Abstract
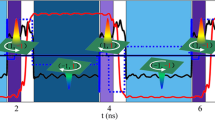
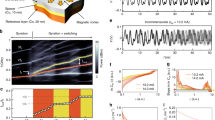
Synchronized spin-valve oscillators may lead to nanosized microwave generators that do not require discrete elements such as capacitors or inductors. Uniformly magnetized oscillators have been synchronized, but offer low power. Gyrating magnetic vortices offer greater power, but vortex synchronization has yet to be demonstrated. Here we find that vortices can interact with each other through the mediation of antivortices, leading to synchronization when they are closely spaced. The synchronization does not require a magnetic field, making the system attractive for electronic device integration. Also, because each vortex is a topological soliton, this work presents a model experimental system for the study of interacting solitons.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shinjo, T., Okuno, T., Hassdorf, R., Shigeto, K. & Ono, T. Magnetic vortex core observation in circular dots of permalloy. Science 289, 930–932 (2000).
Wachowiak, A. et al. Direct observation of internal spin structure of magnetic vortex cores. Science 298, 577–580 (2002).
Pribiag, V. S. et al. Magnetic vortex oscillator driven by d.c. spin-polarized current. Nature Phys. 3, 498–503 (2007).
Slonczewski, J. C. Current-driven excitation of magnetic multilayers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 159, L1–L7 (1996).
Berger, L. Emission of spin waves by a magnetic multilayer traversed by a current. Phys. Rev. B 54, 9353–9358 (1996).
Katine, J. A., Albert, F. J., Buhrman, R. A., Myers, E. B. & Ralph, D. C. Current-driven magnetization reversal and spin-wave excitations in Co/Cu/Co pillars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 4212–4215 (2000).
Grollier, J. et al. Spin-polarized current induced switching in Co/Cu/Co pillars. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 3663–3665 (2001).
Tsoi, M. et al. Excitation of a magnetic multilayer by an electric current. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4281–4284 (1998).
Kiselev, S. I. et al. Microwave oscillations of a nanomagnet driven by a spin-polarized current. Nature 425, 380–383 (2003).
Pufall, M. R., Rippard, W. H., Schneider, M. L. & Russek, S. E. Low-field current-hysteretic oscillations in spin-transfer nanocontacts. Phys. Rev. B 75, 140404(R) (2007).
Mistral Q. et al. Current-driven vortex oscillations in metallic nanocontacts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 257201 (2008).
Mancoff, F. B., Rizzo, N. D., Engel, B. N. & Tehrani, S. Phase-locking in double-point-contact spin-transfer devices. Nature 437, 393–395 (2005).
Kaka, S. et al. Mutual phase-locking of microwave spin torque nano-oscillators. Nature 437, 389–392 (2005).
Bouzehouane, K. et al. Nanolithography based on real-time electrically controlled indentation with an atomic force microscope for nanocontact elaboration. Nano Lett. 3, 1599–1602 (2003).
Georges, B., Grollier, J., Cros, V. & Fert, A. Impact of the electrical connection of spin transfer nano-oscillators on their synchronization: an analytical study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 232504 (2008).
Huber, D. L. Dynamics of spin vortices in two-dimensional planar magnets. Phys. Rev. B 26, 3758–3765 (1982).
Bishop, J. E. L., Galkin, A. Y. & Ivanov, B. A. Ground states of an array of magnetic dots with Ising-type anisotropy and subject to a normal magnetic field. Phys. Rev. B 65, 174403 (2002).
Guslienko, K. Y. Magnetostatic interdot coupling in two-dimensional magnetic dot arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 394–396 (1999).
Usov, N. A. & Peschany, S. E. Magnetization curling in a fine cylindrical particle. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 118, L290–L294 (1993).
Van Waeyenberge, B. et al. Magnetic vortex core reversal by excitation with short bursts of an alternating field. Nature 444, 461–464 (2006).
Yamada, K. et al. Electrical switching of the vortex core in a magnetic disk. Nature Mater. 6, 269–273 (2007).
Paraoanu, G.S. Running-phase state in a Josephson washboard potential. Phys. Rev. B 72, 134528 (2005).
Tatarkova, S. A., Sibbett, W. & Dholakia, K. Brownian particle in an optical potential of the washboard type. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 038101 (2003).
Kosterlitz, M. & Thouless, D. J. Ordering, metastability and phase transitions in two-dimensional systems. J. Phys. C 6, 1181–1203 (1973).
Bose, S. N. Plancks gesetz und lichtquantenhypothese. Z. Phys. 26, 178–181 (1924).
Anderson, M. H., Ensher, J. R., Matthews, M. R., Wieman, C. E. & Cornell, E. A. Observation of Bose–Einstein condensation in a dilute atomic vapor. Science 269, 198–201 (1995).
Guslienko, K. Y. Magnetic vortex state stability, reversal and dynamics in restricted geometries. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 8, 2745–2760 (2008).
Acknowledgements
A.R. is supported by the the EU network SPINSWITCH (MRTN-CT-2006-035327). The authors acknowledge financial support from the ANR agency (NANOMASER PNANO-06-067-04 and ALICANTE PNANO-06-064-03) and EU grant MASTER No. NMP-FP7-212257.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 392 kb)
Supplementary movie
Supplementary movie 1 (MOV 3419 kb)
Supplementary movie
Supplementary movie 2 (MOV 887 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruotolo, A., Cros, V., Georges, B. et al. Phase-locking of magnetic vortices mediated by antivortices. Nature Nanotech 4, 528–532 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.143
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.143
This article is cited by
-
Easy-plane spin Hall oscillator
Communications Physics (2023)
-
Second harmonic injection locking of coupled spin torque vortex oscillators with an individual phase access
Communications Physics (2023)
-
Electrically connected spin-torque oscillators array for 2.4 GHz WiFi band transmission and energy harvesting
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Creating polar antivortex in PbTiO3/SrTiO3 superlattice
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Creation and annihilation of topological meron pairs in in-plane magnetized films
Nature Communications (2019)