Abstract
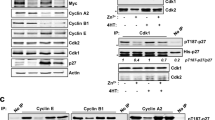
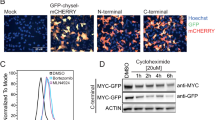
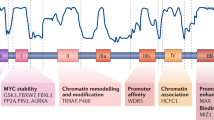
The oncoprotein transcription factor Myc plays a crucial role in the control of cell growth and proliferation. Consistent with its potent growth-promoting properties, cells have evolved a number of mechanisms to limit the activity and accumulation of the Myc protein. One of the most striking of these mechanisms is ubiquitin (Ub)-mediated proteolysis, which typically destroys Myc within minutes of its synthesis. Here we show that, despite the extreme instability of the Myc protein, cells contain a pool of Myc that is metabolically stable. Entry of Myc into the stable pool is signaled by an element within the carboxy-terminus of the protein, and is a cell-specific process that is regulated during mitosis and by interaction with Max. These data demonstrate that – even for a rapidly turned-over protein such as Myc – metabolically stable and unstable forms of a protein can co-exist in cells, and suggest that the rate of destruction of Myc molecules is linked to their specific functions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Hatoum O, Gross-Mesilaty S, Breitschopf K, Hoffman A, Gonen H, Ciechanover A, Bengal E . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 5670–5677
Blackwood EM, Eisenman RN . 1991 Science 251: 1211–1217
Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A, Pagano M . 1999 Nat. Cell Biol. 1: 193–199
Ciechanover A, DiGiuseppe JA, Bercovich B, Orian A, Richter JD, Schwartz AL, Brodeur GM . 1991 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 139–143
Evan GI, Hancock DC . 1985 Cell 43: 253–261
Furstenthal L, Swanson C, Kaiser BK, Eldridge AG, Jackson PK . 2001 Nat. Cell Biol. 3: 715–722
Gregory MA, Hann SR . 2000 Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 2423–2435
Hancock R . 2000 Chromosoma 109: 219–225
Hann SR, Eisenman RN . 1984 Mol. Cell. Biol. 4: 2486–2497
Henriksson M, Luscher B . 1996 Adv. Cancer Res. 68: 109–182
Land H, Parada LF, Weinberg RA . 1983 Nature 304: 596–602
Mendez J, Stillman B . 2000 Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 8602–8612
Mendez J, Zou-Yang XH, Kim SY, Hidaka M, Tansey WP, Stillman B . 2002 Mol. Cell 9: 481–491
Molinari E, Gilman M, Natesan S . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 6439–6447
Niklinski J, Claassen G, Meyers C, Gregory MA, Allegra CJ, Kaye FJ, Hann SR, Zajac-Kaye M . 2000 Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 5276–5284
Peukert K, Staller P, Schneider A, Carmichael G, Hanel F, Eilers M . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 5672–5686
Prescott DM, Bender MA . 1962 Exp. Cell Res. 26: 260–268
Rudolph C, Adam G, Simm A . 1999 Anal. Biochem. 269: 66–71
Sacco-Bubulya P, Spector DL . 2002 J. Cell Biol. 156: 425–436
Salghetti SE, Caudy AA, Chenoweth JG, Tansey WP . 2001 Science 293: 1651–1653
Salghetti SE, Kim SY, Tansey WP . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 717–726
Salghetti SE, Muratani M, Wijnen H, Futcher B, Tansey WP . 2000 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 3118–3123
Sears R, Nuckolls F, Haura E, Taya Y, Tamai K, Nevins JR . 2000 Genes Dev. 14: 2501–2514
Treier M, Staszewski LM, Bohmann D . 1994 Cell 78: 787–798
Varshavsky A . 1997 Trends Biochem. Sci. 22: 383–387
Acknowledgements
For reagents we thank C Bautista, D Bohmann, M Eilers, W Herr, N Hernandez and R Whittaker. We thank A Herbst, S Kim, Y Lazebnik, M Muratani and S Muthuswamy for discussions and critical comments on the manuscript. WP Tansey is a Leukemia and Lymphoma Society of America Scholar. KA Tworkowski is supported by training grant NIGMS-NIH 1T32-GM08468. This work was supported by the CSHL Cancer Center Support Grant CA45508 and by US Public Health Service grant CA-13106 from the National Cancer Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tworkowski, K., Salghetti, S. & Tansey, W. Stable and unstable pools of Myc protein exist in human cells. Oncogene 21, 8515–8520 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205976
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205976
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Partition of Myc into Immobile vs. Mobile Complexes within Nuclei
Scientific Reports (2013)
-
TLX1 and NOTCH coregulate transcription in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
Molecular Cancer (2010)
-
The 26S proteasome system degrades the ERM transcription factor and regulates its transcription-enhancing activity
Oncogene (2007)
-
Kinetics of albumin- and alpha-fetoprotein-production during rat liver development
Histochemistry and Cell Biology (2007)
-
Multiple cell-type-specific elements regulate Myc protein stability
Oncogene (2004)