Abstract
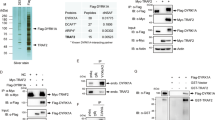
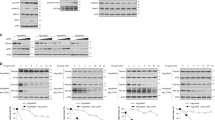
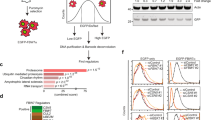
Inactivation of the neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) tumor suppressor gene function has been observed not only in familial schwannomas and other central nervous system tumors, but also in malignant tumors unrelated to the NF2 syndrome, indicating a broader role of NF2 in human tumorigenesis. The NF2-encoded protein Merlin is closely related to the Ezrin-Radixin-Moesin family of membrane/cytoskeleton linker proteins, and has been demonstrated to suppress tumor growth by inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Rac1 activation. Interestingly, serum deprivation has been shown to regulate Merlin at the protein level, however, exactly how such condition affects Merlin remains elusive. In this study, we provide evidence to show that Merlin is regulated in a Roc1-Cullin4A-DDB1-dependent manner. Following serum stimulation, Merlin is recruited to the E3 ligase complex through a direct interaction with the WD40-containing adaptor protein VprBP. Loading of Merlin to the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex resulted in its polyubiquitination, and consequently its proteasome-mediated degradation. Consistently, VprBP depletion abolished the in vivo interaction of Merlin and Roc1-Cullin4A-DDB1, which resulted in Merlin stabilization and inhibited ERK and Rac activation. Together, our data revealed a novel regulatory mechanism for the tumor suppressor function of Merlin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfthan K, Heiska L, Gronholm M, Renkema GH, Carpen O . (2004). Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates Merlin at serine 518 independently of p21-activated kinase and promotes Merlin-Ezrin heterodimerization. J Biol Chem 279: 18559–18566.
Angers S, Li T, Yi X, MacCoss MJ, Moon RT, Zheng N . (2006). Molecular architecture and assembly of the DDB1-CUL4A ubiquitin ligase machinery. Nature 443: 590–593.
Belzile JP, Duisit G, Rougeau N, Mercier J, Finzi A, Cohen EA . (2007). HIV-1 Vpr-mediated G2 arrest involves the DDB1-CUL4A(VPRBP) E3 ubiquitin ligase. PLoS Pathog 3: e85.
Bretscher A, Chambers D, Nguyen R, Reczek D . (2000). ERM-Merlin and EBP50 protein families in plasma membrane organization and function. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16: 113–143.
Den Bakker MA, Riegman PH, Suurmeijer AP, Vissers CJ, Sainio M, Carpen O et al. (2000). Evidence for a cytoskeleton attachment domain at the N-terminus of the NF2 protein. J Neurosci Res 62: 764–771.
Gonzalez-Agosti C, Wiederhold T, Herndon ME, Gusella J, Ramesh V . (1999). Interdomain interaction of Merlin isoforms and its influence on intermolecular binding to NHE-RF. J Biol Chem 274: 34438–34442.
Gutmann DH . (1997). Molecular insights into neurofibromatosis 2. Neurobiol Dis 3: 247–261.
He YJ, McCall CM, Hu J, Zeng Y, Xiong Y . (2006). DDB1 functions as a linker to recruit receptor WD40 proteins to CUL4-ROC1 ubiquitin ligases. Genes Dev 20: 2949–2954.
Higa LA, Wu M, Ye T, Kobayashi R, Sun H, Zhang H . (2006). CUL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase interacts with multiple WD40-repeat proteins and regulates histone methylation. Nat Cell Biol 8: 1277–1283.
Higa LA, Zhang H . (2007). Stealing the spotlight: CUL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase docks WD40-repeat proteins to destroy. Cell Div 2: 5.
Hofer B, Backhaus S, Timmis KN . (1994). The biphenyl/polychlorinated biphenyl-degradation locus (bph) of Pseudomonas sp. LB400 encodes four additional metabolic enzymes. Gene 144: 9–16.
Hrecka K, Gierszewska M, Srivastava S, Kozaczkiewicz L, Swanson SK, Florens L et al. (2007). Lentiviral Vpr usurps Cul4-DDB1[VprBP] E3 ubiquitin ligase to modulate cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 11778–11783.
Jin H, Sperka T, Herrlich P, Morrison H . (2006a). Tumorigenic transformation by CPI-17 through inhibition of a Merlin phosphatase. Nature 442: 576–579.
Jin J, Arias EE, Chen J, Harper JW, Walter JC . (2006b). A family of diverse Cul4-Ddb1-interacting proteins includes Cdt2, which is required for S phase destruction of the replication factor Cdt1. Mol Cell 23: 709–721.
Kissil JL, Wilker EW, Johnson KC, Eckman MS, Yaffe MB, Jacks T . (2003). Merlin, the product of the Nf2 tumor suppressor gene, is an inhibitor of the p21-activated kinase, Pak1. Mol Cell 12: 841–849.
Le Rouzic E, Belaidouni N, Estrabaud E, Morel M, Rain JC, Transy C et al. (2007). HIV1 Vpr arrests the cell cycle by recruiting DCAF1/VprBP, a receptor of the Cul4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase. Cell Cycle 6: 182–188.
Lee J, Zhou P . (2007). DCAFs, the missing link of the CUL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell 26: 775–780.
Lee JY, Moon HJ, Lee WK, Chun HJ, Han CW, Jeon YW et al. (2006). Merlin facilitates ubiquitination and degradation of transactivation-responsive RNA-binding protein. Oncogene 25: 1143–1152.
McClatchey AI, Saotome I, Mercer K, Crowley D, Gusella JF, Bronson RT et al. (1998). Mice heterozygous for a mutation at the Nf2 tumor suppressor locus develop a range of highly metastatic tumors. Genes Dev 12: 1121–1133.
Morrison H, Sperka T, Manent J, Giovannini M, Ponta H, Herrlich P . (2007). Merlin/neurofibromatosis type 2 suppresses growth by inhibiting the activation of Ras and Rac. Cancer Res 67: 520–527.
Okada T, Lopez-Lago M, Giancotti FG . (2005). Merlin/NF-2 mediates contact inhibition of growth by suppressing recruitment of Rac to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 171: 361–371.
Rouleau GA, Merel P, Lutchman M, Sanson M, Zucman J, Marineau C et al. (1993). Alteration in a new gene encoding a putative membrane-organizing protein causes neuro-fibromatosis type 2. Nature 363: 515–521.
Shaw RJ, McClatchey AI, Jacks T . (1998). Regulation of the neurofibromatosis type 2 tumor suppressor protein, Merlin, by adhesion and growth arrest stimuli. J Biol Chem 273: 7757–7764.
Shaw RJ, Paez JG, Curto M, Yaktine A, Pruitt WM, Saotome I et al. (2001). The Nf2 tumor suppressor, Merlin, functions in Rac-dependent signaling. Dev Cell 1: 63–72.
Tan L, Ehrlich E, Yu XF . (2007). DDB1 and Cul4A are required for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr-induced G2 arrest. J Virol 81: 10822–10830.
Trofatter JA, MacCollin MM, Rutter JL, Murrell JR, Duyao MP, Parry DM et al. (1993). A novel moesin-, ezrin-, radixin-like gene is a candidate for the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor. Cell 75: 826.
Wen X, Duus KM, Friedrich TD, De Noronha CM . (2007). The HIV1 protein Vpr acts to promote G2 cell cycle arrest by engaging a DDB1 and Cullin4A-containing ubiquitin ligase complex using VprBP/DCAF1 as an adaptor. J Biol Chem 282: 27046–27057.
Xu HM, Gutmann DH . (1998). Merlin differentially associates with the microtubule and actin cytoskeleton. J Neurosci Res 51: 403–415.
Zhang S, Feng Y, Narayan O, Zhao LJ . (2001). Cytoplasmic retention of HIV-1 regulatory protein Vpr by protein–protein interaction with a novel human cytoplasmic protein VprBP. Gene 263: 131–140.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the Chen Laboratory for helpful discussions and technical support. We also thank Michael Huen and Jamie Wood for proofreading the paper. This work was supported by the DOD Era of Hope Scholar Award to JC (W81XWH-05-1-0470).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Chen, J. VprBP targets Merlin to the Roc1-Cul4A-DDB1 E3 ligase complex for degradation. Oncogene 27, 4056–4064 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.44
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.44
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Phosphorylation and stabilization of EZH2 by DCAF1/VprBP trigger aberrant gene silencing in colon cancer
Nature Communications (2023)
-
DCAF1 controls T-cell function via p53-dependent and -independent mechanisms
Nature Communications (2016)
-
VprBP (DCAF1): a promiscuous substrate recognition subunit that incorporates into both RING-family CRL4 and HECT-family EDD/UBR5 E3 ubiquitin ligases
BMC Molecular Biology (2013)
-
VprBP binds full-length RAG1 and is required for B-cell development and V(D)J recombination fidelity
The EMBO Journal (2012)
-
Targeting protein ubiquitylation: DDB1 takes its RING off
Nature Cell Biology (2009)