Abstract
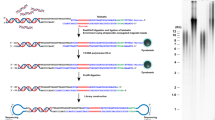
Accurate measurement of telomeric 3′-overhang (G-tail) lengths is essential for investigation of the biological effects of telomere dysfunction. G-tail telomere hybridization protection assay (Gt-telomere HPA) has the advantages of being simple to perform, accurate and highly sensitive for G tails as short as 20 nucleotides. Furthermore, Gt-telomere HPA is specific and quantitative for human G tails, and can be used to assay cell lysates as well as genomic DNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Makarov, V.L., Hirose, Y. & Langmore, J.P. Cell 88, 657–666 (1997).
Wright, W.E., Tesmer, V.M., Huffman, K.E., Levene, S.D. & Shay, J.W. Genes Dev. 11, 2801–2809 (1997).
Blackburn, E.H. Nature 408, 53–56 (2000).
de Lange, T. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 323–329 (2004).
Chai, W., Shay, J.W. & Wright, W.E. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 2158–2168 (2005).
Cimino-Reale, G. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, E35 (2001).
Saldanha, S.N., Andrews, L.G. & Tollefsbol, T.O. Eur. J. Biochem. 270, 389–403 (2003).
Nakamura, Y. et al. Clin. Chem. 45, 1718–1724 (1999).
Hirose, M. et al. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 123, 337–344 (1997).
Stewart, S.A. et al. Nat. Genet. 33, 492–496 (2003).
van Steensel, B., Smogorzewska, A. & de Lange, T. Cell 92, 401–413 (1998).
McElligott, R. & Wellinger, R.J. EMBO J. 16, 3705–3714 (1997).
Riha, K., McKnight, T.D., Fajkus, J., Vyskot, B. & Shippen, D.E. Plant J. 23, 633–641 (2000).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. We thank T. de Lange for providing the pBabepuro-NmycTRF2ΔBΔM. We thank A.M. Sera for critical reading of the manuscript and for technical assistance. We thank A. Shimamoto for helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
AE-labeled telomere HPA probes (29 mer) specifically detect mammalian telomere DNA 5′-TTAGGG-3′ sequences. (PDF 541 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Time dependent increase of luminescence by T7 exonuclease treatment. (PDF 523 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
T7 exonuclease treatment of genomic DNA from SiHa cancer cell line generated G-tails with mean lengths of over 1,600 nt. (PDF 517 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Structure of synthetic telomeric G-tail DNA and possible hybridization patterns of the telomere HPA probe. (PDF 622 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 5
Point mutations 6 bases away from the acridinium ester (AE) labeled position do not affect the HPA signals on telomeres. (PDF 662 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 6
Linearity of HPA for the detection of Alu DNA. (PDF 571 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 7
Estimated mean G-tail lengths in cultured cells using Gt-telomere HPA. (PDF 550 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahara, H., Kusunoki, M., Yamanaka, Y. et al. G-tail telomere HPA: simple measurement of human single-stranded telomeric overhangs. Nat Methods 2, 829–831 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth797
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth797
This article is cited by
-
Cell-based chemical fingerprinting identifies telomeres and lamin A as modifiers of DNA damage response in cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Insights into the biomedical effects of carboxylated single-wall carbon nanotubes on telomerase and telomeres
Nature Communications (2012)
-
G-Quadruplex stabilization by telomestatin induces TRF2 protein dissociation from telomeres and anaphase bridge formation accompanied by loss of the 3′ telomeric overhang in cancer cells
Oncogene (2006)
-
POT1b protects telomeres from end-to-end chromosomal fusions and aberrant homologous recombination
The EMBO Journal (2006)