Abstract
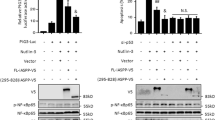
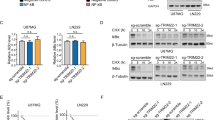
In the present study, we describe the function of a novel protein, ECop (EGFR-Coamplified and overexpressed protein), in the regulation of NF-κB activity. Ectopic expression of ECop increases NF-κB transcriptional activity by promoting nuclear translocation and DNA binding of NF-κB, and ECop-induced NF-κB activation confers cellular resistance to apoptotic challenge. In ECop knockdown cells, NF-κB transcriptional activity is suppressed due to delayed IκBα degradation, which results in a delayed nuclear translocation as well as decreased DNA binding of NF-κB. Suppression of NF-κB activation by ECop knockdown increases cellular susceptibility to apoptosis. These results suggest that ECop is a key regulator of NF-κB signaling, and that high-level, amplification-mediated ECop expression, such as that occurring in tumors with amplified EGFR, could contribute to resistance to apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts B, Bray D, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K and Watson JD . (1994). Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland Publishing, Inc.: New York, pp 551–598.
Amit S and Ben-Neriah Y . (2003). Semin Cancer Biol., 13, 15–28.
Amler LC, Schurmann J and Schwab M . (1996). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 15, 134–137.
Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC, Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD and Baldwin AS . (2003). Nature, 423, 659–663.
Beg AA and Baltimore D . (1996). Science, 274, 782–784.
Birbach A, Gold P, Binder BR, Hofer E, de Martin R and Schmid JA . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 10842–10851.
Eley GD, Reiter JL, Pandita A, Park S, Jenkins RB, Maihle NJ and James CD . (2002). Neuro-oncology, 4, 86–94.
Forus A, Florenes VA, Maelandsmo GM, Meltzer PS, Fodstad O and Myklebost O . (1993). Cell Growth Differ., 4, 1065–1070.
Karin M and Ben-Neriah Y . (2000). Annu. Rev. Immunol., 18, 621–663.
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR and Li ZW . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 301–310.
Karin M and Lin A . (2002). Nat. Immunol., 3, 221–227.
Kawai H, Nie L and Yuan ZM . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 6079–6088.
Khatib ZA, Matsushime H, Valentine M, Shapiro DN, Sherr CJ and Look AT . (1993). Cancer Res., 53, 5535–5541.
King CR, Kraus MH and Aaronson SA . (1985). Science, 229, 974–976.
Kucharczak J, Simmons MJ, Fan Y and Gelinas C . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 8961–8982.
Liu ZG, Hsu H, Goeddel DV and Karin M . (1996). Cell, 87, 565–576.
Matsuda A, Suzuki Y, Honda G, Muramatsu S, Matsuzaki O, Nagano Y, Doi T, Shimotohno K, Harada T, Nishida E, Hayashi H and Sugano S . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 3307–3318.
Park S and James CD . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 723–727.
Schuuring E, Verhoeven E, Mooi WJ and Michalides RJ . (1992). Oncogene, 7, 355–361.
Schwab M . (1999). Semin. Cancer Biol., 9, 319–325.
Schwab M, Alitalo K, Klempnauer KH, Varmus HE, Bishop JM, Gilbert F, Brodeur G, Goldstein M and Trent J . (1983). Nature, 305, 245–248.
Smith K, Houlbrook S, Greenall M, Carmichael J and Harris AL . (1993). Oncogene, 8, 933–938.
Tanigami A, Tokino T, Takita K, Ueda M, Kasumi F and Nakamura Y . (1992). Genomics, 13, 21–24.
Tomasetto C, Regnier C, Moog-Lutz C, Mattei MG, Chenard MP, Lidereau R, Basset P and Rio MC . (1995). Genomics, 28, 367–376.
Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, Green DR and Verma IM . (1996). Science, 274, 787–789.
Wang XY, Smith DI, Frederick L and James CD . (1998). Oncogene, 16, 191–195.
Wei N and Deng XW . (2003). Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol., 19, 261–286.
Whiteside ST and Israel A . (1997). Semin. Cancer. Biol., 8, 75–82.
Acknowledgements
We thank James D Orth for help with microscopy and Dr Ralf Janknecht for his generous gift of c-Jun plasmid and experimental advice. We also acknowledge Dr Fergus Couch for helpful discussions throughout the development of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by NCI grant CA85799 (CDJ)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., James, C. ECop (EGFR-Coamplified and overexpressed protein), a novel protein, regulates NF-κB transcriptional activity and associated apoptotic response in an IκBα-dependent manner. Oncogene 24, 2495–2502 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208496
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208496
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
VOPP1 promotes breast tumorigenesis by interacting with the tumor suppressor WWOX
BMC Biology (2018)
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor-coamplified and overexpressed protein (VOPP1) is a putative oncogene in gastric cancer
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2015)
-
Progress of research in miR-218 and cervical cancer
The Chinese-German Journal of Clinical Oncology (2013)
-
Loss of VOPP1 overexpression in squamous carcinoma cells induces apoptosis through oxidative cellular injury
Laboratory Investigation (2011)
-
Intracellular localization of GASP/ECOP/VOPP1
Journal of Molecular Histology (2010)