Abstract
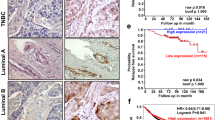
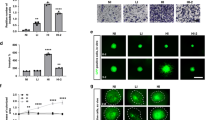
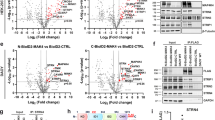
Human enhancer of invasion, clone 10 (HEI10) (CCNB1IP1) was first described as a RING-finger family ubiquitin ligase that regulates cell cycle by interacting with cyclin B and promoting its degradation. Subsequently, other studies suggested specific upregulation of HEI10 in metastatic melanoma and demonstrated direct interaction between HEI10 and the tumor suppressor Merlin, encoded by the neurofibromatosis 2 gene. These and other results led us to hypothesize that HEI10 also influences the processes of cell migration and metastasis. We here show that cells with depleted HEI10 both migrate more rapidly and invade more effectively than control cells. HEI10 depletion post-transcriptionally increases the expression of a group of promotility regulatory proteins including p130Cas, paxillin, Cdk1 and cyclin B2, but excluding Merlin. Among these, only inhibition of Cdk1/cyclin B activity specifically reversed the motility and invasion of HEI10-depleted cells. Finally, HEI10 is abundantly transcribed in many human tissues, and particularly abundant in some tumor cell lines, suggesting that it may be commonly involved in coordinating cell cycle with cell migration and invasion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouton AH, Burnham MR . (1997). Detection of distinct pools of the adapter protein p130CAS using a panel of monoclonal antibodies. Hybridoma 16: 403–411.
Brabek J, Constancio SS, Siesser PF, Shin NY, Pozzi A, Hanks SK . (2005). Crk-associated substrate tyrosine phosphorylation sites are critical for invasion and metastasis of SRC-transformed cells. Mol Cancer Res 3: 307–315.
Draviam VM, Orrechia S, Lowe M, Pardi R, Pines J . (2001). The localization of human cyclins B1 and B2 determines CDK1 substrate specificity and neither enzyme requires MEK to disassemble the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol 152: 945–958.
Evans DG, Sainio M, Baser ME . (2000). Neurofibromatosis type 2. J Med Genet 37: 897–904.
Fesik SW . (2005). Promoting apoptosis as a strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 876–885.
Gronholm M, Muranen T, Toby GG, Utermark T, Hanemann CO, Golemis EA et al. (2006). A functional association between merlin and HEI10, a cell cycle regulator. Oncogene 25: 4389–4398.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100: 57–70.
Hirokawa Y, Tikoo A, Huynh J, Utermark T, Hanemann CO, Giovannini M et al. (2004). A clue to the therapy of neurofibromatosis type 2: NF2/merlin is a PAK1 inhibitor. Cancer J 10: 20–26.
Jackson PK, Eldridge AG, Freed E, Furstenthal L, Hsu JY, Kaiser BK et al. (2000). The lore of the RINGs: substrate recognition and catalysis by ubiquitin ligases. Trends in Cell Biol 10: 429–439.
James MF, Beauchamp RL, Manchanda N, Kazlauskas A, Ramesh V . (2004). A NHERF binding site links the betaPDGFR to the cytoskeleton and regulates cell spreading and migration. J Cell Sci 117: 2951–2961.
Juliano R . (2003). Movin' on through with Cdc2. Nat Cell Biol 5: 589–590.
Kaempchen K, Mielke K, Utermark T, Langmesser S, Hanemann CO . (2003). Upregulation of the Rac1/JNK signaling pathway in primary human schwannoma cells. Hum Mol Genet 12: 1211–1221.
Klemke RL, Leng J, Molander R, Brooks PC, Vuori K, Cheresh DA . (1998). CAS/Crk coupling serves as a ‘molecular switch’ for induction of cell migration. J Cell Biol 140: 961–972.
Manes T, Zheng DQ, Tognin S, Woodard AS, Marchisio PC, Languino LR . (2003). Alpha(v)beta3 integrin expression up-regulates cdc2, which modulates cell migration. J Cell Biol 161: 817–826.
Mine N, Kurose K, Konishi H, Araki T, Nagai H, Emi M . (2001). Fusion of a sequence from HEI10 (14q11) to the HMGIC gene at 12q15 in a uterine leiomyoma. Jpn J Cancer Res 92: 135–139.
Nymark P, Wikman H, Ruosaari S, Hollmen J, Vanhala E, Karjalainen A et al. (2006). Identification of specific gene copy number changes in asbestos-related lung cancer. Cancer Res 66: 5737–5743.
Poulikakos PI, Xiao GH, Gallagher R, Jablonski S, Jhanwar SC, Testa JR . (2006). Re-expression of the tumor suppressor NF2/merlin inhibits invasiveness in mesothelioma cells and negatively regulates FAK. Oncogene 25: 5960–5968.
Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N et al. (2005). Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature 437: 1173–1178.
Ruest PJ, Roy S, Shi E, Mernaugh RL, Hanks SK . (2000). Phosphospecific antibodies reveal focal adhesion kinase activation loop phosphorylation in nascent and mature focal adhesions and requirement for the autophosphorylation site. Cell Growth Differ 11: 41–48.
Schwikowski B, Uetz P, Fields S . (2000). A network of protein–protein interactions in yeast. Nat Biotechnol 18: 1257–1261.
Smith AP, Weeraratna AT, Spears JR, Meltzer PS, Becker D . (2004). SAGE identification and fluorescence imaging analysis of genes and transcripts in melanomas and precursor lesions. Cancer Biol Ther 3: 104–109.
Toby GG, Gherraby W, Coleman TR, Golemis EA . (2003). A novel RING-finger protein, Human Enhancer of Invasion 10 (HEI10), alters mitotic progression through regulation of cyclin B levels. Mol Cell Biol 23: 2109–2122.
Wade R, Vande Pol S . (2006). Minimal features of paxillin that are required for the tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase. Biochem J 393: 565–573.
Worthylake RA, Burridge K . (2003). RhoA and ROCK promote migration by limiting membrane protrusions. J Biol Chem 278: 13578–13584.
Xiao GH, Gallagher R, Shetler J, Skele K, Altomare DA, Pestell RG et al. (2005). The NF2 tumor suppressor gene product, merlin, inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by repressing cyclin D1 expression. Mol Cell Biol 25: 2384–2394.
Zhao ZS, Manser E, Loo TH, Lim L . (2000). Coupling of PAK-interacting exchange factor PIX to GIT1 promotes focal complex disassembly. Mol Cell Biol 20: 6354–6363.
Acknowledgements
We thank Margret Einarson, Cynthia Spittle, Meenhard Herlyn and Hong Wu for help with the collection and preparation of cell lines for RNA analysis. We also thank Ilya Serebriiskii for help with some experiments. We greatly appreciate the efforts of Dr Brian Egleston in the statistical analysis of data. We thank Dr Tony Yeung, director of the FCCC Biochemistry and Biotechnology facility for Real-Time PCR and DNA synthesis services This work and the authors were supported by NIH RO1 CA63366 and by Translational Pilot Project funding from the Tobacco Settlement from the State of Pennsylvania, Department of Health (to EAG) and by an Appropriation from the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, by NIH core Grant CA-06927 and support from the Pew Charitable Fund (to Fox Chase Cancer Center). DD was a recipient of the Plain and Fancy Fellowship of the Fox Chase Cancer Center Board of Associates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Nicolas, E., Gherraby, W. et al. HEI10 negatively regulates cell invasion by inhibiting cyclin B/Cdk1 and other promotility proteins. Oncogene 26, 4825–4832 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210282
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210282
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The RING Domain of Rice HEI10 is Essential for Male, But Not Female Fertility
Rice (2024)
-
Targeting CDK1 in cancer: mechanisms and implications
npj Precision Oncology (2023)
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors exert distinct effects on patient-derived 2D and 3D glioblastoma cell culture models
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
RNF212 is a dosage-sensitive regulator of crossing-over during mammalian meiosis
Nature Genetics (2013)