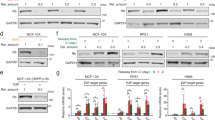
Abstract
We have previously demonstrated that overexpression of p204, a member of the Ifi 200 gene family, inhibits growth, delays G0/G1 progression into S phase, and impairs E2F-mediated transcriptional activity. In this study, we show that p204 directly binds the retinoblastoma protein (pRb) in vivo to exert its activity. Transient p204 overexpression in Rb+/+ mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEF) inhibits cell proliferation, but does not affect cell growth in MEF derived from Rb−/− mice. Two human cell lines, Saos2 and C33A, bearing an inactive pRb, but not primary human embryo fibroblasts, are resistant to the p204 antiproliferative activity. p204 contains two 200 amino acid motifs, designated as type a or b domains, each containing a canonical Rb binding motif (LXCXE). When dominant-negative mutants at the Rb binding motif were transfected in Rb+/+ MEF, p204 lost its ability to inhibit cell growth, delay cell transition from G1 to S phase, and impair DNA synthesis. Moreover p204 overexpression in Rb+/+ MEF led to a significant decrease of both DHFR and PCNA proteins, two S phase markers. By contrast, this effect was not observed when Rb+/+ MEF were transfected with a p204 mutated at both Rb binding sites. Finally, overexpression of the LXCXE p204 mutant rendered Rb+/+ MEF resistant to the IFN-α antiproliferative activity, in comparison to the untransfected Rb+/+ MEF. As expected, Rb−/− cells were unsensitive to the IFN-α induced growth inhibition. Taken as a whole, these results suggest that (i) p204 contributes to the IFN-α antiproliferative activity and (ii) the primary target of p204 leading to efficient G1 arrest as well as to blockade of DNA replication from G1 phase is the pRb regulatory system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartek J, Lukas J and Bartkova J. . 1999 J. Pathol. 187: 95–99.
Brejm A, Miska E, Reid J, Bannister A and Kouzarides T. . 1999 Br. J. Cancer 80: 38–41.
Choubey D and Lengyel P. . 1992 J. Cell. Biol. 116: 1333–1341.
Choubey D and Lengyel P. . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 6134–6140.
Choubey D, Li SJ, Datta B, Gutterman JU and Lengyel P. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 5668–5678.
Cobrinik D, Lee MH, Hannon G, Mulligan G, Bronson RT, Dyson N, Harlow E, Beach D, Weinberg RA and Jacks T. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 1633–1644.
Datta B, Min W, Burma S and Lengyel P. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 1074–1083.
Dawson MJ and Trapani A. . 1996 J. Leuk. Biol. 60: 1–7.
De Maeyer E and De Mayer-Guignard J. . 1988 Interferons and Other Regulatory Cytokines. New York: Wiley and Sons
DePinho R. . 1998 Nature 391: 533–534.
Dyson N. . 1998 Genes Dev. 12: 2245–2262.
Evinger M, Maeda S and Pestka S. . 1981a J. Biol. Chem. 256: 2113–2114.
Evinger M, Rubinstein M and Pestka S. . 1981b Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 210: 319–329.
Gale M and Katze MG. . 1998 Pharmacol. Ther. 78: 29–46.
Gariglio M, De Andrea M, Lembo M, Ravotto M, Zappador C, Valente G and Landolfo S. . 1998 J. Leuk. Biol. 64: 608–614.
Gariglio M, Gaboli M, Mana C, Ying GG, Gribaudo G, Cavallo R and Landolfo S. . 1994 Eur. J. Biochem. 221: 731–739.
Gariglio M, Panico S, Cavallo G, Choubey D, Lengyel P and Landolfo S. . 1992 Virology 187: 115–123.
Gieni RS, Li Y and Glass KT. . 1995 J. Immunol. Methods 187: 85–93.
Gribaudo G, Ravaglia S, Guandalini L, Riera L, Gariglio M and Landolfo S. . 1997 Eur. J. Biochem. 249: 258–264.
Gribaudo G, Riera L, De Andrea M and Landolfo S. . 1999 FEBS 456: 31–36.
Hertel L, De Andrea M, Bellomo G, Santoro P, Landolfo S and Gariglio M. . 1999a Exp. Cell Res. 250: 313–328.
Hertel L, De Andrea M, Azzimonti B, Rolle S, Gariglio M and Landolfo S. . 1999b Virology 262: 1–8.
Jacks T, Fazeli A, Schmitt EM, Bronson RT, Goodell MA and Weinberg RA. . 1992 Nature 359: 295–300.
Johnstone RW and Trapani JA. . 1999 Mol. Cell Biol. 19: 5833–5838.
Kaelin Jr WG. . 1997 Cancer Invest. 15: 243–254.
Landolfo S, Gribaudo G, Angeretti A and Gariglio M. . 1995 Pharmacol. Ther. 65: 415–442.
Landolfo S, Gariglio M, Gribaudo G and Lembo D. . 1998 Biochimie 80: 721–728.
Lee M-H, Williams BO, Mulligan G, Mukai S, Bronson RT, Dyson N, Harlow E and Jacks T. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 1621–1632.
Lembo D, Angeretti A, Benefazio S, Hertel L, Gariglio M, Novelli F and Landolfo S. . 1995 J. Biol. Reg. Homeost. Ag. 9: 42–46.
Lembo M, Sacchi C, Zappador C, Bellomo G, Gaboli M, Pandolfi PP, Gariglio M and Landolfo S. . 1998 Oncogene 16: 1543–1551.
Lengyel P, Choubey D, Li S-J and Datta B. . 1995 Semin. Virol. 6: 203–213.
Liu C, Wang H and Lengyel P. . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 2845–2854.
Min W, Ghosh S and Lengyel P. . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 359–368.
Mulligan G and Jacks T. . 1998 TIG 14: 223–228.
Nevins JR, Leone G, DeGregori J and Jakoi L. . 1997 J. Cell Physiol. 173: 233–236.
Peeper DS, Upton TM, Ladha MH, Neuman E, Zalvide J, Bernards R, DeCaprio JA and Ewen ME. . 1997 Nature 386: 177–181.
Sokawa Y, Watanabe Y, Watanabe Y and Kawade Y. . 1977 Nature 268: 236–238.
Staehli P, Pitossi F and Pavlovic J. . 1993 Trends Cell Biol. 3: 268–272.
Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BRG, Silverman RH and Schreiber RD. . 1998 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67: 227–264.
Stiegler P and Giordano A. . 1998 Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 20: 25–42.
Thomas NSB, Pizzey AR, Tiwari S, Williams CD and Ya J. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 23659–23667.
Verona R, Moberg K, Estes S, Starz M, Vernon JP and Lees JA. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 7268–7282.
Wang JYJ. . 1997 Curr. Opin. Gen. Dev. 7: 39–45.
Wang JY, Knudsen ES and Welch PJ. . 1994 Adv. Cancer Res. 64: 25–85.
Weinberg RA. . 1995 Cell 81: 323–330.
Yan D-H, Wen Y, Sporn B, Choubey D, Gutterman JU and Hung M-C. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 807–811.
Zalvide J and DeCaprio JA. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 5800–5810.
Zhu X, Pattenden S and Brenner R. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 4940–4947.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Massimo Geuna (IRCC, Turin) for performing flow cytometry analysis. This work was supported by grants from Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), Istituto Superiore di Sanità (PF ‘AIDS’) and MURST-CNR (‘Biotechnology Program L95/95’ and ‘Program 40%’).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hertel, L., Rolle, S., De Andrea, M. et al. The retinoblastoma protein is an essential mediator that links the interferon-inducible 204 gene to cell-cycle regulation. Oncogene 19, 3598–3608 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203697
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203697
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RNA-Seq analysis of interferon inducible p204-mediated network in anti-tumor immunity
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Role of IFI 16, a member of the interferon-inducible p200-protein family, in prostate epithelial cellular senescence
Oncogene (2003)
-
Retinoblastoma (Rb) protein upregulates expression of the Ifi202 gene encoding an interferon-inducible negative regulator of cell growth
Oncogene (2003)
-
p202, an interferon-inducible negative regulator of cell growth, is a target of the adenovirus E1A protein
Oncogene (2001)