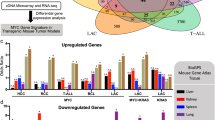
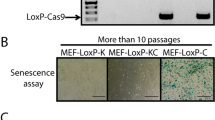
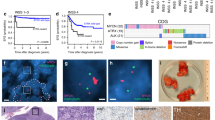
Abstract
The c-myc gene is frequently over-expressed in human cancers and is involved in regulation of proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. c-Myc is a transcription factor that acts primarily by regulating the expression of other genes. However, it has been very difficult to identify bona fide c-Myc target genes that explain its diverse biological activities. The recent generation of c-myc deficient Rat1A fibroblasts with a profound and stable growth defect provides a new system to search for genes that can substitute for c-myc in proliferation. In this study, we have attempted to identify genes that rescue the slow growth phenotype of c-myc null cells through introduction of a series of potent cell cycle regulatory genes and several retroviral cDNA expression libraries. None of the candidate genes tested, including SV40 T-antigen and adenovirus E1A, caused reversal of the c-myc null growth defect. Furthermore, extensive screens with high-complexity retroviral cDNA libraries from three different tissue sources revealed that only c-myc and N-myc rescued the c-myc null slow-growth phenotype. Our data support the notion that there are no functional equivalents of the myc family of proto-oncogenes and also suggest that there are no c-Myc-activated genes that alone can substitute for c-Myc in control of cell proliferation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bello FC, Packham G and Cleveland JL. . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 7804–7808.
Bernards R, Dessain SK and Weinberg RA. . 1986 Cell 47: 667–674.
Berns K, Hijmans EM and Bernards R. . 1997 Oncogene 15: 1347–1356.
Biro S, Fu YM, Yu ZX and Epstein SE. . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 654–658.
Blackwood EM and Eisenman RN. . 1991 Science 251: 1211–1217.
Bouchard C, Thieke K, Maier A, Saffrich R, Hanley HJ, Ansorge W, Reed S, Sicinski P, Bartek J and Eilers M. . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 5321–5333.
Bush A, Mateyak M, Dugan K, Obaya A, Adachi S, Sedivy J and Cole M. . 1998 Genes Dev. 12: 3797–3802.
Eilers M, Schirm S and Bishop JM. . 1991 EMBO J. 10: 133–141.
Einat M, Resnitzky D and Kimchi A. . 1985 Nature 313: 597–600.
Galaktionov K, Chen X and Beach D. . 1996 Nature 382: 511–517.
Grandori C, Mac J, Siebelt F, Ayer DE and Eisenman RN. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 4344–4357.
Heikkila R, Schwab G, Wickstrom E, Loke SL, Pluznik DH, Watt R and Neckers LM. . 1987 Nature 328: 445–449.
Henriksson M and Luscher B. . 1996 Adv. Cancer Res. 68: 109–182.
Hermeking H, Rago C, Schuhmacher M, Li Q, Barrett JF, Obaya AJ, O’Connell BC, Mateyak MK, Tam W, Kohlhuber F, Dang CV, Sedivy JM, Eick D, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW. . 2000 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 2229–2234.
Kato GJ, Barrett J, Villa GM and Dang CV. . 1990 Mol. Cell. Biol. 10: 5914–5920.
Kelly K, Cochran BH, Stiles CD and Leder P. . 1983 Cell 35: 603–610.
Kretzner L, Blackwood EM and Eisenman RN. . 1992 Nature 359: 426–429.
Lewis BC, Shim H, Li Q, Wu CS, Lee LA, Maity A and Dang CV. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 4967–4978.
Li LH, Nerlov C, Prendergast G, MacGregor D and Ziff EB. . 1994 EMBO J. 13: 4070–4079.
Marhin WW, Chen S, Facchini LM, Fornace AJ and Penn LZ. . 1997 Oncogene 14: 2825–2834.
Mateyak MK, Obaya AJ, Adachi S and Sedivy JM. . 1997 Cell Growth Differ. 8: 1039–1048.
Mateyak MK, Obaya AJ and Sedivy JM. . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 4672–4683.
Miltenberger RJ, Sukow KA and Farnham PJ. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 2527–2535.
Morgenstern JP and Land H. . 1990 Nucleic Acids Res. 18: 3587–3596.
Penn LJ, Brooks MW, Laufer EM and Land H. . 1990 EMBO J. 9: 1113–1121.
Perez-Roger I, Solomon DL, Sewing A and Land H. . 1997 Oncogene 14: 2373–2381.
Pietenpol JA, Stein RW, Moran E, Yaciuk P, Schlegel R, Lyons RM, Pittelkow MR, Munger K, Howley PM and Moses HL. . 1990 Cell 61: 777–785.
Prochownik EV, Kukowska J and Rodgers C. . 1988 Mol. Cell. Biol. 8: 3683–3695.
Ralston R. . 1991 Nature 353: 866–868.
Reisman D, Elkind NB, Roy B, Beamon J and Rotter V. . 1993 Cell Growth Differ. 4: 57–65.
Rosenwald IB. . 1996 Cancer Lett. 102: 113–123.
Serrano M, Gomez LE, DePinho RA, Beach D and Bar SD. . 1995 Science 267: 249–252.
Stone J, de LT, Ramsay G, Jakobovits E, Bishop JM, Varmus H and Lee W. . 1987 Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 1697–1709.
Vigo E, Muller H, Prosperini E, Hateboer G, Cartwright P, Moroni MC and Helin K. . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 6379–6395.
Wolfel T, Hauer M, Schneider J, Serrano M, Wolfel C, Klehmann-Hieb E, De Plaen E, Hankeln T, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH and Beach D. . 1995 Science 269: 1281–1284.
Xiao Q, Claassen G, Shi J, Adachi S, Sedivy J and Hann SR. . 1998 Genes Dev. 12: 3803–3808.
Acknowledgements
We thank J Sedivy for the kind gift of the myc null cells, Drs B Amati, AJ van der Eb, W Krek, D Peeper and M van Lohuizen for the gift of plasmids and antisera. This work was supported by the Dutch Cancer Society (KWF) and a Biomed 2 program grant from the European Community to R Bernards and by grants from the Edward Mallinckrodt, Jr. Foundation and NCI CA76418-01 to GQ Daley.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berns, K., Hijmans, E., Koh, E. et al. A genetic screen to identify genes that rescue the slow growth phenotype of c-myc null fibroblasts. Oncogene 19, 3330–3334 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203639
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203639
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
N-Myc overexpression increases cisplatin resistance in neuroblastoma via deregulation of mitochondrial dynamics
Cell Death Discovery (2016)
-
MYC activity is negatively regulated by a C-terminal lysine cluster
Oncogene (2014)
-
AP4 directly downregulates p16 and p21 to suppress senescence and mediate transformation
Cell Death & Disease (2013)
-
c-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism
Nature (2009)
-
Akt and 14-3-3η regulate Miz1 to control cell-cycle arrest after DNA damage
Nature Cell Biology (2005)