Abstract
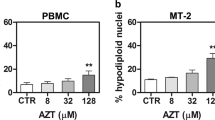
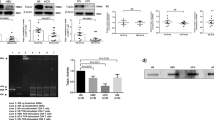
The transition from interleukin-2 (IL-2)-dependent to IL-2-independent growth is considered one of the key steps in the transformation of human T-cell leukemia virus type-I (HTLV-I)-infected T cells. The expression of thioredoxin-binding protein-2 (TBP-2) is lost during the transition of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines. Here, we analysed the mechanism of loss of TBP-2 expression and the role of TBP-2 in IL-2-dependent growth in the in vitro model to investigate multistep transformation of HTLV-I. CpGs in the TBP-2 gene are methylated in IL-2-independent but not in IL-2-dependent cells. Sequential treatment with 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine and a histone deacetylase inhibitor augmented histone acetylation and TBP-2 expression, suggesting that loss of TBP-2 expression is due to DNA methylation and histone deacetylation. In IL-2-dependent cells, a basal level of TBP-2 expression was maintained by IL-2 associated with cellular growth, whereas TBP-2 expression was upregulated on deprivation of IL-2 associated with growth suppression. Overexpression of TBP-2 in IL-2-independent cells suppressed the growth and partially restored responsiveness to IL-2. Knockdown of TBP-2 caused the IL-2-dependent cells to show partial growth without IL-2. These results suggested that epigenetic silencing of the TBP-2 gene results in a loss of responsiveness to IL-2, contributing to uncontrolled IL-2-independent growth in HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butler LM, Zhou X, Xu WS, Scher HI, Rifkind RA, Marks PA et al. (2002). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 11700–11705.
Cameron EE, Bachman KE, Myohanen S, Herman JG, Baylin SB . (1999). Nat Genet 21: 103–107.
Chen KS, DeLuca HF . (1994). Biochim Biophys Acta 1219: 26–32.
Coombes MM, Briggs KL, Bone JR, Clayman GL, El-Naggar AK, Dent SY . (2003). Oncogene 22: 8902–8911.
Gardiner-Garden M, Frommer M . (1987). J Mol Biol 196: 261–282.
Goldberg SF, Miele ME, Hatta N, Takata M, Paquette-Straub C, Freedman LP et al. (2003). Cancer Res 63: 432–440.
Han SH, Jeon JH, Ju HR, Jung U, Kim KY, Yoo HS et al. (2003). Oncogene 22: 4035–4046.
Holmgren A . (1985). Annu Rev Biochem 54: 237–271.
Jeang KT, Giam C, Majone F, Aboud M . (2004). J Biol Chem 279: 31991–31994.
Maeda M, Shimizu A, Ikuta K, Okamoto H, Kashihara M, Uchiyama T et al. (1985). J Exp Med 162: 2169–2174.
Maeda M . (1992). Hum Cell 5: 70–78.
Makino S, Masutani H, Maekawa N, Konishi I, Fujii S, Yamamoto R et al. (1992). Immunology 76: 578–583.
Masutani H, Yodoi J . (2002). Methods Enzymol 347: 279–286.
Matsuoka M . (2003). Oncogene 22: 5131–5140.
Migone TS, Lin JX, Cereseto A, Mulloy JC, O'Shea JJ, Franchini G et al. (1995). Science 269: 79–81.
Morgan DA, Ruscetti FW, Gallo R . (1976). Science 193: 1007–1008.
Nishinaka Y, Nishiyama A, Masutani H, Oka S, Ahsan MK, Nakayama Y et al. (2004a). Cancer Res 64: 1287–1292.
Nishinaka Y, Masutani H, Oka S, Matsuo Y, Yamaguchi Y, Nishio K et al. (2004b). J Biol Chem 279: 37559–37565.
Nishiyama A, Matsui M, Iwata S, Hirota K, Masutani H, Nakamura H et al. (1999). J Biol Chem 274: 21645–21650.
Nosaka K, Maeda M, Tamiya S, Sakai T, Mitsuya H, Matsuoka M . (2000). Cancer Res 60: 1043–1048.
Okamoto T, Ohno Y, Tsugane S, Watanabe S, Shimoyama M, Tajima K et al (1989). Jpn J Cancer Res 80: 191–195.
Satoh A, Toyota M, Itoh F, Sasaki Y, Suzuki H, Ogi K et al. (2003). Cancer Res 63: 8606–8613.
Spencer VA, Sun JM, Li L, Davie JR . (2003). Methods 31: 67–75.
Tagaya Y, Maeda Y, Mitsui A, Kondo N, Matsui H, Hamuro J et al. (1989). EMBO J 13: 2244.
Uchiyama T, Yodoi J, Sagawa K, Takatsuki K, Uchino H . (1977). Blood 50: 481–492.
Ushijima T, Okochi-Takada E . (2005). Cancer Sci 96: 206–211.
Yasunaga J, Taniguchi Y, Nosaka K, Yoshida M, Satou Y, Sakai T et al. (2004). Cancer Res 64: 6002–6009.
Yodoi J, Takatsuki K, Masuda T . (1974). New Engl J Med 290: 572–573.
Yoshida M, Miyoshi I, Hinuma Y . (1982). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 2031–2035.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Koichi Ikuta for discussions, and Ms Yoko Kanekiyo and Ms Satoko Maeji for secretarial assistance. This work was supported by a grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and by the Research and Development Program for New Bio-Industry Initiatives.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahsan, M., Masutani, H., Yamaguchi, Y. et al. Loss of interleukin-2-dependency in HTLV-I-infected T cells on gene silencing of thioredoxin-binding protein-2. Oncogene 25, 2181–2191 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209256
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209256
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Tumor necrosis factor induces rapid down-regulation of TXNIP in human T cells
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Development of a novel cell-based assay system EPISSAY for screening epigenetic drugs and liposome formulated decitabine
BMC Cancer (2013)
-
Molecular characterization of differentially expressed TXNIP gene and its association with porcine carcass traits
Molecular Biology Reports (2012)
-
Thioredoxin-binding protein-2 (TBP-2/VDUP1/TXNIP) regulates T-cell sensitivity to glucocorticoid during HTLV-I-induced transformation
Leukemia (2011)
-
Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 10 Induces Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein and Causes Accumulation of Reactive Oxygen Species in SNU-620 Human Gastric Cancer Cells
Molecules and Cells (2010)