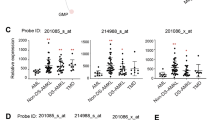
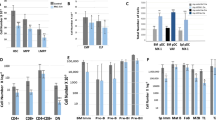
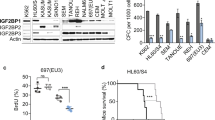
Abstract
PEBP2/CBF is a heterodimeric transcription factor essential for genetic regulation of hematopoiesis and osteogenesis. DNA binding by PEBP2/CBFα is accomplished by a highly conserved DNA binding domain, the Runt domain (RD), whose structure adopts an S-type immunoglobulin fold when bound to DNA. The supplementary subunit β enhances DNA binding by the RD in vitro , but its role in the control of gene expression has remained largely unknown in vivo. Chromosome 16 inversion creates a chimeric gene product fusing PEBP2/CBFβ to a portion of the smooth muscle myosin heavy chain (PEBP2/CBFβ-SMMHC) that is causally associated with the onset of acute myeloid leukemia in humans. The three-dimensional structure of PEBP2/CBFβ has been determined in solution and is shown to adopt a fold related to the β-barrel oligomer binding motif. Direct analysis of a 43.6kD ternary RD–β–DNA complex identifies the likely surface of β in contact with the RD. The structure of PEBP2/CBFβ enables a molecular understanding of the capacity of PEBP2/CBFβ-SMMHC to sequester PEBP2/CBFα in the cytoplasm and therefore provides a molecular basis for understanding leukemogenic transformation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Nagata, T. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 6, 615– 619 (1999).
Look, A. T. Science 278, 1059–1064 ( 1997).
Bax, A. & Grzesiek, S. Acc. Chem. Res. 26, 131–138 (1993).
Clore, G.M. & Gronenborn, A.M. Prot. Sci. 3, 372–390 (1994).
Omichinski, J.G., Pedone, P. V., Felsenfeld, G., Gronenborn, A.M. & Clore, G.M. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 122–132 (1997).
Laskowski, R.A., Rullmann, J.A., MacArthur, M.W., Kaptein, R. & Thornton, J.M. J. Biomol. NMR 8, 477–486 (1996).
Sippl, M.J. Proteins 17, 355–362 ( 1993).
Murzin, A.G. EMBO J. 12, 861–867 ( 1993).
Holm, L. & Sander, C. J. Mol. Biol. 233, 123–138 (1993).
Peat, T.S., Newman, J., Waldo, G., Berendzen, J. & Terwilliger, T.C. Structure 6, 1207– 1214 (1998).
Stein, P.E., Boodhoo, A., Tyrrell, G.J., Brunton, J.L. & Read, R.J. Nature 355, 748–750 (1992).
Hynes, T. R. & Fox, R.O. Proteins 10, 92–105 (1991).
Ruff, M. et al. Science 252, 1682–1689 (1991).
Akamatsu, Y. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 14497– 14500 (1997).
Huang, X. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 2480– 2487 (1998).
Huang, X., Peng, J. W., Speck, N. A. & Bushweller, J. H. Nature Struct. Biol. 6, 624–627 (1999).
Ogawa, E. et al. Virol. 194, 314–331 (1993).
Wang, S. et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 3324– 3339 (1993).
Kagoshima, H., Akamatsu, Y., Ito, Y. & Shigesada, K. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 33074–33082 ( 1996).
Golling, G., Li, L., Pepling, M., Stebbins, M. & Gergen, J.P. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 932– 942 (1996).
Kanno, Y., Kanno, T., Sakakura, C., Bae S-C. & Ito Y. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 4252–4261 (1998).
Adya, N., Stacy, T., Speck, N. A. & Liu, P. P. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 7432–7443 ( 1998).
Bax, A. et al. Methods Enzymol. 239, 79– 105 (1994).
Spera, S. & Bax, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113, 5490–5492 (1991).
Wishart, D. S. & Sykes, B.D. J. Biomol. NMR 4, 171–180 ( 1994).
Wüthrich, K. NMR of proteins and nucleic acids (Wiley, New York; 1986).
Groft, C. M., Uljon, S.N., Wang, R. & Werner, M.H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 9117–9122 ( 1998).
Nilges, M. Prot. Struct. Funct. Genet. 17, 295– 309 (1993).
Brünger, A. T. X-PLOR Manual, Version 3.1 (Yale University Press, New Haven, Conecticut; 1992).
Garrett, D.S. et al. J. Magn. Reson. (B) 104, 99– 103 (1994).
Kuszewski, J., Gronenborn, A.M., Clore, G.M. J. Magn. Reson. 125, 171– 177 (1997).
Carson, M. J. Mol. Graphics 5, 103–106 (1987).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K. & Honig, B. Proteins 11, 281– 296 (1991).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge many stimulating discussions with T. Nagata, L. Glaser, J. Hill, A. Kim, D. Sorce, A. Seth and M. Osato. This work was supported in part by generous grants from the Sidney Kimmel Cancer Foundation, the Alexander and Alexandrine Sinsheimer Foundation and the New York Community Trust to M.H.W., a postdoctoral fellowship from the Leukemia Research Foundation to V.G. and grants from the Ministry of Education, Science, Culture and Sports of Japan to Y.I. and K.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goger, M., Gupta, V., Kim, WY. et al. Molecular insights into PEBP2/CBFβ-SMMHC associated acute leukemia revealed from the structure of PEBP2/CBFβ. Nat Struct Mol Biol 6, 620–623 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/10664
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/10664
This article is cited by
-
Oncogenic potential of the RUNX gene family: ‘Overview’
Oncogene (2004)
-
Core-binding factors in haematopoiesis and leukaemia
Nature Reviews Cancer (2002)
-
Karyotype instability between diagnosis and relapse in 117 patients with acute myeloid leukemia: implications for resistance against therapy
Leukemia (2002)
-
AML1 and the AML1-ETO fusion protein in the pathogenesis of t(8;21) AML
Oncogene (2001)
-
Molecular biology of leukemia
Current Oncology Reports (2000)