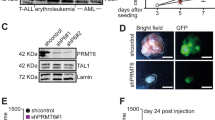
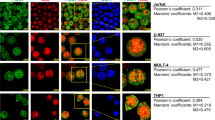
Abstract
The polycomb group (PcG) proteins are known to be involved in maintaining the silenced state of several developmentally regulated genes. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (Ezh2), a member of this large protein family, has also been shown to be deregulated in different tumor types and its role, both as a potential primary effector and as a mediator of tumorigenesis, has become a subject of increased interest. We observed that Ezh2 binds to pRb2/p130, a member of the retinoblastoma family; as such, we were led to consider the possible ability of Ezh2 to modulate cell cycle progression. Both Ezh2 and pRb2/p130 repress gene expression by recruiting histone deacetylase (HDAC1), which decreases DNA accessibility for activating transcription factors. Additionally, we observed that Ezh2 interacts with the C-terminal region of pRb2/p130, essential for interaction with HDAC1. We show that Ezh2 is able to reverse pRb2/p130-HDAC1-mediated repression of the cyclin A promoter. This indicates a functional role of this complex in regulating cyclin A expression, known to be crucial in mediating cell cycle advancement. We also detected a significant decrease in the retention of HDAC1 activity associated with pRb2/p130 when Ezh2 was overexpressed. Finally, electromobility shift assays (EMSA) demonstrated that overexpression of Ezh2 caused the abrogation of the pRb2/p130–HDAC1 complex on the cyclin A promoter. These data, taken together, suggest that Ezh2 competes with HDAC1 in binding to pRb2/p130, disrupting their occupancy on the cyclin A promoter. In this study, we propose a new mechanism for the functional inactivation of pRb2/p130 that ultimately contributes to cell cycle progression and malignant transformation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews NC and Faller DV . (1991). Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 2499.
Bardos JI, Saurin AJ, Tissot C, Duprez E. and Freemont PS . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 28785–28792.
Bellan C, De Falco G, Tosi GM, Lazzi S, Ferrari F, Morbini G, Bartolomei S, Toti P, Mangiavacchi P, Cevenini G, Trimarchi C, Cinti C, Giordano A, Leoncini L, Tosi P and Cottier H . (2002). Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 43, 3602–3608.
Bracken AP, Pasini D, Capra M, Prosperini E, Colli E. and Helin K . (2003). EMBO J., 22, 5323–5335.
Carbone M, Rizzo P and Pass HI . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 1877–1888.
Claudio PP, Tonini T and Giordano A . (2002a). Genome Biol., 3, reviews3012.
Claudio PP, Zamparelli A, Garcia FU, Claudio L, Ammirati G, Farina A, Bovicelli A, Russo G, Giordano GG, McGinnis DE, Giordano A. and Cardi G . (2002b). Clin. Cancer Res., 8, 1808–1815.
Cohen KJ, Hanna JS, Prescott JE and Dang CV . (1996). Mol. Cell Biol., 16, 5527–5535.
De Luca A, Baldi A, Esposito V, Howard CM, Bagella L, Rizzo P, Caputi M, Pass H.I, Giordano GG, Baldi F, Carbone M and Giordano A . (1997a). Nat. Med., 3, 913–916.
De Luca A, MacLachlan TK, Bagella L, Dean C, Howard CM, Claudio PP, Baldi A, Khalili K and Giordano A . (1997b). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 20971–20974.
Ewen ME, Xing YG, Lawrence JB. and Livingston DM . (1991). Cell, 66, 1155–1164.
Ferreira R, Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Robin P, Harel-Bellan A and Trouche D . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 10493–10498.
Fukuyama T, Otsuka T, Shigematsu H, Uchida N, Arima F, Ohno Y, Iwasaki H, Fukuda T. and Niho Y . (2000). Br. J. Haematol., 108, 842–847.
Galderisi U, Melone MA, Jori FP, Piegari E, Di Bernardo G, Cipollaro M, Cascino A, Peluso G, Claudio PP and Giordano A . (2001). Mol. Cell. Neurosci., 17, 415–425.
Gould A . (1997). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 7, 488–494.
Guadagno TM and Newport JW . (1996). Cell, 84, 73–82.
Gunster MJ, Satijn DP, Hamer KM, den Blaauwen JL, de Bruijn D, Alkema MJ, van Lohuizen M, van Driel R and Otte AP . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 2326–2335.
Haupt Y, Alexander WS, Barri G, Klinken SP and Adams JM . (1991). Cell, 65, 753–763.
Hobert O, Jallal B and Ullrich A . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 3066–3073.
Jacobs JJ, Kieboom K, Marino S, DePinho RA and van Lohuizen M . (1999a). Nature, 397, 164–168.
Jacobs JJ, Scheijen B, Voncken JW, Kieboom K, Berns A and van Lohuizen M . (1999b). Genes Dev., 13, 2678–2690.
Kennison JA . (1995). Annu. Rev. Genet., 29, 289–303.
Kleer CG, Cao Q, Varambally S, Shen R, Ota I, Tomlins SA, Ghosh D, Sewalt RG, Otte AP, Hayes DF, Sabel MS, Livant D, Weiss SJ, Rubin MA. and Chinnaiyan AM . (2003). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 100, 11606–11611.
La Thangue NB . (1996). Biochem. Soc. Trans., 24, 54–59.
Lee WH, Bookstein R, Hong F, Young LJ, Shew JY and Lee EY . (1987). Science, 235, 1394–1399.
Macaluso M, Paggi MG and Giordano A . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 6472–6478.
Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Groisman R, Naguibneva I, Robin P, Lorain S, Le Villain JP, Troalen F, Trouche D and Harel-Bellan A . (1998). Nature, 391, 601–605.
Mayol X, Grana X, Baldi A, Sang N, Hu Q and Giordano A . (1993). Oncogene, 8, 2561–2566.
Muller J . (1995). EMBO J., 14, 1209–1220.
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO and Botstein D . (2000). Nature, 406, 747–752.
Pipas JM . (1992). J. Virol., 66, 3979–3985.
Pirrotta V . (1997a). Trends Genet., 13, 314–318.
Pirrotta V . (1997b). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 7, 249–258.
Pirrotta V . (1998). Cell, 93, 333–336.
Pupa SM, Howard CM, Invernizzi AM, De Vecchi R, Giani C, Claudio PP, Colnaghi MI, Giordano A and Menard S . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 651–656.
Raaphorst FM, Van Kemenade FJ, Blokzijl T, Fieret E, Hamer KM, Satijn DP, Otte AP and Meijer CJ . (2000). Am. J. Pathol., 157, 709–715.
Raschella G, Tanno B, Bonetto F, Negroni A, Amendola R and Paggi MG . (2001). Med. Pediatr. Oncol., 36, 104–107.
Raschella G, Tanno B, Bonetto F, Negroni A, Claudio PP, Baldi A, Amendola R, Calabretta B, Giordano A and Paggi MG . (1998). Cell Death Differ., 5, 401–407.
Rhodes DR, Sanda MG, Otte AP, Chinnaiyan AM and Rubin MA . (2003). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 95, 661–668.
Sanseverino F, Torricelli M, Petraglia F and Giordano A . (2003). Cancer Biol. Ther., 2, 636–641.
Satijn DP and Otte AP . (1999a). Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1447, 1–16.
Satijn DP and Otte AP . (1999b). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 57–68.
Schumacher A. and Magnuson T . (1997). Trends Genet., 13, 167–170.
Sellers WR and Loda M . (2002). Cancer Cell, 2, 349–350.
Sewalt RG, van der Vlag J, Gunster MJ, Hamer KM, den Blaauwen JL, Satijn DP, Hendrix T, van Driel R and Otte AP . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 3586–3595.
Sidle A, Palaty C, Dirks P, Wiggan O, Kiess M, Gill RM, Wong AK. and Hamel PA . (1996). Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 31, 237–271.
Simon J. . (1995). Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol., 7, 376–385.
Stiegler P, De Luca A, Bagella L and Giordano A . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 5049–5052.
Tonini T, Hillson C and Claudio PP . (2002). J. Cell Physiol., 192, 138–150.
Tonini T, Rossi F and Claudio PP . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 6549–6556.
Turner BM . (1991). J. Cell Sci., 99 (Part 1), 13–20.
van der Vlag J and Otte AP . (1999). Nat. Genet., 23, 474–478.
van Kemenade FJ, Raaphorst FM, Blokzijl T, Fieret E, Hamer KM, Satijn DP, Otte AP and Meijer CJ . (2001). Blood, 97, 3896–3901.
Van Lohuizen M, Frasch M, Wientjens E and Berns A . (1991). Nature, 353, 353–355.
Varambally S, Dhanasekaran SM, Zhou M, Barrette TR, Kumar-Sinha C, Sanda MG, Ghosh D, Pienta KJ, Sewalt RG, Otte AP, Rubin MA and Chinnaiyan AM . (2002). Nature, 419, 624–629.
Visser HP, Gunster MJ, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Manders EM, Raaphorst FM, Meijer CJ, Willemze R and Otte AP . (2001). Br. J. Haematol., 112, 950–958.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr A Otte for the monoclonal anti-Ezh2 antibody and Dr A Ullrich for the polyclonal anti-Ezh2. We are grateful to Dr AM Chinnaiyan who kindly provided the myc-tagged Ezh2 and Dr GP Tuszynski for providing Hs 578Bst, Hs 578T and NPTX-1532 cell lines. We thank Dr K Reiss for his critical suggestions. We are grateful to Dr C Gabellini for her expertise in editing the figures, and Ms M Basso for her assistance in editing the manuscript. This work was supported by Sbarro Health Research Organization and NIH grants (AG and by the WW Shith Charitable Trust (PPC)). TT was supported by “Dottorato in Patologia Diagnostica e Quantitativa”, University of Siena, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tonini, T., Bagella, L., D'Andrilli, G. et al. Ezh2 reduces the ability of HDAC1-dependent pRb2/p130 transcriptional repression of cyclin A. Oncogene 23, 4930–4937 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207608
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207608
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The novel EZH2 inhibitor, GSK126, suppresses cell migration and angiogenesis via down-regulating VEGF-A
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2016)
-
Functional characterization of EZH2β reveals the increased complexity of EZH2 isoforms involved in the regulation of mammalian gene expression
Epigenetics & Chromatin (2013)
-
EZH2 inhibition decreases p38 signaling and suppresses breast cancer motility and metastasis
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2013)
-
Quantitative analysis of EZH2 expression and its correlations with lung cancer patients’ clinical pathological characteristics
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2013)
-
Polycomb and the Emerging Epigenetics of Pancreatic Cancer
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer (2011)