Abstract
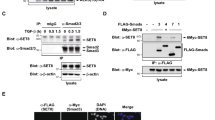
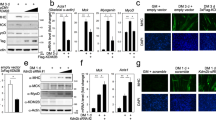
Smad proteins are crucial for the intracellular signaling of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). Upon their receptor-induced activation, Smad proteins are phosphorylated and translocated to the nucleus to activate the transcription of a select set of target genes. Here, we show that the co-activator p300/CBP bound and acetylated Smad3 as well as Smad2 in vivo, and that the acetylation was stimulated by TGF-β. A major acetylation site of Smad3 by p300/CBP is Lys-378 in the MH2 domain (Smad3C) known to be critical for the regulation of transcriptional activity. Replacement of Lys-378 with Arg decreased the transcriptional activity of GAL4-Smad3C in a luciferase assay. Moreover, p300/CBP potentiated the transcriptional activity of GAL4-Smad3C, but not the acetylation-resistant GAL4-Smad3C(K378R) mutant. These results suggest that acetylation of Smad3 by p300/CBP regulates positively its transcriptional activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMP:
-
bone morphogenetic protein
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- MH:
-
Mad homology
- PAGE:
-
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor-β
References
Abdollah S, Macias-Silva M, Tsukazaki T, Hayashi H, Attisano L, Wrana JL . (1997). TβRI phosphorylation of Smad2 on Ser465 and Ser467 is required for Smad2-Smad4 complex formation and signaling. J Biol Chem 272: 27678–27685.
Akiyoshi S, Inoue H, Hanai J, Kusanagi K, Nemoto N, Miyazono K et al. (1999). c-Ski acts as a transcriptional co-repressor in transforming growth factor-beta signaling through interaction with smads. J Biol Chem 274: 35269–35277.
Attisano L, Wrana JL . (2000). Smads as transcriptional co-modulators. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12: 235–243.
Boyes J, Byfield P, Nakatani Y, Ogryzko V . (1998). Regulation of activity of the transcription factor GATA-1 by acetylation. Nature 396: 594–598.
Callahan JF, Burgess JL, Fornwald JA, Gaster LM, Harling JD, Harrington FP et al. (2002). Identification of novel inhibitors of the transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) type 1 receptor (ALK5). J Med Chem 45: 999–1001.
Carcamo J, Weis FM, Ventura F, Wieser R, Wrana JL, Attisano L et al. (1994). Type I receptors specify growth-inhibitory and transcriptional responses to transforming growth factor beta and activin. Mol Cell Biol 14: 3810–3821.
Enari M, Ohmori K, Kitabayashi I, Taya Y . (2006). Requirement of clathrin heavy chain for p53-mediated transcription. Genes Dev 20: 1087–1099.
Feng XH, Zhang Y, Wu RY, Derynck R . (1998). The tumor suppressor Smad4/DPC4 and transcriptional adaptor CBP/p300 are coactivators for smad3 in TGF-beta-induced transcriptional activation. Genes Dev 12: 2153–2163.
Freiman RN, Tjian R . (2003). Regulating the regulators: lysine modifications make their mark. Cell 112: 11–17.
Gronroos E, Hellman U, Heldin CH, Ericsson J . (2002). Control of Smad7 stability by competition between acetylation and ubiquitination. Mol Cell 10: 483–493.
Gu W, Roeder RG . (1997). Activation of p53 sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal domain. Cell 90: 595–606.
Hasan S, Hottiger MO . (2002). Histone acetyl transferases: a role in DNA repair and DNA replication. J Mol Med 80: 463–474.
Hattori T, Ohoka N, Inoue Y, Hayashi H, Onozaki K . (2003). C/EBP family transcription factors are degraded by the proteasome but stabilized by forming dimer. Oncogene 22: 1273–1280.
Hayashi H, Abdollah S, Qiu Y, Cai J, Xu YY, Grinnell BW et al. (1997). The MAD-related protein Smad7 associates with the TGFbeta receptor and functions as an antagonist of TGFbeta signaling. Cell 89: 1165–1173.
Heldin CH, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P . (1997). TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature 390: 465–471.
Huse M, Muir TW, Xu L, Chen YG, Kuriyan J, Massagué J . (2001). The TGF beta receptor activation process: an inhibitor-to substrate-binding switch. Mol Cell 8: 671–682.
Imamura T, Takase M, Nishihara A, Oeda E, Hanai J, Kawabata M et al. (1997). Smad6 inhibits signalling by the TGF-beta superfamily. Nature 389: 622–626.
Inman GJ, Nicolas FJ, Callahan JF, Harling JD, Gaster LM, Reith AD et al. (2002). Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Smads 2, 3, and 4 permits sensing of TGF-beta receptor activity. Mol Pharmacol 62: 65–74.
Inoue Y, Kitagawa M, Onozaki, Hayashi H . (2004). Contribution of the constitutive and inducible degradation of Smad3 by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway to transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Interferon Cytokine Res 24: 43–54.
Itoh S, Ericsson J, Nishikawa J, Heldin CH, ten Dijke P . (2000). The transcriptional co-activator P/CAF potentiates TGF-beta/Smad signaling. Nucleic Acid Res 28: 4291–4298.
Janknecht R, Wells NJ, Hunter T . (1998). TGF-beta-stimulated cooperation of smad proteins with the coactivators CBP/p300. Genes Dev 12: 2114–2119.
Kawabata H, Kawahara K, Kanekura T, Araya N, Daitoku H, Hatta M et al. (2002). Possible role of transcriptional coactivator P/CAF and nuclear acetylation in calcium-induced keratinocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 277: 8099–8105.
Martinez-Balbas MA, Bauer UM, Nielsen SJ, Brehm A, Kouzarides T . (2000). Regulation of E2F1 activity by acetylation. EMBO J 19: 662–671.
Massagué J, Blain SW, Lo RS . (2000). TGFbeta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell 103: 295–309.
Massagué J, Wotton D . (2000). Transcriptional control by the TGF-beta/Smad signaling system. EMBO J 19: 1745–1754.
Matsuzaki H, Daitoku H, Hatta M, Aoyama H, Yoshimochi K, Fukamizu A . (2005). Acetylation of Foxo1 alters its DNA-binding ability and sensitivity to phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 11278–11283.
Miyazono K . (2000). Positive and negative regulation of TGF-beta signaling. J Cell Sci 113: 1101–1109.
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Moren A, Nakayama T, Christian JL, Heuchel R et al. (1997). Identification of Smad7, a TGFbeta-inducible antagonist of TGF-beta signalling. Nature 389: 631–635.
Nishihara A, Hanai JI, Okamoto N, Yanagisawa J, Kato S, Miyazono M et al. (1998). Role of p300, a transcriptional coactivator, in signalling of TGF-beta. Genes Cells 3: 613–623.
Sartorelli V, Puri PL, Hamamori Y, Ogryzko V, Chung G, Nakatani Y et al. (1999). Acetylation of MyoD directed by PCAF is necessary for the execution of the muscle program. Mol Cell 4: 725–734.
Souchelnytskyi S, Tamaki K, Engstrom U, Wernstedt C, ten Dijke P, Heldin CH . (1997). Phosphorylation of Ser465 and Ser467 in the C terminus of Smad2 mediates interaction with Smad4 and is required for transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem 272: 28107–28115.
Takahashi N, Tetsuka T, Uranishi H, Okamoto T . (2002). Inhibition of the NF-kappaB transcriptional activity by protein kinase A. Eur J Biochem 269: 4559–4565.
Wu JW, Hu M, Chai J, Seoane J, Huse M, Li C et al. (2001). Crystal structure of a phosphorylated Smad2. Recognition of phosphoserine by the MH2 domain and insights on Smad function in TGF-beta signaling. Mol Cell 8: 1277–1289.
Wu RY, Zhang Y, Feng XH, Derynck R . (1997). Heteromeric and homomeric interactions correlate with signaling activity and functional cooperativity of Smad3 and Smad4/DPC4. Mol Cell Biol 17: 2521–2528.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr JL Wrana (Samuel Lunenfeld Research Institute) and Dr K Miyazono (University of Tokyo) for providing plasmids. We also thank Dr C Uchida (Hamamatsu University) for kind suggestions. This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas (C) from the Ministry of Education, Science Sports and Culture, Welfide Medical Research Foundation, Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Nagoya City University and the Kudo Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, Y., Itoh, Y., Abe, K. et al. Smad3 is acetylated by p300/CBP to regulate its transactivation activity. Oncogene 26, 500–508 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209826
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209826
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
SET8 is a novel negative regulator of TGF-β signaling in a methylation-independent manner
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Pharmacological inhibition of HDAC6 improves muscle phenotypes in dystrophin-deficient mice by downregulating TGF-β via Smad3 acetylation
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Periplocin and cardiac glycosides suppress the unfolded protein response
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Shen Shuai IIRecipe attenuates renal injury and fibrosis in chronic kidney disease by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome and Sirt1/Smad3 deacetylation pathway
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2019)
-
Integrative modeling reveals key chromatin and sequence signatures predicting super-enhancers
Scientific Reports (2019)