Abstract
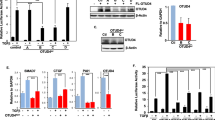
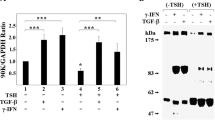
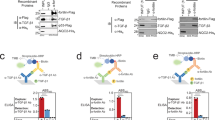
The FLRG gene encodes a secreted glycoprotein that binds to activin and is highly homologous to follistatin, an activin ligand. We cloned the promoter region of the human FLRG gene, and defined the minimal region necessary for transcription activation in a reporter-system assay. We showed that the fragment between positions −130 and +6, which consists of multiple consensus Sp1-binding sites, is required for the constitutive expression of the FLRG gene. We demonstrate here that FLRG mRNA expression is rapidly induced by TGFβ or by transfection with Smad protein expression vectors in human HepG2 cells. We investigated the transcription-regulation mechanism of FLRG expression in HepG2 cells following treatment with TGFβ. By deletion and point-mutation analysis of the FLRG promoter, we identified a Smad-binding element involved in the TGFβ-inducible expression of the FLRG gene. Moreover, transactivation of the FLRG promoter by TGFβ was compromised by dominant-negative mutants of Smad3 and Smad4 proteins. In addition, gel electrophoresis mobility-shift assays demonstrated the specific interaction of Smad3 and Smad4 proteins with the Smad-binding element consensus motif found in the FLRG promoter. Taken together, our data imply that Smad proteins participate in the regulation of expression of FLRG, a new target of TGFβ transcription activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brodin G, Ahgren A, ten Dijke P, Heldin CH, Heuchel R . 2000 J. Biol. Chem. 275: 29023–29030
Chen X, Rubock MJ, Whitman M . 1996a Nature 383: 691–696
Chen Y, Lebrun JJ, Vale W . 1996b Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 12992–12997
Cook T, Gebelein B, Urrutia R . 1999 Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 880: 94–102
Denissova NG, Pouponnot C, Long J, He D, Liu F . 2000 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 6397–6402
Dennler S, Itoh S, Vivien D, ten Dijke P, Huet S, Gauthier JM . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 3091–3100
DePaolo LV . 1997 Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 214: 328–339
Derynck R, Zhang Y, Feng XH . 1998 Cell 95: 737–740
Dybedal I, Jacobsen SE . 1995 Blood 86: 949–957
Feng XH, Lin X, Derynck R . 2000 EMBO J. 19: 5178–5193
Hayette S, Gadoux M, Martel S, Bertrand S, Tigaud I, Magaud JP, Rimokh R . 1998 Oncogene. 16: 2949–2954
Heldin CH, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P . 1997 Nature 390: 465–471
Hua X, Miller ZA, Wu G, Shi Y, Lodish HF . 1999 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 13130–13135
Johansson BM, Wiles MV . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 141–151
Jonk LJ, Itoh S, Heldin CH, ten Dijke P, Kruijer W . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 21145–21152
Kawabata M, Inoue H, Hanyu A, Imamura T, Miyazono K . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 4056–4065
Kingsley DM . 1994 Genes Dev. 8: 133–146
Kitamura K, Aota S, Sakamoto R, Yoshikawa SI, Okazaki K . 2000 Blood 95: 3371–3379
Krystal G, Lam V, Dragowska W, Takahashi C, Appel J, Gontier A, Jenkins A, Lam H, Quon L, Lansdorp P . 1994 J. Exp. Med. 180: 851–860
Lagna G, Hata A, Hemmati-Brivanlou A, Massague J . 1996 Nature 383: 832–836
Maguer-Satta V, Bartholin L, Jeanpierre S, Gadoux M, Bertrand S, Martel S, Magaud J, Rimokh R . 2001 Exp. Hematol. 29: 301–308
Massague J, Wotton D . 2000 EMBO J. 19: 1745–1754
Moustakas A, Kardassis D . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 6733–6738
Nagarajan RP, Zhang J, Li W, Chen Y . 1999 J. Biol. Chem. 274: 33412–33418
Nakao A, Imamura T, Souchelnytskyi S, Kawabata M, Ishisaki A, Oeda E, Tamaki K, Hanai J, Heldin CH, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 5353–5362
Pardali K, Kurisaki A, Moren A, ten Dijke P, Kardassis D, Moustakas A . 2000 J. Biol. Chem. 275: 29244–29256
Phillips DJ, de Kretser DM . 1998 Front Neuroendocrinol 19: 287–322
Pierelli L, Marone M, Bonanno G, Mozzetti S, Rutella S, Morosetti R, Rumi C, Mancuso S, Leone G, Scambia G . 2000 Blood 95: 3001–3009
Shao L, Frigon Jr NL, Young AL, Yu AL, Mathews LS, Vaughan J, Vale W, Yu J . 1992 Blood 79: 773–781
Shiozaki M, Sakai R, Tabuchi M, Nakamura T, Sugino K, Sugino H, Eto Y . 1992 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 1553–1556
Song CZ, Siok TE, Gelehrter TD . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 29287–29290
Suske G . 1999 Gene 238: 291–300
ten Dijke P, Miyazono K, Heldin CH . 2000 Trends Biochem. Sci. 25: 64–70
Tsuchida K, Arai KY, Kuramoto Y, Yamakawa N, Hasegawa Y, Sugino H . 2000 J. Biol. Chem. 275: 40788–40796
Vindevoghel L, Kon A, Lechleider RJ, Uitto J, Roberts AB, Mauviel A . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 13053–13057
Wrana JL . 2000 Cell 100: 189–192
Xiong Y, Connolly T, Futcher B, Beach D . 1991 Cell 65: 691–699
Yamashita T, Takahashi S, Ogata E . 1992 Blood 79: 304–307
Ying SY, Zhang Z, Furst B, Batres Y, Huang G, Li G . 1997 Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 214: 114–122
Yu J, Dolter KE . 1997 Cytokines Cell Mol. Ther. 3: 169–177
Zawel L, Dai JL, Buckhaults P, Zhou S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Kern SE . 1998 Mol. Cell 1: 611–617
Zhang W, Ou J, Inagaki Y, Greenwel P, Ramirez F . 2000 J. Biol. Chem. 275: 39237–39245
Zhang Y, Feng X, We R, Derynck R . 1996 Nature 383: 168–172
Zhang YQ, Kanzaki M, Shibata H, Kojima I . 1997 Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1354: 204–210
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from INSERM, the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer, the Ligue contre le Cancer (Comités du Rhône et de la Saône et Loire). We would like to thank JM Gauthier for providing the pGL3-MLP plasmid, P ten Dijke for the mammalian expression vectors encoding the flag-tagged human Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4, R Derynck for the mammalian expression vectors encoding human dominant-negative Smad3 (Smad3ΔC) and Smad4 (Smad4ΔC), and A Mauviel for bacterial vectors encoding GST-Smad proteins. We would like to thank MJ N'Guyen for her technical assistance. L Bartholin held a doctoral fellowship from the Ligue contre le Cancer, comité de la Haute Savoie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartholin, L., Maguer-Satta, V., Hayette, S. et al. FLRG, an activin-binding protein, is a new target of TGFβ transcription activation through Smad proteins. Oncogene 20, 5409–5419 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204720
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204720
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Follistatin-Like 3 Mediates Paracrine Fibroblast Activation by Cardiomyocytes
Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research (2012)
-
The Role of Activin in Mammary Gland Development and Oncogenesis
Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia (2011)
-
Human placenta and fetal membranes express follistatin-related gene mRNA and protein
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2003)
-
Transcription activation of FLRG and follistatin by activin A, through Smad proteins, participates in a negative feedback loop to modulate activin A function
Oncogene (2002)