Abstract
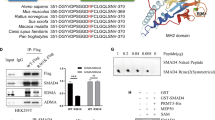
Smad4 is a critical component in transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling and frequently mutated in pancreatic and colorectal cancers. Smad4 has two important functional domains, MH1 and MH2, that are involved in different biological processes. The MH1 domain comprises a DNA binding domain and the MH2 domain is mainly implicated in transcriptional activation and homo- and heteromeric complex formation among Smad proteins. In the present study, a total of nine Smad4 mutations at both MH1 and MH2 domains were analysed and all of them had a reduced activity to stimulate transcription of a TGF-β-responsive reporter gene. All four MH1 mutations had a markedly reduced ability to bind a consensus Smad binding element by an in vitro assay using GST fusion proteins. Among the MH2 mutations, R497H, K507Q, and R515G mutations of Smad4 gave rise to a reduced DNA binding capacity. The R497H mutation had a slightly reduced interaction with Smad2 upon activation of TGF-β receptor. However, the K507Q and R515G mutations greatly lost their ability to associate with Smad2. Using a GST pull-down assay, it was found that the Smad4 MH2 domain bearing R497H and R515G mutations had an enhanced interaction with the MH1 region of the Smad4 protein, indicating that an increased intramolecular interaction by these mutations may alleviate the DNA binding activity at the MH1 domain. Consistent with these observations, the MH2 domain with R497H mutation had an enhanced ability to inhibit TGF-β receptor-mediated transcription. In addition, the full-length R497H mutation was able to antagonize TGF-β signaling in a dominant-negative manner. Therefore, these studies revealed novel mechanisms by which the Smad4 mutations utilize to abrogate their functions in transducing the signaling of TGF-β, which plays an important role in various stages of cancer formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALK:
-
activin receptor-like kinase
- HEK293:
-
human embryonic kidney 293 cells
- kb:
-
kilobase pairs
- MH:
-
Mad homologue domain of Smad proteins
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RT–PCR:
-
reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction
- SBE:
-
Smad binding element
- Smad:
-
Sma-, and Mad-related protein
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor-β.
References
Andrews NC and Faller DV . (1991). Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 2499.
Chacko BM, Qin B, Correia JJ, Lam SS, de Caestecker MP and Lin K . (2001). Nat. Struct. Biol., 8, 248–253.
Chen CR, Kang Y, Siegel PM and Massague J . (2002). Cell, 110, 19–32.
Chen Y, Bhushan A and Vale W . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 12938–12943.
Datto MB, Yu Y and Wang XF . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 28623–28628.
de Caestecker MP, Piek E and Roberts AB . (2000). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 92, 1388–1402.
Hahn SA, Schutte M, Hoque AT, Moskaluk CA, da Costa LT, Rozenblum E, Weinstein CL, Fischer A, Yeo CJ, Hruban RH and Kern SE . (1996). Science, 271, 350–353.
Hannon GJ and Beach D . (1994). Nature, 371, 257–261.
Hata A, Lo RS, Wotton D, Lagna G and Massague J . (1997). Nature, 388, 82–87.
Heldin CH, Miyazono K and ten Dijke P . (1997). Nature, 390, 465–471.
Howe JR, Roth S, Ringold JC, Summers RW, Jarvinen HJ, Sistonen P, Tomlinson IP, Houlston RS, Bevan S, Mitros FA, Stone EM and Aaltonen LA . (1998). Science, 280, 1086–1088.
Lagna G, Hata A, Hemmati-Brivanlou A and Massague J . (1996). Nature, 383, 832–836.
Li W, Chen F, Nagarajan RP, Liu X and Chen Y . (2001). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 286, 1163–1169.
Liu F, Pouponnot C and Massague J . (1997). Genes Dev., 11, 3157–3167.
Lo RS, Chen YG, Shi Y, Pavletich NP and Massague J . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 996–1005.
Massague J . (1998). Annu. Rev. Biochem., 67, 753–791.
Massague J and Wotton D . (2000). EMBO J., 19, 1745–1754.
Miyaki M, Iijima T, Konishi M, Sakai K, Ishii A, Yasuno M, Hishima T, Koike M, Shitara N, Iwama T, Utsunomiya J, Kuroki T and Mori T . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 3098–3103.
Miyazono K, Kusanagi K and Inoue H . (2001). J. Cell Physiol., 187, 265–276.
Moren A, Itoh S, Moustakas A, Dijke P and Heldin CH . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 4396–4404.
Moustakas A and Kardassis D . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 6733–6738.
Nagarajan RP and Chen Y . (2000). Biochem. J., 350 (Part 1), 253–259.
Nagarajan RP, Zhang J, Li W and Chen Y . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 33412–33418.
Polyak K, Kato JY, Solomon MJ, Sherr CJ, Massague J, Roberts JM and Koff A . (1994). Genes Dev., 8, 9–22.
Schutte M, Hruban RH, Hedrick L, Cho KR, Nadasdy GM, Weinstein CL, Bova GS, Isaacs WB, Cairns P, Nawroz H, Sidransky D, Casero Jr RA, Meltzer PS, Hahn SA and Kern SE . (1996). Cancer Res., 56, 2527–2530.
Shi Y, Hata A, Lo RS, Massague J and Pavletich NP . (1997). Nature, 388, 87–93.
Shi Y, Wang YF, Jayaraman L, Yang H, Massague J and Pavletich NP . (1998). Cell, 94, 585–594.
Wrana JL, Attisano L, Wieser R, Ventura F and Massague J . (1994). Nature, 370, 341–347.
Xiao Z, Latek R and Lodish HF . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 1057–1069.
Acknowledgements
We thank R Harland for the mouse Smad2 clone and M Schutte for the human Smad4 clone. This work was supported by a research grant from American Cancer Society (PRG-00-273-01-MGO), a Scientist Development Award from American Heart Association, and a grant from National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases (R01 DK55991) to YC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuang, C., Chen, Y. Tumor-derived C-terminal mutations of Smad4 with decreased DNA binding activity and enhanced intramolecular interaction. Oncogene 23, 1021–1029 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207219
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207219
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
“Proteotranscriptomic analysis of advanced colorectal cancer patient derived organoids for drug sensitivity prediction”
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
Spatiotemporal modulation of SMAD4 by HBx is required for cellular proliferation in hepatitis B-related liver cancer
Cellular Oncology (2022)
-
A complex pattern of mutations and abnormal splicing of Smad4 is present in thyroid tumours
Oncogene (2005)