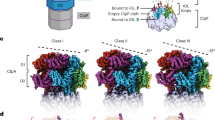
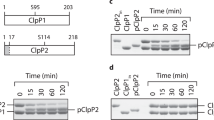
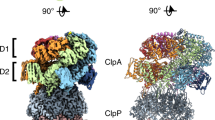
Abstract
The Clp/Hsp100 ATPases are hexameric protein machines that catalyze the unfolding, disassembly and disaggregation of specific protein substrates in bacteria, plants and animals. Many family members also interact with peptidases to form ATP-dependent proteases. In Escherichia coli, for instance, the ClpXP protease is assembled from the ClpX ATPase and the ClpP peptidase. Here, we have used multiple sequence alignments to identify a tripeptide 'IGF' in E. coli ClpX that is essential for ClpP recognition. Mutations in this IGF sequence, which appears to be part of a surface loop, disrupt ClpXP complex formation and prevent protease function but have no effect on other ClpX activities. Homologous tripeptides are found only in a subset of Clp/Hsp100 ATPases and are a good predictor of family members that have a ClpP partner. Mapping of the IGF loop onto a homolog of known structure suggests a model for ClpX–ClpP docking.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, J., Hartling, J.A. & Flanagan, J.M. Cell 91, 447–456 (1997).
Gottesman, S., Maurizi, M.R. & Wickner, S. Cell 91, 435–438 (1997).
Kessel, M. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 250, 587–594 (1995).
Rohrwild, M. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 133–139 (1997).
Hoskins, J.R., Pak, M., Maurizi, M.R. & Wickner, S. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 12135–12140 (1998).
Schrimer, E.C., Glover, J.R., Singer, M.A. & Lindquist, S. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21, 289–296 (1996).
Bochtler, M. et al. Nature 403, 800–805 (2000).
Sousa, M.C., Trame, C.B., Tsuruta, H., Wilbanks, S.M., Reddy, V.S. & McKay, D.B. Cell 103, 633–643 (2000).
Neuwald, A.F., Aravind, L., Spouge, J.L. & Koonin, E.V. Genome Res. 9, 27–43 (1999).
Levchenko, I., Luo, L. & Baker, T.A. Genes Dev. 9, 2399–2408 (1995).
Kruklitis, R., Welty, D.J. & Nakai, H. EMBO J. 15, 935–944 (1996).
Mhammedi-Alaoui, A., Pato, M., Gama, M. & Toussaint, A. Mol. Microbiol. 11, 1109–1116 (1994).
Makovets, S., Doronina, V.A. & Murray, N.E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 9757–9762 (1999).
Levchenko, I., Yamauchi, M. & Baker, T.A. Genes Dev. 11, 1561–1572 (1997).
Kim, Y.-I. et al. Mol. Cell 5, 639–648 (2000).
Baker, T. A., Mizuuchi, M., Savilahti, H. & Mizuuchi, K. Cell 74, 723–733 (1993).
Yakhnin, A.V., Vinokurov, L.M., Surin, A.K. & Alakhov, Y.B. Protein Expr. Purif. 14, 382–386 (1998).
Gibson, T. & Higgins, Thompson, J. http://www.visac.uq.edu.au/course/ClustalX/clustalx.html (1994).
Acknowledgements
We thank E. Beade for preparation of Fig. 4b, L. Roldan for assistance with figures, and N. Murray for advice on the restriction alleviation assay. This work was supported by an NIH grant and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YI., Levchenko, I., Fraczkowska, K. et al. Molecular determinants of complex formation between Clp/Hsp100 ATPases and the ClpP peptidase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 8, 230–233 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/84967
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/84967
This article is cited by
-
Functional cooperativity between the trigger factor chaperone and the ClpXP proteolytic complex
Nature Communications (2021)
-
The functional ClpXP protease of Chlamydia trachomatis requires distinct clpP genes from separate genetic loci
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Staphylococcus aureus ClpX localizes at the division septum and impacts transcription of genes involved in cell division, T7-secretion, and SaPI5-excision
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Molecular and structural insights into an asymmetric proteolytic complex (ClpP1P2) from Mycobacterium smegmatis
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
The proteOMIC era: a useful tool to gain deeper insights into plastid physiology
Theoretical and Experimental Plant Physiology (2019)