Abstract
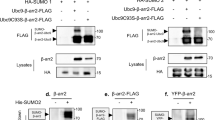
The p53 tumor suppressor is regulated by MDM2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation. Ubiquitination of p53 is regulated by ARF, which binds to MDM2 and inhibits its E3 ligase function. P53 is also subjected to modification by conjugation of SUMO-1. We found that a p53 mutant deficient for MDM2 binding (p5314Q19S) is poorly sumoylated in vivo compared to wild-type p53. Overexpression of MDM2 increases the level of p53 sumoylation, which is further stimulated by expression of ARF. Stimulation of p53 sumoylation requires a highly conserved region (102–116) encoded by exon 2 of ARF and correlates with the ability of ARF to target p53 to the nucleolus. An MDM2 deletion mutant (MDM2Δ222–437) with activated cryptic nucleolar localization signal also targets p53 to the nucleolus and efficiently promotes p53 sumoylation in the absence of ARF. Direct targeting of p53 to the nucleolus enhances its sumoylation in an MDM2- and ARF-dependent fashion. These results show that p53 sumoylation is regulated by MDM2- and ARF-mediated nucleolar targeting.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen J, Lin J and Levine AJ . (1995). Mol. Med., 1, 142–152.
Chen J, Marechal V and Levine AJ . (1993). Mol. Cell. Biol., 13, 4107–4114.
Gong L, Millas S, Maul GG and Yeh ET . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 3355–3359.
Gostissa M, Hengstermann A, Fogal V, Sandy P, Schwarz SE, Scheffner M and Del Sal G . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 6462–6471.
Hochstrasser M . (2002). Cell, 107, 5–8.
Ito A, Kawaguchi Y, Lai CH, Kovacs JJ, Higashimoto Y, Appella E and Yao TP . (2002). EMBO J., 21, 6236–6245.
Ito A, Lai CH, Zhao X, Saito S, Hamilton MH, Appella E and Yao TP . (2001). EMBO J., 20, 1331–1340.
Kahyo T, Nishida T and Yasuda H . (2002). Mol. Cell, 8, 713–718.
Kobet E, Zeng X, Zhu Y, Keller D and Lu H . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 12547–12552.
Kwek SS, Derry J, Tyner AL, Shen Z and Gudkov AV . (2002). Oncogene, 20, 2587–2599.
Lin J, Chen J, Elenbaas B and Levine AJ . (1994). Genes Dev., 8, 1235–1246.
Llanos S, Clark PA, Rowe J and Peters G . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 3, 445–452.
Lohrum MA, Ashcroft M, Kubbutat MH and Vousden KH . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 2, 179–181.
Luo J, Nikolaev AY, Imai S, Chen D, Su F, Shiloh A, Guarente L and Gu W . (2001). Cell, 107, 137–148.
Melchior F and Hengst L . (2002). Cell Cycle, 1, 245–249.
Midgley CA, Desterro JM, Saville MK, Howard S, Sparks A, Hay RT and Lane DP . (2001). Oncogene, 19, 2312–2323.
Minty A, Dumont X, Kaghad M and Caput D . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 36316–36323.
Miyauchi Y, Yogosawa S, Honda R, Nishida T and Yasuda H . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 50131–50136.
Muller S, Berger M, Lehembre F, Seeler JS, Haupt Y and Dejean A . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 13321–13329.
Prives C and Hall PA . (1999). J. Pathol., 187, 112–126.
Rodriguez MS, Dargemont C and Hay RT . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 12654–12669.
Rodriguez MS, Desterro JM, Lain S, Midgley CA, Lane DP and Hay RT . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 6455–6461.
Schmidt D and Muller S . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 2872–2887.
Sherr CJ . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 2984–2991.
Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng Eaton E, Imai SI, Frye RA, Pandita TK, Guarente L and Weinberg RA . (2001). Cell, 107, 149–159.
Weber JD, Kuo ML, Bothner B, DiGiammarino EL, Kriwacki RW, Roussel MF and Sherr CJ . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 2517–2528.
Weber JD, Taylor LJ, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ and Bar-Sagi D . (1999). Nat. Cell Biol., 1, 20–26.
Xirodimas DP, Chisholm J, Desterro JM, Lane DP and Hay RT . (2002b). FEBS Lett., 528, 207–211.
Xirodimas D, Saville MK, Edling C, Lane DP and Lain S . (2002a). Oncogene, 20, 4972–4983.
Zhang Y and Xiong Y . (1999). Mol. Cell, 3, 579–591.
Zhang Y and Xiong Y . (2001). Cell Growth Differ., 12, 175–186.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Yue Xiong for the ARF mutant constructs and helpful discussions. We also thank Dr Edward Yeh for providing the SENP1 plasmid. This work was supported by grants from the American Cancer Society and National Institutes of Health to J Chen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Chen, J. MDM2-ARF complex regulates p53 sumoylation. Oncogene 22, 5348–5357 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206851
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206851
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The SUMOylation and ubiquitination crosstalk in cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
p53 regulation by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications
Genome Instability & Disease (2022)
-
p53 signaling in cancer progression and therapy
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Desumoylase SENP6 maintains osteochondroprogenitor homeostasis by suppressing the p53 pathway
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Arf tumor suppressor disrupts the oncogenic positive feedback loop including c-Myc and DDX5
Oncogene (2015)