Volume 21
-
No. 12 December 2022
Two-dimensional monolayer active pixel sensorsLow-power and compact active pixel sensor (APS) matrices are desired for resource-limited edge devices. Here, the authors report a small-footprint APS matrix based on monolayer MoS2 phototransistor arrays exhibiting spectral uniformity, reconfigurable photoresponsivity and de-noising capabilities at low energy consumption.
See Dodda et al.
-
No. 11 November 2022
Cells soften into migrationCells from embryonic tissues dynamically decrease their stiffness to initiate collective cell migration, a process that traditionally is associated with stiffer environments and cellular states.
See Marchant et al.
-
No. 10 October 2022
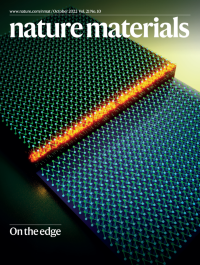
On the edgeAn insulating bulk state and helical edge state are reported to coexist in Bi4Br4 up to room temperature.
See Shumiya et al.
-
No. 9 September 2022
20 years onWe celebrate our twentieth anniversary by looking back at how materials research has evolved and consider future directions.
-
No. 8 August 2022
Gear-based mechanical metamaterialsA design paradigm to create robust robotic metamaterials using versatile gear clusters is demonstrated. It enables intriguing programmability of elastic properties and shape while preserving stability for intelligent machines.
See Fang et al.
-
No. 7 July 2022
Hierarchical electrodes for semi-artificial photosynthesisWiring photosynthetic biomachineries to electrodes is promising for sustainable bio-electricity and fuel generation, but designing such interfaces is challenging. Aerosol jet printing is now used to generate hierarchical pillar array electrodes using indium tin oxide nanoparticles for high-performance semi-artificial photosynthesis.
See Chen et al.
-
No. 6 June 2022
Double-fibril network for highly efficient organic photovoltaicsThe morphology of donor–acceptor blends in organic photovoltaics dictates the efficiency of the exciton dissociation and charge diffusion, and thus the final device performance. Here, the authors show that filament assembly helps to maximize the output, further enabling a power conversion efficiency greater than 19%.
See Zhu et al.
-
No. 5 May 2022
Hollow spheres enable tandem catalysisMetal oxide–zeolite bifunctional catalysts allow coupling of reactions and so enhance catalytic processes, but structure and reactivity control is difficult. Here, a general synthesis is presented for metal oxide–zeolite double-shelled hollow spheres, which outperform other catalysts for petroleum production.
See Xiao et al.
-
No. 4 April 2022
Photo-enhanced ionic conductorsGrain boundary conductivity limitations are ubiquitous in materials science. Illumination with above-bandgap light is now shown to decrease grain boundary resistance in a model gadolinium-doped ceria solid ionic conductor.
See Defferriere et al.
-
No. 3 March 2022
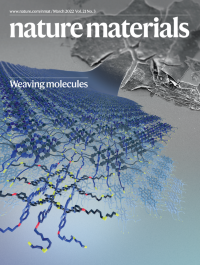
Weaving moleculesMolecular weaving is the entanglement of one-dimensional flexible molecules into higher-dimensional networks. This Perspective provides an overview of the progress so far, and discusses the future challenges and potentials of this field.
See Zhang et al.
-
No. 2 February 2022
Structural mapping of porous intercalation electrodesDesigning electrode architectures for Li-ion batteries that can be reversibly accessible for ion storage can be challenging. Using operando techniques, the mechanistic origin of lithiation-induced phase transformations in a V2O5 model cathode is now clarified.
See Luo et al.
-
No. 1 January 2022
Ferrimagnetic and topological spintronicsFerrimagnets offer the combined advantages of both ferromagnets and antiferromagnets for spintronics applications. This Review surveys recent progress.
See Kim et al.