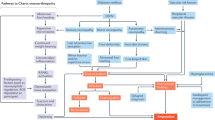
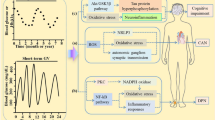
Abstract
Diabetic neuropathy is the most common neuropathy in industrialized countries, and it is associated with a wide range of clinical manifestations. The vast majority of patients with clinical diabetic neuropathy have a distal symmetrical form of the disorder that progresses following a fiber-length-dependent pattern, with sensory and autonomic manifestations predominating. This pattern of neuropathy is associated with a progressive distal axonopathy. Patients experience pain, trophic changes in the feet, and autonomic disturbances. Occasionally, patients with diabetes can develop focal and multifocal neuropathies that include cranial nerve involvement and limb and truncal neuropathies. This neuropathic pattern tends to occur after 50 years of age, and mostly in patients with long-standing diabetes mellitus. Length-dependent diabetic polyneuropathy does not show any trend towards improvement, and either relentlessly progresses or remains relatively stable over a number of years. Conversely, the focal diabetic neuropathies, which are often associated with inflammatory vasculopathy on nerve biopsies, remain self-limited, sometimes after a relapsing course.
Key Points
-
Length-dependent peripheral neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes, and carries a high risk of pain, trophic changes and autonomic dysfunction
-
Optimum glycemic control is the best preventive treatment for diabetic neuropathy
-
Inflammatory lesions are common in focal and multifocal neuropathies
-
If motor deficit or proprioceptive involvement predominates, it is important to consider nondiabetic causes of neuropathy
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Diabetes Federation [http://www.idf.org/]
Pirart J (1978) Diabetes mellitus and its degenerative complications: a prospective study of 4400 patients observed between 1947 and 1973. Diabetes Care 1: 168–188, 253–263
Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group (1993) The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329: 977–986
Martin CL et al. (2006) Neuropathy among the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Cohort 8 years after trial completion. Diabetes Care 29: 340–344
Said G et al. (1998) Uncommon early onset neuropathy in diabetic patients. J Neurol 245: 61–68
Palumbo PJ et al. (1978) Neurologic complications of diabetic mellitus: transient ischemic attack, stroke and peripheral neuropathy. In Advances in Neurology, vol 19, 593–601 (Ed Schoenberg BS) New York: Raven Press
De Freitas MRG et al. (1992) Diabetic neuropathy. I—epidemiology, classification, clinical and electrophysiological aspects. A study of 210 cases [Portuguese]. Rev Brasileira Neurol 28: 69–73
Said G (1981) Progressive centripetal degeneration in polyneuropathies [French]. Rev Neurol 137: 573–588
Said G et al. (1983) Progressive centripetal degeneration of axons in small fibre type diabetic polyneuropathy: a clinical and pathological study. Brain 106: 791–807
Guy RJC et al. (1985) Evaluation of thermal and vibration sensation in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 28: 131–137
Vergely P (1893) Sensory changes in the lower limbs in diabetic patients: syringomyelic dissociation of sensations in diabetic patients [French]. Gazette Hebdomadaire de Médecine et de Chirurgie 32: 376–381
Shun CT et al. (2004) Skin denervation in type 2 diabetes: correlations with diabetic duration and functional impairments. Brain 127: 1593–1605
Charcot JM (1890) A case of diabetic paraplegia [French]. Arch Neurol (Paris) 19: 305–330
Andreassen CS et al. (2006) Muscle weakness—a progressive late complication in diabetic distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Diabetes 55: 806–812
Cornblath D et al. (1987) Demyelinating motor neuropathy in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol 22: 126–132
Pavy FW (1887) Address on diabetes, Washington International Congress. Med News (Philadelphia) 24: 357–361
Brown MJ et al. (1976) Painful diabetic neuropathy: a morphological study. Arch Neurol 33: 164–171
Llewelyn JG et al. (1991) Sural nerve morphometry in diabetic autonomic and painful sensory neuropathy. Brain 114: 867–892
Sorensen L et al. (2006) The relationship among pain, sensory loss, and small nerve fibers in diabetes. Diabetes Care 29: 883–887
Orstavik K et al. (2006) Abnormal function of C-fibers in patients with diabetic neuropathy. J Neurosci 26: 11287–11294
Waxman SG (2006) Neurobiology: a channel sets the gain on pain. Nature 444: 831–832
Ellenberg M (1974) Diabetic neuropathic cachexia. Diabetes 23: 418–423
Archer AG et al. (1983) The natural history of acute painful neuropathy in diabetes mellitus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46: 491–499
Said G (1980) Acrodystrophic neuropathies. Muscle Nerve 3: 491–501
Landrieu P et al. (1990) Dominantly transmitted congenital indifference to pain. Ann Neurol 27: 574–578
Shaw JE and Boulton AJM (1998) The pathogenesis of foot problems. In Contemporary Endocrinology: Management of Diabetic Neuropathy, 291–301 (Ed Veves A) Totowa, NJ: Humana Press
Akbari CM and LoGerfo FW (1998) The impact of micro- and macrovascular disease on diabetic neuropathy and foot problems. In Contemporary Endocrinology: Management of Diabetic Neuropathy, 319–331 (Ed Veves A) Totowa, NJ: Humana Press
Llewelyn JG et al. (2005) Diabetic neuropathies. In Peripheral Neuropathy, vol 2, 1951–1991 (Eds Dyck PJ and Thomas PK) Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders
Vinik AI et al. (2003) Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 26: 1553–1579
Dreyfus PM et al. (1957) Diabetic ophthalmoplegia; report of case, with postmortem study and comments on vascular supply of human oculomotor nerve. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry 77: 337–349
Asbury AK et al. (1970) Oculomotor palsy in diabetes mellitus: a clinico-pathological study. Brain 93: 555–566
Ellenberg M (1978) Diabetic truncal mononeuropathy: a new clinical syndrome. Diabetes Care 1: 10–13
Stewart JD (1989) Diabetic truncal neuropathy: topography of the sensory deficit. Ann Neurol 25: 233–238
Bruns L (1890) Neuropathic paralysis in diabetes mellitus [German]. Berl Klin Wochenschr 27: 509–515
Said G and Thomas PK (1999) Proximal diabetic neuropathy. In Diabetic Neuropathy, 474–480 (Eds Dyck PJ and Thomas PK) Philadelphia: WB Saunders
Coppack SW and Watkins PJ (1991) The natural history of diabetic femoral neuropathy. QJ Med 79: 307–313
Said G et al. (1994) Nerve biopsy findings in different patterns of proximal diabetic neuropathy. Ann Neurol 35: 559–569
Said G et al. (2003) Inflammatory vasculopathy in multifocal diabetic neuropathy. Brain 126: 376–385
Behse F et al. (1977) Nerve biopsy and conduction studies in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40: 1072–1082
Malik RA et al. (2005) Sural nerve pathology in diabetic patients with minimal but progressive neuropathy. Diabetologia 48: 578–585
Caselli A et al. (2006) Validation of the nerve axon reflex for the assessment of small nerve fibre dysfunction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77: 927–932
Thamotharampillai K et al. (2006) Decline in neurophysiological function after 7 years in an adolescent diabetic cohort and the role of aldose reductase gene polymorphisms. Diabetes Care 29: 2053–2057
Johnson PC et al. (1986) Pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Ann Neurol 19: 450–457
King RHM et al. (1989) Diabetic neuropathy: abnormalities of Schwann cells and perineurial basal laminae: implications for diabetic vasculopathy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 15: 339–355
Dyck PJ et al. (1986) Fibre loss is primary and multifocal in sural nerves in diabetic polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol 19: 425–439
Llewelyn JG et al. (1998) Epineurial microvasculitis in proximal diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol 245: 159–165
Dyck PJ et al. (1999) Microvasculitis and ischemia in diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy. Neurology 10: 2113–2121
Said G et al. (1997) Painful proximal diabetic neuropathy: inflammatory nerve lesions and spontaneous favourable outcome. Ann Neurol 41: 762–770
Hotamisligil GS (2006) Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444: 860–867
Sumner CJ et al. (2003) The spectrum of neuropathy in diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Neurology 60: 108–111
Leinninger GM et al. (2006) Mechanisms of disease: mitochondria as new therapeutic targets in diabetic neuropathy. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2: 620–628
King RH (2001) The role of glycation in the pathogenesis of diabetic polyneuropathy. Mol Pathol 54: 400–408
Ziegler D et al. (2006) Oral treatment with alpha-lipoic acid improves symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: the SYDNEY 2 trial. Diabetes Care 29: 2365–2370
Lozeron P et al. (2002) Symptomatic diabetic and non-diabetic neuropathies in a series of 100 diabetic patients. J Neurol 249: 569–575
Gorson KC and Ropper AH (2006) Additional causes for distal sensory polyneuropathy in diabetic patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77: 354–358
Mulder DW et al. (1961) The neuropathies associated with diabetes: a clinical and electromyographic study of 103 unselected diabetic patients. Neurology 11: 275–284
Daube JR (1987) Electrophysiologic testing in diabetic neuropathy. In Diabetic Neuropathy, 162–176 (Eds PJ Dyck et al.) Philadelphia: WB Saunders
Stewart JD et al. (1996) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIPD) in diabetics. J Neurol Sci 142: 59–64
Vinik AI et al. (2006) Diabetic nerve conduction abnormalities in the primary care setting. Diabetes Technol Ther 8: 654–662
Giurini JM et al. (1998) Management of the diabetic foot. In Contemporary Endocrinology: Management of Diabetic Neuropathy, 303–318 (Ed Veves A) Totowa, NJ: Humana Press
Navarro X et al. (1997) Long-term effects of pancreatic transplantation on diabetic neuropathy. Ann Neurol 42: 727–736
Said G et al. (1992) Severe early-onset polyneuropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 326: 1257–1263
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Said, G. Diabetic neuropathy—a review. Nat Rev Neurol 3, 331–340 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpneuro0504
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpneuro0504
This article is cited by
-
Facial nerve neurographies in intensive care unit-acquired weakness
Neurological Research and Practice (2023)
-
Effectiveness of neuromuscular taping on balance, proprioception, pain, and nerve conduction parameters in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a two-group pretest-posttest randomized sham-controlled trial study protocol
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2023)
-
Metabolic and lifestyle risk factors for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in taxane and platinum-treated patients: a systematic review
Journal of Cancer Survivorship (2023)
-
The effect of exercise therapy on balance in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2022)
-
Prospective dietary radical scavengers: Boon in Pharmacokinetics, overcome insulin obstruction via signaling cascade for absorption during impediments in metabolic disorder like Diabetic Mellitus
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2022)