Abstract
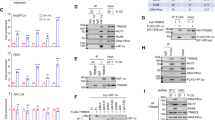
Hypoxia inducible factors (HIF1, 2 and 3), consisting of α and β subunits, play an essential role in various responses to hypoxia. Nuclear entry of α subunits is a necessary step for the formation of DNA-binding complex with β subunit, which is constitutively localized in the nucleus. We show here that the nuclear accumulation of HIF2α induced by hypoxia is mediated through a novel variant of bipartite-type nuclear localization signal (NLS) in the C-terminus of the protein, which has an unusual length of spacer sequence between two adjacent basic domains. We further show that when the ubiquitin-proteasome system was deficient or inhibited, HIF2α accumulated in the nucleus even under normoxia, also mediated through the bipartite NLS. These findings indicate that the protein stability is critical for the nuclear localization of HIF2α and hypoxia is not a necessary factor for the process. Importantly, the NLS of HIF2α is also conserved in the other HIF family members, HIF1α and HIF3α. Mutational analyses proved that the NLS mediating the nuclear localization of HIF1α is indeed bipartite-, but not monopartite-type as thought before. Our results suggest that the newly identified NLS is crucial for the functional regulation of HIF family.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews NC, Faller DV . 1991 Nucl. Acids. Res. 19: 2499
Bear J, Tan W, Zolotukhin AS, Tabernero C, Hudson EA, Felber BK . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 6306–6317
Burglin TR, Mattaj IW, Newmeyer DD, Zeller R, De Robertis EM . 1987 Genes Dev. 1: 97–107
Chilov D, Camenisch G, Kvietikova I, Ziegler U, Gassmann M, Wenger RH . 1999 J. Cell Sci. 112: 1203–1212
Cockman ME, Masson N, Mole DR, Jaakkola P, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Maher ER, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH . 2000 J. Biol. Chem. 275: 25733–25741
Conrad PW, Freeman TL, Beitner-Johnson D, Millhorn DE . 1999 J. Biol. Chem. 274: 33709–33713
Dingwall C, Laskey RA . 1991 Trends Biochem. Sci. 16: 478–481
Eguchi H, Ikuta T, Tachibana T, Yoneda Y, Kawajiri K . 1997 J. Biol. Chem. 272: 17640–17647
Ema M, Hirota K, Mimura J, Abe H, Yodoi J, Sogawa K, Poellinger L, Fujii-Kuriyama Y . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 1905–1914
Ema M, Taya S, Yokotani N, Sogawa K, Matsuda Y, Fujii-Kuriyama Y . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 4273–4278
Gu YZ, Moran SM, Hogenesch JB, Wartman L, Bradfield CA . 1998 7: Gene Expr 205–213
Hogenesch JB, Gu YZ, Jain S, Bradfield CA . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 5474–5479
Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M, Bunn HF . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 7987–7992
Ikuta T, Eguchi H, Tachibana T, Yoneda Y, Kawajiri K . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 2895–2904
Iliopoulos O, Levy AP, Jiang C, Kaelin Jr WG, Goldberg MA . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 10595–10599
Imai Y, Matsushima Y, Sugimura T, Terada M . 1991 Nucl. Acids., Res. 19: 2785
Jans DA, Hubner S . 1996 Physiol. Rev. 76: 651–685
Kaelin Jr WG, Maher E . 1998 Trends Genet. 14: 423–426
Kallio PJ, Okamoto K, O'Brien S, Carrero P, Makino Y, Tanaka H, Poellinger L . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 6573–6586
Luo JC, Yamaguchi S, Shinkai A, Shitara K, Shibuya M . 1998 Cancer Res. 58: 2652–2660
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER, Ratcliffe PJ . 1999 Nature 399: 271–275
Ohh M, Park CW, Ivan M, Hoffman MA, Kim TY, Huang LE, Pavletich N, Chau V, Kaelin Jr WG . 2000 Nat. Cell. Biol. 2: 423–427
Salceda S, Caro J . 1997 J. Biol. Chem. 272: 2642–2647
Semenza GL . 1998 Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 8: 588–594
Stebbins CE, Kaelin Jr WG, Pavletich NP . 1999 Science 284: 455–461
Tanimoto K, Makino Y, Pereira T, Poellinger L . 2000 EMBO J. 19: 4298–4309
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL . 1995 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 5510–5514
Wiesener MS, Turley H, Allen WE, Willam C, Eckardt KU, Talks KL, Wood SM, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH . 1998 Blood 92: 2260–2268
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Dr Tetsuya Nosaka and Dr Yoshiharu Amasaki for their helpful discussions. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Special Project Research on Cancer-Bioscience 04253204 from the Ministry of Education (to M Shibuya) and a fellowship from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (to JC Luo).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, J., Shibuya, M. A variant of nuclear localization signal of bipartite-type is required for the nuclear translocation of hypoxia inducible factors (1α, 2α and 3α). Oncogene 20, 1435–1444 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204228
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204228
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Liposome-coated CaO2 nanoblockers for enhanced checkpoint blockade therapy by inhibiting PD-L1 de novo biosynthesis
Nano Research (2023)
-
Heat shock protein-90alpha (Hsp90α) stabilizes hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in support of spermatogenesis and tumorigenesis
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)
-
HIF Inhibitors: Status of Current Clinical Development
Current Oncology Reports (2019)
-
HIF1α drives chemokine factor pro-tumoral signaling pathways in acute myeloid leukemia
Oncogene (2018)
-
Nuclear-cytoplasmatic shuttling of proteins in control of cellular oxygen sensing
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2015)