Abstract
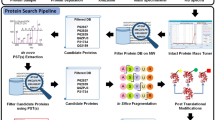
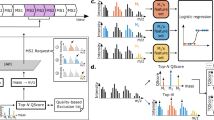
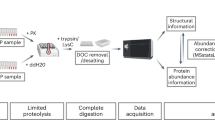
The overall study of post-translational modifications (PTMs) of proteins is gaining strong interest. Beside phosphorylation and glycosylation, truncations of the nascent polypeptide chain at the amino or carboxy terminus are by far the most common types of PTMs in proteins. In contrast to the analysis of phosphorylation and glycosylation sites, relatively little attention has been paid to the development of approaches for the systematic analysis of proteolytic processing events. Here we present a new mass spectrometry (MS)-based strategy that allows the identification of the C-terminal sequence of proteins. The method can be directly applied to proteins cleaved with cyanogen bromide (CNBr) and purified either by SDS-PAGE, by two-dimensional (2D) PAGE or in solution, and it therefore eliminates the need for specific isolation of the C-terminal peptide. Using Shewanella oneidensis as a model system, we have demonstrated that this approach can be used for C-terminal sequence analysis at a proteomic scale. We also applied the method to study the C-terminal proteolytic processing of procardosin A.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rappsilber, J. & Mann, M. What does it mean to identify a protein in proteomics? Trends Biochem. Sci. 27, 74–78 (2002).
Mann, M. & Jensen, O.N. Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 255–261 (2003).
Knight, Z.A. et al. Phosphospecific proteolysis for mapping sites of protein phosphorylation. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1047–1054 (2003).
Zhou, H., Watts, J.D. & Aebersold, R. A systematic approach to the analysis of protein phosphorylation. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 375–378 (2001).
Dove, A. The bittersweet promise of glycobiology. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 913–917 (2001).
Bailey, J.M., Nikfarjam, F., Shenoy, N.R. & Shively, J.E. Automated carboxyl-terminal sequence analysis of peptides and proteins using diphenyl phosphoroisothiocyanatidate. Protein Sci. 1, 1622–1633 (1992).
Boyd, V.L., Bozzini, M., Zon, G., Noble, R.L. & Mattaliano, R.J. Sequencing of peptides and proteins from the carboxy terminus. Anal. Biochem. 206, 344–352 (1992).
Samyn, B., Hardeman, K., Van der Eycken, J. & Van Beeumen, J. Applicability of the alkylation chemistry for chemical C-terminal protein sequence analysis. Anal. Chem. 72, 1389–1399 (2000).
Bailey, J.M. Chemical methods of protein sequence analysis. J. Chromat. A 705, 47–65 (1995).
Hardeman, K., Samyn, B., Van der Eycken, J. & Van Beeumen, J. An improved chemical approach toward the C-terminal sequence analysis of proteins containing all natural amino acids. Protein Sci. 7, 1593–1602 (1998).
Aebersold, R. & Mann, M. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422, 198–207 (2003).
Meng, F. et al. Informatics and multiplexing of intact protein identification in bacteria and the archaea. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 952–957 (2001).
Meng, F. et al. Processing complex mixtures of intact proteins for direct analysis by mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 74, 2923–2929 (2002).
Suckau, D. & Resemann, A. Targeted characterization of the N- and C-termini of undigested proteins by mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 75, 5817–5824 (2003).
Sechi, S. & Chait, B.T. A method to define the carboxyl terminal of proteins. Anal. Chem. 72, 3374–3378 (2000).
Kosaka, T., Takazawa, T. & Nakamura, T. Identification and C-terminal characterization of proteins from two-dimensional polyacrylamide gels by a combination of isotopic labeling and nano-electrospray Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 72, 1179–1185 (2000).
Zhou, X.W., Blackman, M.J., Howell, S.A. & Carruthers, V.B. Proteomic analysis of cleavage events reveals a dynamic two-step mechanism for proteolysis of a key parasite adhesive complex. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 3, 565–576 (2004).
Chait, B.T., Wang, R., Beavis, R.C. & Kent, S.B.H. Protein ladder sequencing. Science 262, 89–92 (1993).
Murphy, C.M. & Fenselau, C. Recognition of the carboxy-terminal peptide in cyanogen bromide digests of proteins. Anal. Chem. 67, 1644–1645 (1995).
Patterson, D.H., Tarr, G.E., Regnier, F.E. & Martin, S.A. C-terminal ladder sequencing via matrix-assisted laser desorption mass spectrometry coupled with carboxypeptidase Y time dependent and concentration-dependent digestions. Anal. Chem. 67, 3971–3978 (1995).
Glasauer, S., Langley, S. & Beveridge, T.J. Intracellular iron minerals in a dissimilatory iron-reducing bacterium. Science 295, 117–119 (2002).
Vanrobaeys, F. et al. Proteomics of the dissimilatory iron-reducing bacterium Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, using a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-tandem-time of flight mass spectrometer. Proteomics 3, 2249–2257 (2003).
Perkins, D.N., Pappin, D.J., Creasy, D.M. & Cottrell, J.S. Probability-based identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 20, 3551–3567 (1999).
Simões, I. & Faro, C. Structure and function of plant aspartic proteinases. Eur. J. Biochem. 271, 2067–2075 (2004).
Ramalho-Santos, M. et al. Identification and proteolytic processing of procardosin A. Eur. J. Biochem. 255, 133–138 (1998).
Oda, Y., Nagasu, T. & Chait, B.T. Enrichment analysis of phosphorylated proteins as a tool for probing the proteome. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 379–382 (2001).
Jones, J.J. et al. Investigation of MALDI-TOF and FT-MS techniques for analysis of Escherichia coli whole cells. Anal. Chem. 75, 1340–1347 (2003).
Washburn, M.P., Wolters, D. & Yates, J.R., III. Large-scale analysis of the yeast proteome by multdimensional protein identification technology. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 242–247 (2001).
Quadroni, M. & James, P. Proteomics and automation. Electrophoresis 20, 664–677 (1999).
Mitchell, P. Microfluidics – downsizing large-scale biology. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 717–721 (2001).
Oleschuk, R.D. & Harrison, D.J. Analytical microdevices for mass spectrometry. Trends Anal. Chem. 19, 379–388 (2000).
Astorga-Wells, J., Jörnvall, H. & Bergman, T. A microfluidic electrocapture device in sample preparation for protein analysis by MALDI mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 75, 5213–5219 (2003).
Caputo, E., Moharram, R. & Martin, B.M. Methods for on-chip protein analysis. Anal. Biochem. 321, 116–124 (2003).
Wilkins, M.R. et al. Protein identification with N- and C-terminal sequence tags in proteome projects. J. Mol. Biol. 278, 599–608 (1998).
Acknowledgements
B.S. is a postdoctoral fellow of the Fund for Scientific Research-Flanders (F.W.O.-Vlaanderen, Belgium). K.S. is funded by a Ph.D. grant of the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation through Science and Technology in Flanders (I.W.T.-Vlaanderen). P.C. is the recipient of a Ph.D. grant of the Portuguese government (PRAXIS XXI Programme–Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia). This work was supported by Research Grant G.0132.02 (F.W.O.-Vlaanderen, Belgium) to J.V.B. and by the PRAI programme of the Centro Region of Portugal (X-PROT project) (C.F.). The authors thank G. Debyser for preparing the figures, F. Vanrobaeys for statistical analysis and E. Lecocq for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
2D-PAGE analysis of Shewanella oneidensis proteins. (PDF 2174 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
SDS-PAGE of the spiked Shewanella oneidensis protein extract. (PDF 1978 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
C-terminal sequence analysis of the Shewanella extract spiked with the intact procardosin protein. (PDF 477 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
C-terminal sequence analysis of standard proteins. (PDF 50 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Proteins of Shewanella oneidensis identified by PMF-analysis of CNBr fragments without characterization of the C termini. (PDF 56 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samyn, B., Sergeant, K., Castanheira, P. et al. A new method for C-terminal sequence analysis in the proteomic era. Nat Methods 2, 193–200 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth738
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth738
This article is cited by
-
Post-translational cleavage of HMW-GS Dy10 allele improves the cookie-making quality in common wheat (Triticum aestivum)
Molecular Breeding (2021)
-
Complementary positional proteomics for screening substrates of endo- and exoproteases
Nature Methods (2010)
-
Multiplicity of aspartic proteinases from Cynara cardunculus L.
Planta (2009)
-
A method for C-terminal sequence analysis in the proteomic era (proteins cleaved with cyanogen bromide)
Nature Protocols (2006)