Abstract
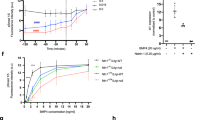
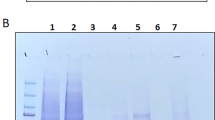
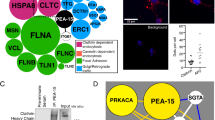
The NRG4 gene is a member of a family of four genes that encode a class of epidermal growth factors. This gene has been reported to express a protein designated here as NRG4A1. We describe here a novel splice variant of the NRG4 gene, NRG4A2, which encodes a C-terminal region containing a predicted type I PDZ-binding peptide. Both NRG4A1 and NRG4A2 were shown to be expressed on the cell surface, as expected by the presence of a predicted transmembrane sequence, and were modified at a single N-linked glycosylation site in the extracellular domain. Significant stabilization of expression of both proteins was seen in the presence of the proteosome inhibitor MG-132 suggesting that they are normally degraded by this system. N-terminal cleavage was inhibited in both isotypes by the broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, galardin (GM 6001). A glycosylated, secreted form of NRG4A1 was detected in the cell medium which showed biological activity in two assays, phosphorylation of the HER4 receptor and stimulation of neurite formation in PC-12 cells stably expressing HER4. Transfection and expression of green fluorescent protein-tagged proteins and immunofluorescent staining with specific anti-peptide antibodies showed that NRG4A1 is localized to membrane ruffles, while NRG4A2 has a more punctate membrane distribution.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buonanno A, Fishbach GD . (2001). Neuregulin and ErbB receptor signaling pathways in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11: 287–296.
Carteron C, Ferrer-Montiel A, Cabedo H . (2006). Characterization of a neural-specific splicing form of the human Neuregulin 3 gene involved in oligodendrocyte survival. J Cell Sci 119: 898–909.
Dunn M, Sinha P, Campbell R, Blackburn E, Levinson N, Rampaul R et al. (2004). Co-expression of neuregulins 1, 2, 3 and 4 in human breast cancer. J Pathol 203: 672–680.
Falls DL . (2003). Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp Cell Res 284: 14–30.
Garrett TP, McKern NM, Lou M, Elleman TC, Adams TE, Lovrecz GO et al. (2002). Crystal structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain bound to transforming growth factor alpha. Cell 110: 763–773.
Harari D, Tzahar E, Romano J, Shelly M, Pierce JH, Andrews GC et al. (1999). Neuregulin-4: a novel growth factor that acts through the ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 18: 2681–2689.
Harris BZ, Lim WA . (2001). Mechanism and role of PDZ domains in signalling complex assembly. J Cell Sci 114: 3219–3231.
Harrison PJ, Law A . (2006). Neuregulin 1 and schizophrenia: genetics, gene expression, and neurobiology. Biol Psychiatry 15: 132–140.
Higashiyama S, Horikawa M, Yamada K, Ichino N, Nakano N, Nakagawa T et al. (1997). A novel brain-derived member of the epidermal growth factor family that interacts with ErbB3 and ErbB4. J Biochem 122: 675–680.
Hobbs SS, Coffing SJ, Le AT, Cameron EM, Williams EE, Andrew M et al. (2002). Neuregulin isoforms exhibit distinct patterns of ErbB family receptor activation. Oncogene 21: 8442–8452.
Montero JC, Yuste L, Diaz-Rodriguez E, Esparis-Ogando A, Pandiella A . (2000). Differential shedding of transmembrane neuregulin isoforms by the tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme. Mol Cell Neurosci 16: 631–648.
Roobol A, Holmes F, Hayes NVL, Baines AJ, Carden MJ . (1995). Cytoplasmic chaperonin complexes enter neurites developing in vitro and differ in subunit composition within single cells. J Cell Sci 108: 1477–1488.
Shirakabe K, Wakatsuki S, Kurisaki T, Fujisawa-Sehara A . (2001). Roles of Meltrin beta/ADAM19 in the processing of Neuregulin. J Biol Chem 276: 9352–9358.
Tastet C, Lescuyer P, Diemer H, Luche S, van Dorsselaer A, Rabilloud T . (2003). A versatile electrophoresis system for the analysis of high- and low-molecular-weight proteins. Electrophoresis 24: 1787–1794.
Vaskovsky A, Lupowitz Z, Erlich S, Pinkas-Kramarski R . (2000). ErbB-4 activation promotes neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 74: 979–987.
Von Heijne G . (2006). Membrane-protein topology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 909–918.
Wakatsuki S, Kurisaki T, Sehara-Fujisawa A . (2004). Lipid rafts identified as locations of ectodomain shedding mediated by Meltrin beta/ADAM19. J Neurochem 89: 119–123.
Yamada K, Ichino N, Nishhii K, Sawada H, Higashiyama S, Ishiguro H et al. (2000). Charaterisation of the human NTAK gene structure and distribution of the isoforms for rat NTAK mRNA. Gene 255: 15–24.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Richard Williamson (Department of Biosciences, University of Kent, Canterbury, Kent, UK) for help with the molecular modelling. NH is supported by Association of International Cancer Research (AICR), Grant no. 20816.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayes, N., Newsam, R., Baines, A. et al. Characterization of the cell membrane-associated products of the Neuregulin 4 gene. Oncogene 27, 715–720 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210689
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210689
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Changes of circulating neuregulin 4 and its relationship with 25-hydroxy vitamin D and other diabetic vascular complications in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2020)
-
The brown fat–enriched secreted factor Nrg4 preserves metabolic homeostasis through attenuation of hepatic lipogenesis
Nature Medicine (2014)
-
The Neuregulin Family of Genes and their Multiple Splice Variants in Breast Cancer
Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia (2008)