Abstract
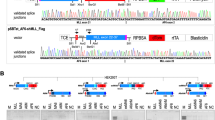
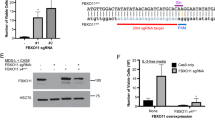
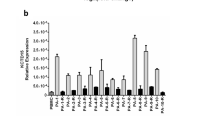
We report here the molecular study of a t(11;19)(q13;p13) translocation observed in a case of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. This translocation leads to the juxtaposition of the CCND1 gene on chromosome 11 to a new transcriptionnal unit on chromosome 19. The cDNA of this new evolutionarily conserved gene (named FLRG for Follistatin-Related Gene) codes for a secreted glycoprotein of the follistatin-module-protein family. FLRG is expressed in a wide range of human and murine adult tissues and its expression seems to be tightly regulated during murine embryogenesis. Its transcripts could not be detected in hematopoietic cells from all lineages and in particular in cells from lymphoid B and T lineage except in the t(11;19)-carrying leukemia described here. A great variability of expression is observed among the other tumoral cell lines analysed. Besides the t(11;19)-carrying leukemia described in this work, structural rearrangements of the FLRG locus have been found in a non-Hodgkin lymphoma, suggesting that it may play a role in leukemogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayette, S., Gadoux, M., Martel, S. et al. FLRG (follistatin-related gene), a new target of chromosomal rearrangement in malignant blood disorders. Oncogene 16, 2949–2954 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201807
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201807
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
FSTL3 is associated with prognosis and immune cell infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2024)
-
A case of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with an unreported combination of chromosomal abnormalities: gain of isochromosome 5p, tetrasomy 8 and unbalanced translocation der(19)t(17;19)(q23;p13)
Molecular Cytogenetics (2013)
-
Activin, neutrophils, and inflammation: just coincidence?
Seminars in Immunopathology (2013)
-
Establishment and characterization of a new hypoxia-resistant cancer cell line, OCUM-12/Hypo, derived from a scirrhous gastric carcinoma
British Journal of Cancer (2010)
-
Activin signaling as an emerging target for therapeutic interventions
Cell Communication and Signaling (2009)