medeiros LJ . (2001). Marginal-zone B-cell lymphoma of extranodal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type: molecular genetics provides new insights into pathogenesis. Adv Anat Pathol 8: 313–326.
Zhang Q, Siebert R, Yan M, Hinzmann B, Cui X, Xue L et al. (1999). Inactivating mutations and overexpression of BCL10, a caspase recruitment domain-containing gene, in MALT lymphoma with t(1;14)(p22;q32). Nat Genetics 22: 63–68.
Zhou H, Wertz I, O'Rourke K, Ultsch M, Seshagiri S, Eby M et al. (2004). Bcl10 activates the NF-êB pathway through ubiquitination of NEMO. Nature 427: 167–171.
Zhou H., Du MQ, Dixit VM . (2005). Constitutive NF-êB activation by the t(11;18)(q21;q21) product in MALT lymphoma is linked to deregulated ubiquitin ligase activity. Cancer Cell 7: 425–431.
Zucca E, Bertoni F, Roggero E, Cavalli F . (2000). The gastric marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT type. Blood 96: 410–419.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrison, J., Samuel, T. & Reed, J. TRAF2-binding BIR1 domain of c-IAP2/MALT1 fusion protein is essential for activation of NF-κB. Oncogene 28, 1584–1593 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.17
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.17